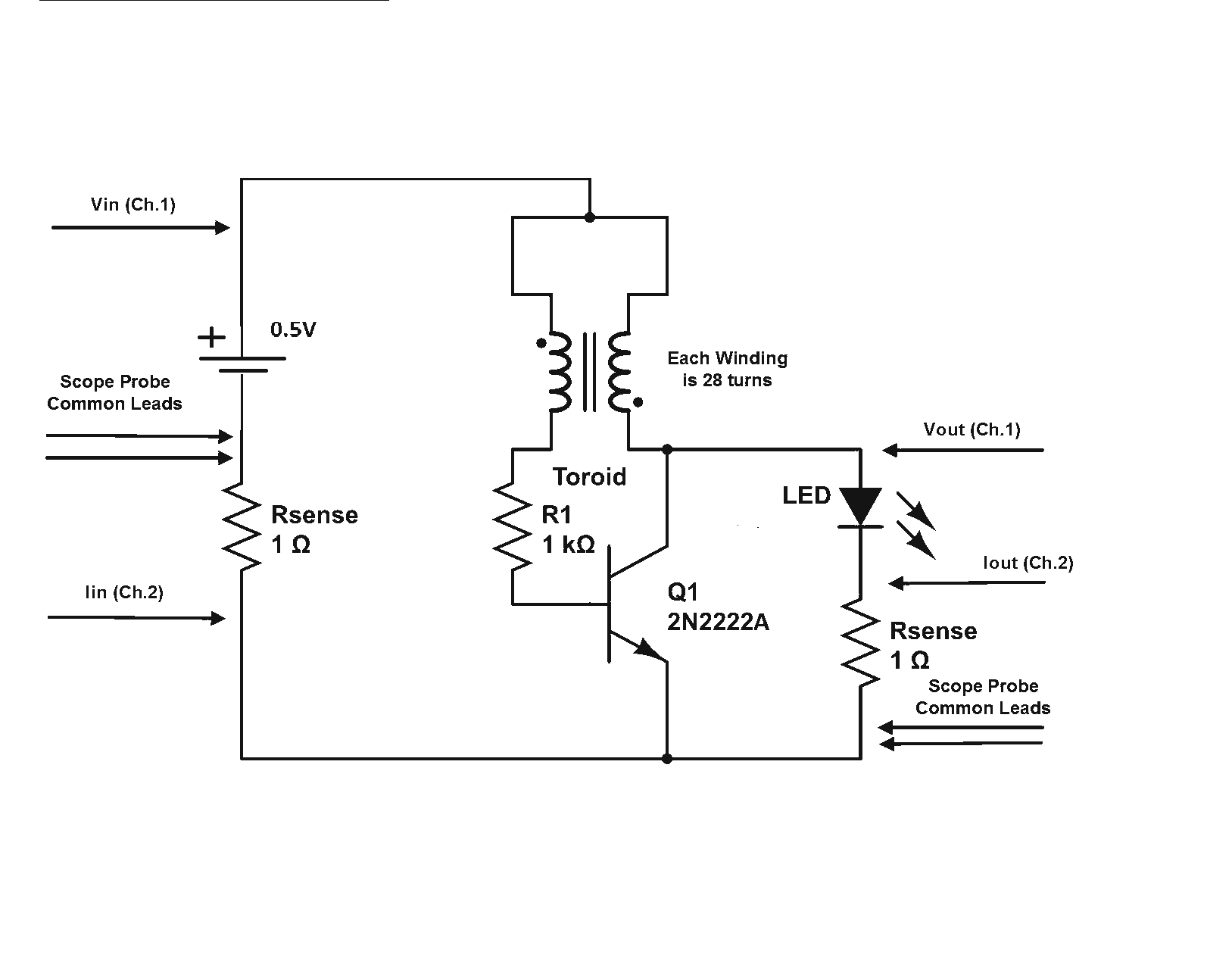
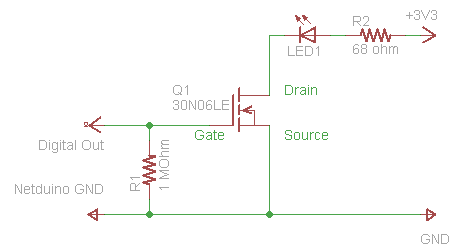
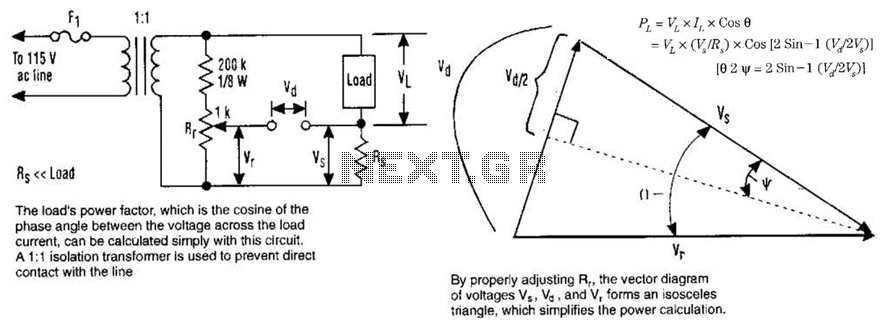
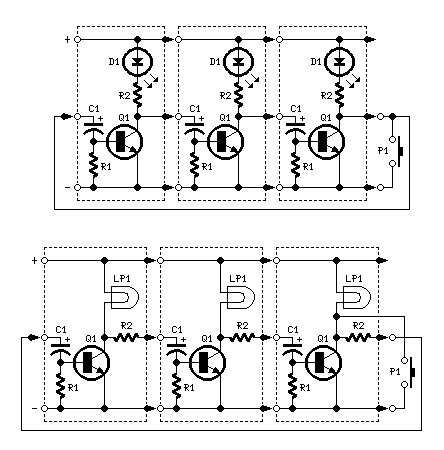
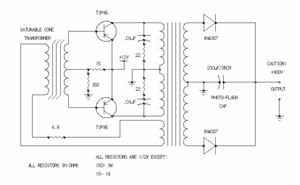
Audio Noise Filter Circuit

This audio noise filter circuit is a bandpass filter designed for the audio frequency range. It effectively filters out unwanted signals that fall below or above the audio frequency spectrum.
The audio noise filter circuit operates as a bandpass filter, which allows signals within a specific frequency range to pass while attenuating frequencies outside this range. Typically, the audio frequency band extends from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, which corresponds to the range of human hearing.
The circuit can be constructed using passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, or it can be implemented using active components such as operational amplifiers to improve performance. In a passive bandpass filter configuration, a combination of low-pass and high-pass filters is used. The low-pass filter attenuates frequencies above the desired range, while the high-pass filter attenuates frequencies below the desired range.
For example, if the target frequency range is from 100 Hz to 10 kHz, the low-pass filter can be designed with a cutoff frequency of 10 kHz, and the high-pass filter can be designed with a cutoff frequency of 100 Hz. The design of the filter can be calculated using standard filter design equations, considering the desired gain, bandwidth, and quality factor (Q).
In an active configuration, operational amplifiers can be utilized to create a more selective and stable bandpass filter. This configuration allows for greater control over gain and impedance matching, making it suitable for various audio applications. The circuit may also incorporate feedback mechanisms to enhance the filter's performance, reduce distortion, and improve signal-to-noise ratio.
