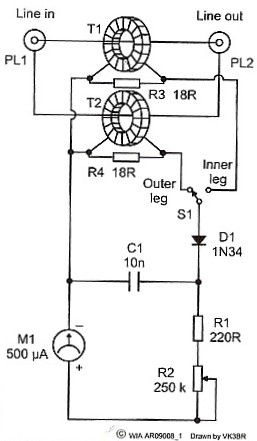
Analog Expanded-Scale Meter For Autos
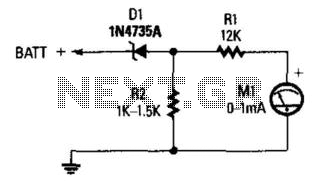
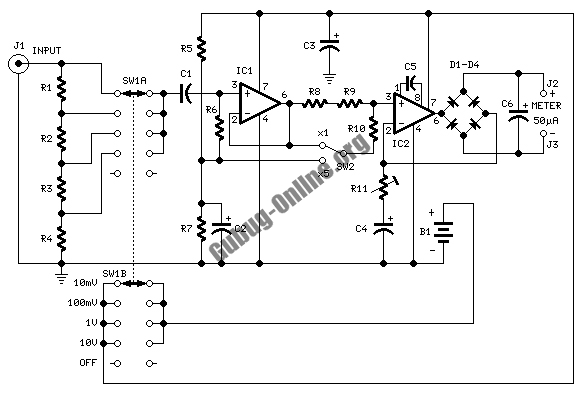
A Zener diode (D1) is utilized to limit the voltage to the first 6 V of the scale, resulting in a meter reading range of 6 to 8 V, which is beneficial for monitoring automotive electrical systems.
The circuit employs a Zener diode, which is a semiconductor device designed to allow current to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage exceeds a specified value, known as the Zener voltage. In this application, Zener diode D1 is selected to clamp the voltage to a threshold of 6 V. This voltage suppression is crucial for ensuring that the subsequent components in the circuit, such as the analog meter or microcontroller, receive a safe and manageable voltage level for accurate readings.
The configuration of the Zener diode in the circuit typically involves connecting it in reverse bias across the input voltage source. When the input voltage exceeds 6 V, the Zener diode conducts, effectively shunting excess voltage and preventing it from reaching the measuring device. This action not only protects sensitive components from overvoltage conditions but also stabilizes the voltage readings within the desired range.
In automotive applications, monitoring the electrical system is vital for diagnosing issues related to battery performance, alternator output, and overall electrical integrity. The specified meter reading range of 6 to 8 V allows for effective monitoring of various parameters, such as battery voltage under load and charging conditions, ensuring that the automotive system operates within safe limits.
For optimal performance, the Zener diode should be chosen based on its power rating and dynamic resistance characteristics to ensure it can handle the expected current without overheating. Additional components, such as resistors, may be included in the circuit to limit the current through the Zener diode, further enhancing the reliability and accuracy of the monitoring system. Zener diode D1 is used to suppress the first 6 V of the scale, which gives a meter reading of 6 to 8 V—useful for automotive electrical system monitoring.
The circuit employs a Zener diode, which is a semiconductor device designed to allow current to flow in the reverse direction when the voltage exceeds a specified value, known as the Zener voltage. In this application, Zener diode D1 is selected to clamp the voltage to a threshold of 6 V. This voltage suppression is crucial for ensuring that the subsequent components in the circuit, such as the analog meter or microcontroller, receive a safe and manageable voltage level for accurate readings.
The configuration of the Zener diode in the circuit typically involves connecting it in reverse bias across the input voltage source. When the input voltage exceeds 6 V, the Zener diode conducts, effectively shunting excess voltage and preventing it from reaching the measuring device. This action not only protects sensitive components from overvoltage conditions but also stabilizes the voltage readings within the desired range.
In automotive applications, monitoring the electrical system is vital for diagnosing issues related to battery performance, alternator output, and overall electrical integrity. The specified meter reading range of 6 to 8 V allows for effective monitoring of various parameters, such as battery voltage under load and charging conditions, ensuring that the automotive system operates within safe limits.
For optimal performance, the Zener diode should be chosen based on its power rating and dynamic resistance characteristics to ensure it can handle the expected current without overheating. Additional components, such as resistors, may be included in the circuit to limit the current through the Zener diode, further enhancing the reliability and accuracy of the monitoring system. Zener diode D1 is used to suppress the first 6 V of the scale, which gives a meter reading of 6 to 8 V—useful for automotive electrical system monitoring.