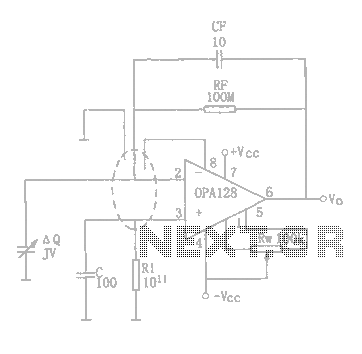
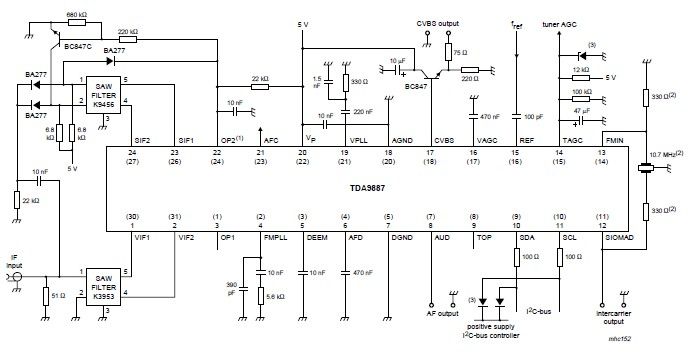
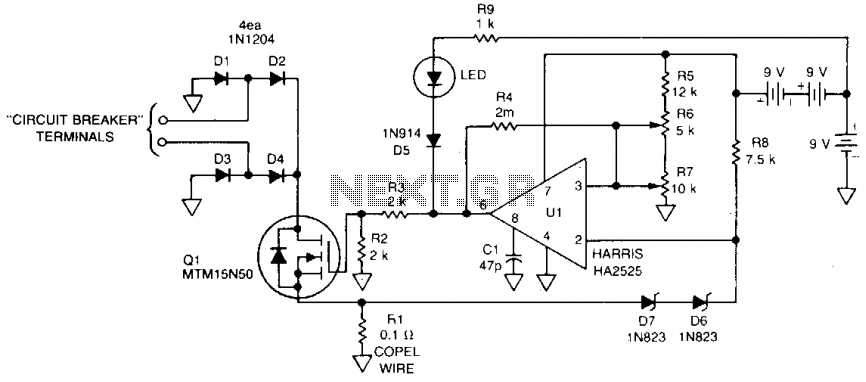
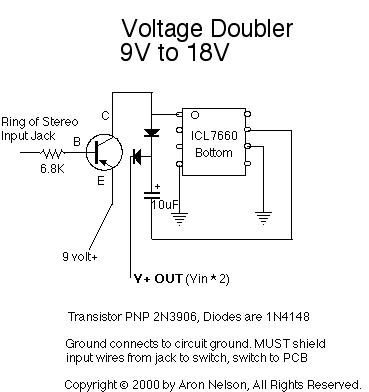
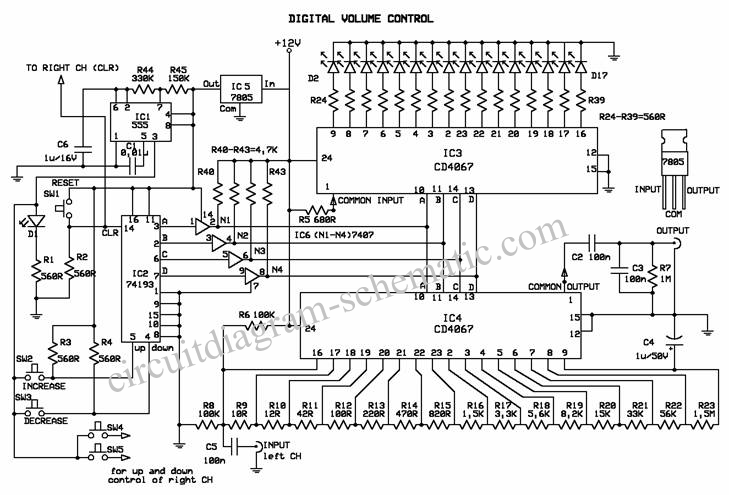
Audio Line Driver Circuit
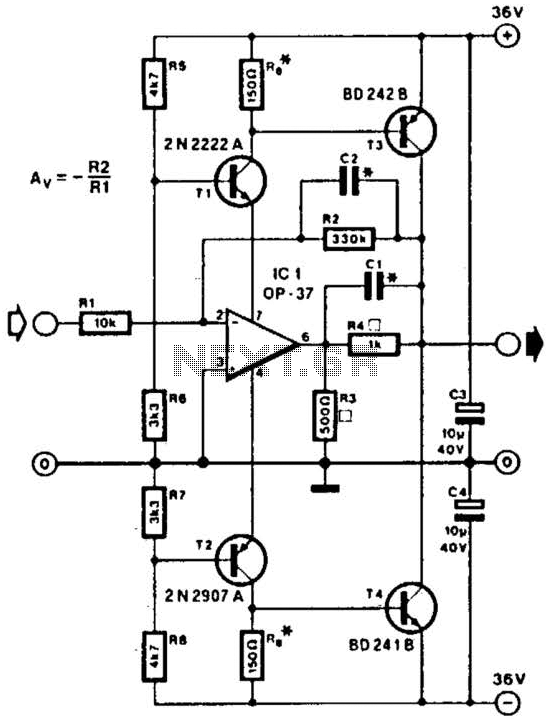
This line driver is capable of driving low-impedance lines with a maximum output of 70 V peak-to-peak. IC1 functions as a low-noise operational amplifier suitable for operation at 15 V. T1 and T2 serve as voltage regulators for the power supply of IC1. T3 and T4 create a complementary power output stage. The frequency response remains flat up to 100 kHz.
The line driver circuit is designed to effectively transmit signals over low-impedance lines, making it suitable for various applications in audio and data communications. The core component, IC1, is selected for its low-noise characteristics, which are critical for maintaining signal integrity, especially in sensitive applications. The operational amplifier operates at a supply voltage of 15 V, ensuring adequate headroom for signal processing while minimizing distortion.
Voltage regulators T1 and T2 are essential for providing a stable power supply to IC1, which is crucial for consistent performance. These regulators ensure that fluctuations in the input voltage do not adversely affect the operation of the amplifier, thus enhancing reliability.
The output stage, consisting of transistors T3 and T4, is configured in a complementary manner, allowing for efficient drive capabilities. This configuration helps achieve higher output currents while maintaining thermal stability, which is vital when driving low-impedance loads. The complementary arrangement also aids in reducing crossover distortion, a common issue in linear amplifiers.
With a frequency response that remains flat up to 100 kHz, this line driver is well-suited for applications requiring high fidelity over a wide bandwidth. The ability to maintain a consistent gain across this frequency range ensures that the integrity of the signal is preserved, making it ideal for high-quality audio transmission and other precision applications. This line driver can drive low-impedance lines with up to 70 V p-p max. IC1 is a low-noise op amp suitable for 15-V operation. T1 and T2 are regulators for the power supply for IC1. T3 and T4 form a complementary power output stage. Frequency response is flat up to 100 kHz.
