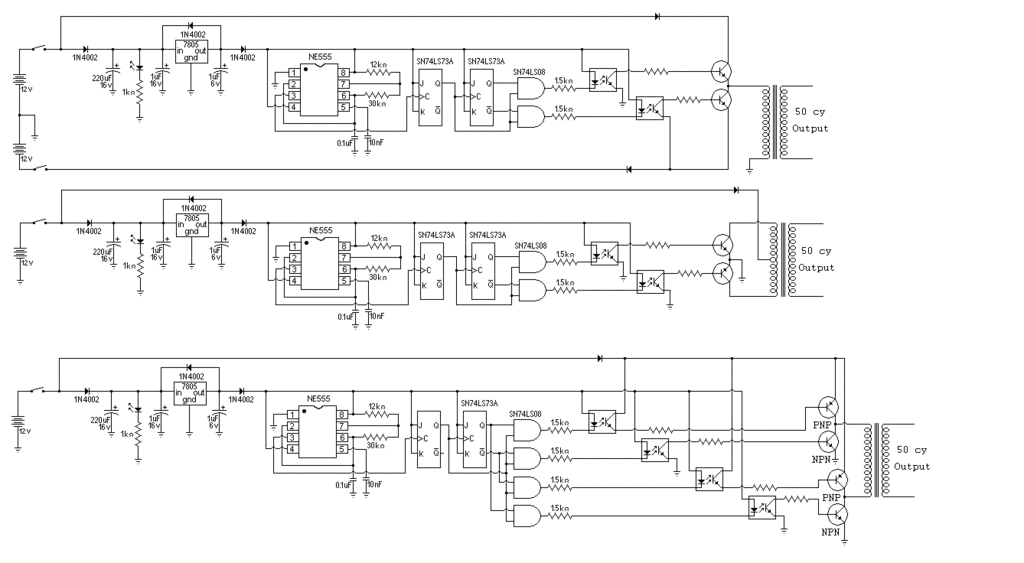
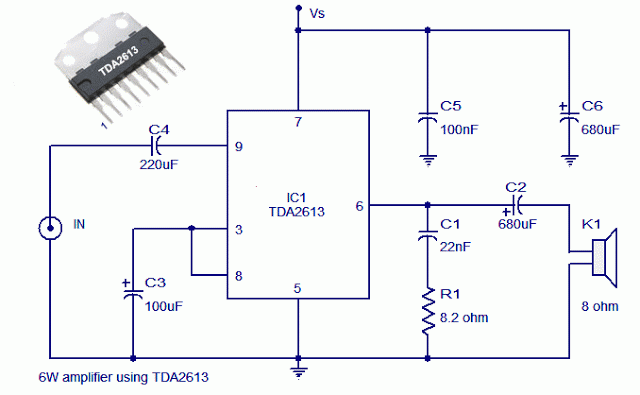
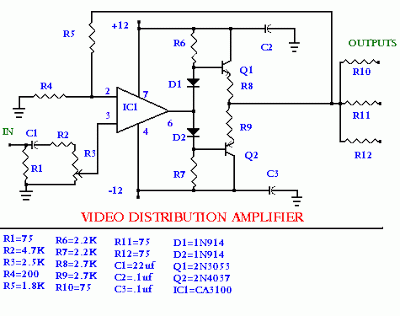
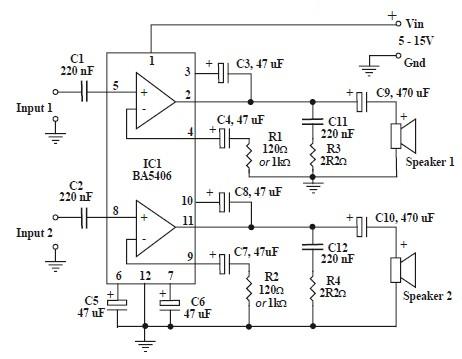
Audio Signal Clipping Indicator
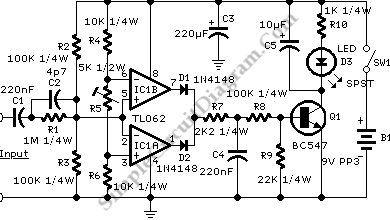
A window comparator formed by two operational amplifiers packaged into IC1 is the heart of the circuit below. With this technique, we can detect precisely and symmetrically.
The window comparator circuit utilizes two operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured to create a defined voltage range, or "window," within which an input signal must fall for the output to indicate a specific state. The circuit employs IC1, which houses the two op-amps, to achieve this functionality efficiently.
The first op-amp is configured as a non-inverting comparator, with its non-inverting input connected to a reference voltage, typically set by a voltage divider. The inverting input is connected to the input signal. When the input signal exceeds the reference voltage, the output of this op-amp transitions to a high state, indicating that the input has crossed the upper threshold of the window.
Conversely, the second op-amp is configured as an inverting comparator. Its inverting input is connected to a lower reference voltage, also established by a voltage divider, while the non-inverting input receives the input signal. When the input signal drops below this lower reference voltage, the output of the second op-amp switches to a high state, indicating that the input has fallen below the lower threshold of the window.
The outputs of both op-amps can be connected to a logic gate or a microcontroller to provide a clear indication of whether the input signal is within the defined window. This configuration allows for precise detection of signals that fall within a specific range, making it suitable for applications in signal conditioning, level detection, and various control systems. The symmetrical design ensures that both upper and lower thresholds are equally significant, providing a balanced response to the input signal variations.A window comparator formed by two op-amps packaged into IC1 is the heart of the circuit below. With this technique, we can detect precisely and symmetrically.. 🔗 External reference
The window comparator circuit utilizes two operational amplifiers (op-amps) configured to create a defined voltage range, or "window," within which an input signal must fall for the output to indicate a specific state. The circuit employs IC1, which houses the two op-amps, to achieve this functionality efficiently.
The first op-amp is configured as a non-inverting comparator, with its non-inverting input connected to a reference voltage, typically set by a voltage divider. The inverting input is connected to the input signal. When the input signal exceeds the reference voltage, the output of this op-amp transitions to a high state, indicating that the input has crossed the upper threshold of the window.
Conversely, the second op-amp is configured as an inverting comparator. Its inverting input is connected to a lower reference voltage, also established by a voltage divider, while the non-inverting input receives the input signal. When the input signal drops below this lower reference voltage, the output of the second op-amp switches to a high state, indicating that the input has fallen below the lower threshold of the window.
The outputs of both op-amps can be connected to a logic gate or a microcontroller to provide a clear indication of whether the input signal is within the defined window. This configuration allows for precise detection of signals that fall within a specific range, making it suitable for applications in signal conditioning, level detection, and various control systems. The symmetrical design ensures that both upper and lower thresholds are equally significant, providing a balanced response to the input signal variations.A window comparator formed by two op-amps packaged into IC1 is the heart of the circuit below. With this technique, we can detect precisely and symmetrically.. 🔗 External reference