Overall, the audio noise filter circuit is essential in audio processing systems, ensuring that only the desired audio signals are amplified and transmitted, thereby improving the overall sound quality.This audio noise filter circuit is a bandpass filter for audio frequency band. It filters unwanted signals that are lower or higher than the audio frequenc.. 🔗 External reference
The audio noise filter circuit operates as a bandpass filter, which allows signals within a specific frequency range to pass while attenuating frequencies outside this range. Typically, the audio frequency band extends from 20 Hz to 20 kHz, which corresponds to the range of human hearing.
The circuit can be constructed using passive components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, or it can be implemented using active components such as operational amplifiers to improve performance. In a passive bandpass filter configuration, a combination of low-pass and high-pass filters is used. The low-pass filter attenuates frequencies above the desired range, while the high-pass filter attenuates frequencies below the desired range.
For example, if the target frequency range is from 100 Hz to 10 kHz, the low-pass filter can be designed with a cutoff frequency of 10 kHz, and the high-pass filter can be designed with a cutoff frequency of 100 Hz. The design of the filter can be calculated using standard filter design equations, considering the desired gain, bandwidth, and quality factor (Q).
In an active configuration, operational amplifiers can be utilized to create a more selective and stable bandpass filter. This configuration allows for greater control over gain and impedance matching, making it suitable for various audio applications. The circuit may also incorporate feedback mechanisms to enhance the filter's performance, reduce distortion, and improve signal-to-noise ratio.
Overall, the audio noise filter circuit is essential in audio processing systems, ensuring that only the desired audio signals are amplified and transmitted, thereby improving the overall sound quality.This audio noise filter circuit is a bandpass filter for audio frequency band. It filters unwanted signals that are lower or higher than the audio frequenc.. 🔗 External reference