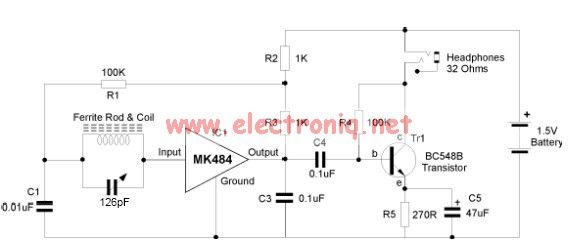
Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit waveform sawtooth oscillator use multivibrator
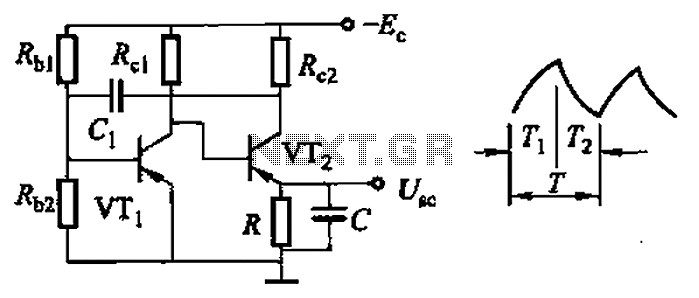
Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - sawtooth oscillator - use multivibrator.
The sawtooth oscillator is a type of non-sinusoidal waveform generator that produces a triangular or sawtooth-shaped output signal. This oscillator is commonly utilized in various applications, including audio synthesis, signal processing, and timing circuits. The fundamental operation of a sawtooth oscillator involves charging and discharging a capacitor through a resistor, which results in a linear ramp-up of voltage followed by a rapid drop to the initial voltage level.
The circuit typically employs a multivibrator configuration, often using operational amplifiers or transistors. In a standard implementation, a capacitor is charged through a resistor until it reaches a predetermined threshold voltage, at which point the output switches state, causing the capacitor to discharge rapidly. The frequency of the sawtooth waveform can be determined by the values of the resistor and capacitor according to the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{T} = \frac{1}{R \cdot C \cdot \ln(\frac{V_{max}}{V_{min}})} \]
where \( f \) is the frequency, \( R \) is the resistance, \( C \) is the capacitance, \( V_{max} \) is the maximum voltage, and \( V_{min} \) is the minimum voltage.
For practical implementation, the circuit can be designed using a 555 timer in astable mode or with a combination of transistors configured as a Schmitt trigger. In both cases, careful selection of resistor and capacitor values is crucial for achieving the desired frequency and waveform characteristics. The output can be further processed or filtered to meet specific application requirements, such as generating audio signals or controlling other electronic components.
Overall, the sawtooth oscillator is a versatile circuit that can be adapted for various electronic applications by modifying component values and configurations to tailor its performance. Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - sawtooth oscillator - use multivibrator
The sawtooth oscillator is a type of non-sinusoidal waveform generator that produces a triangular or sawtooth-shaped output signal. This oscillator is commonly utilized in various applications, including audio synthesis, signal processing, and timing circuits. The fundamental operation of a sawtooth oscillator involves charging and discharging a capacitor through a resistor, which results in a linear ramp-up of voltage followed by a rapid drop to the initial voltage level.
The circuit typically employs a multivibrator configuration, often using operational amplifiers or transistors. In a standard implementation, a capacitor is charged through a resistor until it reaches a predetermined threshold voltage, at which point the output switches state, causing the capacitor to discharge rapidly. The frequency of the sawtooth waveform can be determined by the values of the resistor and capacitor according to the formula:
\[ f = \frac{1}{T} = \frac{1}{R \cdot C \cdot \ln(\frac{V_{max}}{V_{min}})} \]
where \( f \) is the frequency, \( R \) is the resistance, \( C \) is the capacitance, \( V_{max} \) is the maximum voltage, and \( V_{min} \) is the minimum voltage.
For practical implementation, the circuit can be designed using a 555 timer in astable mode or with a combination of transistors configured as a Schmitt trigger. In both cases, careful selection of resistor and capacitor values is crucial for achieving the desired frequency and waveform characteristics. The output can be further processed or filtered to meet specific application requirements, such as generating audio signals or controlling other electronic components.
Overall, the sawtooth oscillator is a versatile circuit that can be adapted for various electronic applications by modifying component values and configurations to tailor its performance. Common non-sinusoidal oscillator circuit, waveform and frequency formula - sawtooth oscillator - use multivibrator