AM base circuit
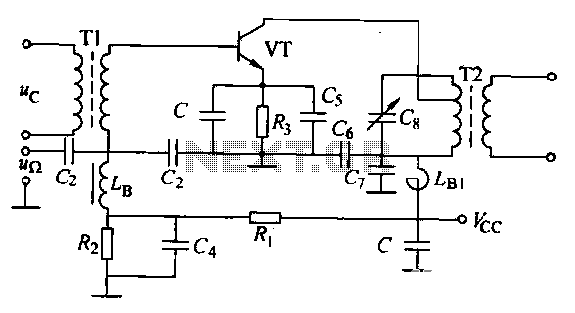
The circuit is designed for small-signal amplitude modulation (AM). Component C functions as a high-frequency bypass capacitor. Transformers T1 and T2 serve as high-frequency transformers, while the LC resonant circuit operates at the carrier frequency with a passband of 2Fr. A low-pass filter is implemented for detection, utilizing a method known as a square-diode detector. The term "small signal square-detector" is used due to the low amplitude of the high-frequency input signal.
The circuit operates within the framework of amplitude modulation, where the information signal modifies the amplitude of a high-frequency carrier wave. The high-frequency bypass capacitor (C) is crucial for stabilizing the circuit by preventing high-frequency noise from affecting the performance of the AM signal. It allows AC signals to pass while blocking DC, ensuring that the modulation process remains unaffected by fluctuations in the power supply.
Transformers T1 and T2 are integral to the circuit, facilitating the transfer of energy between different stages while maintaining the integrity of the high-frequency signals. These transformers are designed to efficiently couple the signal at the desired carrier frequency, ensuring minimal loss and optimal performance.
The LC resonant circuit is tuned to the carrier frequency, enabling selective amplification of the desired signal while filtering out unwanted frequencies. The passband of 2Fr indicates the range of frequencies around the carrier frequency that the circuit can effectively process, allowing for the transmission of modulated signals with minimal distortion.
For the detection of the modulated signal, a low-pass filter is employed to isolate the baseband signal from the high-frequency components. The square-diode detector operates by rectifying the incoming modulated signal, allowing for the recovery of the original information signal. The term "small signal square-detector" highlights the circuit's capability to handle low-amplitude signals, which is essential in applications where the input signal is weak, such as in communication systems and radio receivers. This design emphasizes the importance of precision in signal processing, ensuring reliable detection and reproduction of the transmitted information.AM base for small-signal amplitude modulation, the circuit as shown C is a high frequency bypass capacitor. Tl, T2 is a high frequency transformer, LC resonant circuit at the carrier frequency , passband is 2Fr. . Change, and then implement the detector through a low-pass filter, this detection method called square-diode detector.
Due to the small high-frequency input signal amplitude, fork called small signal square-detector.
The circuit operates within the framework of amplitude modulation, where the information signal modifies the amplitude of a high-frequency carrier wave. The high-frequency bypass capacitor (C) is crucial for stabilizing the circuit by preventing high-frequency noise from affecting the performance of the AM signal. It allows AC signals to pass while blocking DC, ensuring that the modulation process remains unaffected by fluctuations in the power supply.
Transformers T1 and T2 are integral to the circuit, facilitating the transfer of energy between different stages while maintaining the integrity of the high-frequency signals. These transformers are designed to efficiently couple the signal at the desired carrier frequency, ensuring minimal loss and optimal performance.
The LC resonant circuit is tuned to the carrier frequency, enabling selective amplification of the desired signal while filtering out unwanted frequencies. The passband of 2Fr indicates the range of frequencies around the carrier frequency that the circuit can effectively process, allowing for the transmission of modulated signals with minimal distortion.
For the detection of the modulated signal, a low-pass filter is employed to isolate the baseband signal from the high-frequency components. The square-diode detector operates by rectifying the incoming modulated signal, allowing for the recovery of the original information signal. The term "small signal square-detector" highlights the circuit's capability to handle low-amplitude signals, which is essential in applications where the input signal is weak, such as in communication systems and radio receivers. This design emphasizes the importance of precision in signal processing, ensuring reliable detection and reproduction of the transmitted information.AM base for small-signal amplitude modulation, the circuit as shown C is a high frequency bypass capacitor. Tl, T2 is a high frequency transformer, LC resonant circuit at the carrier frequency , passband is 2Fr. . Change, and then implement the detector through a low-pass filter, this detection method called square-diode detector.
Due to the small high-frequency input signal amplitude, fork called small signal square-detector.