The line driver circuit is designed to effectively transmit signals over low-impedance lines, making it suitable for various applications in audio and data communications. The core component, IC1, is selected for its low-noise characteristics, which are critical for maintaining signal integrity, especially in sensitive applications. The operational amplifier operates at a supply voltage of 15 V, ensuring adequate headroom for signal processing while minimizing distortion.
Voltage regulators T1 and T2 are essential for providing a stable power supply to IC1, which is crucial for consistent performance. These regulators ensure that fluctuations in the input voltage do not adversely affect the operation of the amplifier, thus enhancing reliability.
The output stage, consisting of transistors T3 and T4, is configured in a complementary manner, allowing for efficient drive capabilities. This configuration helps achieve higher output currents while maintaining thermal stability, which is vital when driving low-impedance loads. The complementary arrangement also aids in reducing crossover distortion, a common issue in linear amplifiers.
With a frequency response that remains flat up to 100 kHz, this line driver is well-suited for applications requiring high fidelity over a wide bandwidth. The ability to maintain a consistent gain across this frequency range ensures that the integrity of the signal is preserved, making it ideal for high-quality audio transmission and other precision applications. This line driver can drive low-impedance lines with up to 70 V p-p max. IC1 is a low-noise op amp suitable for 15-V operation. T1 and T2 are regulators for the power supply for IC1. T3 and T4 form a complementary power output stage. Frequency response is flat up to 100 kHz.