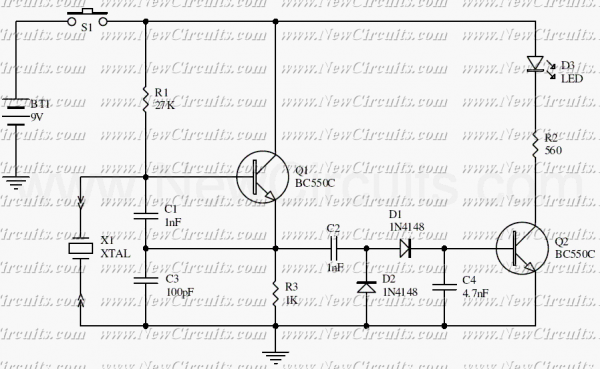
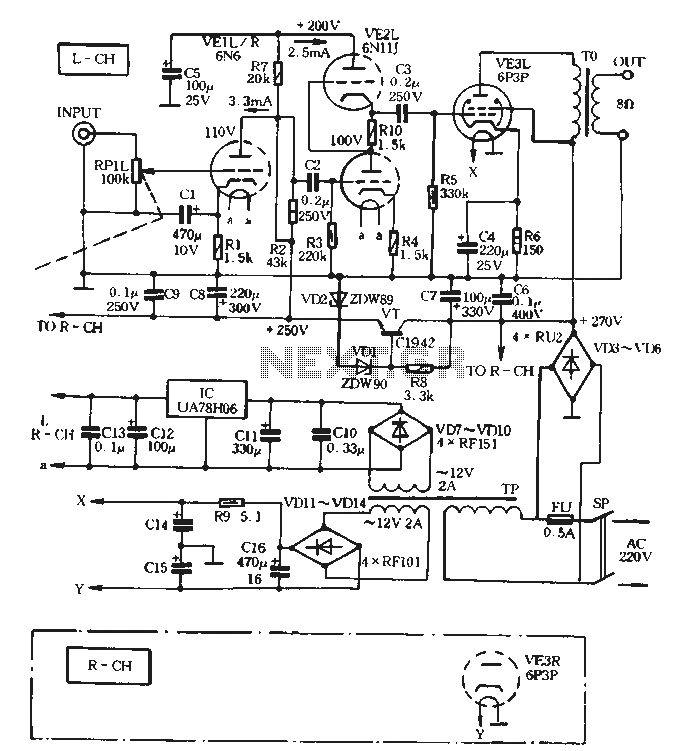
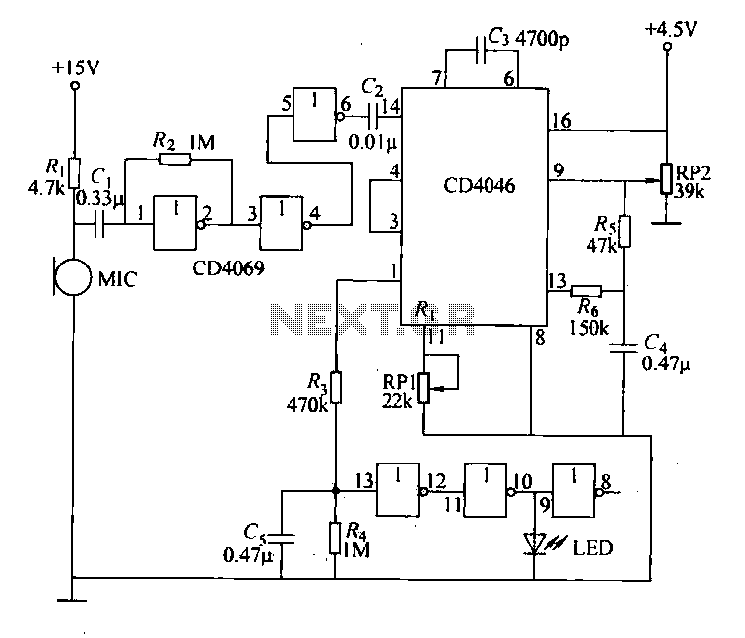
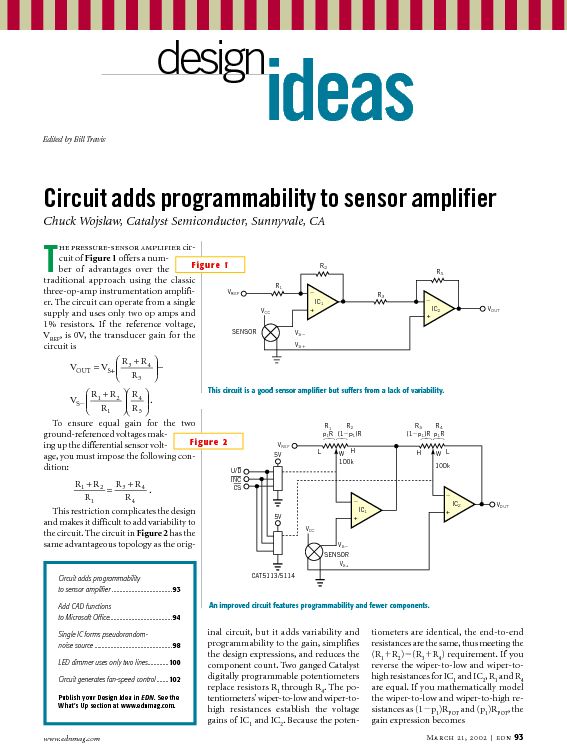
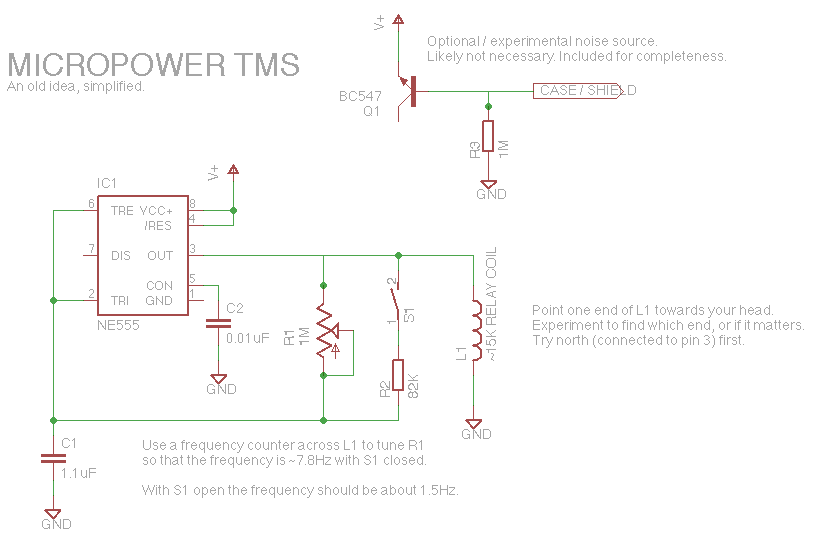
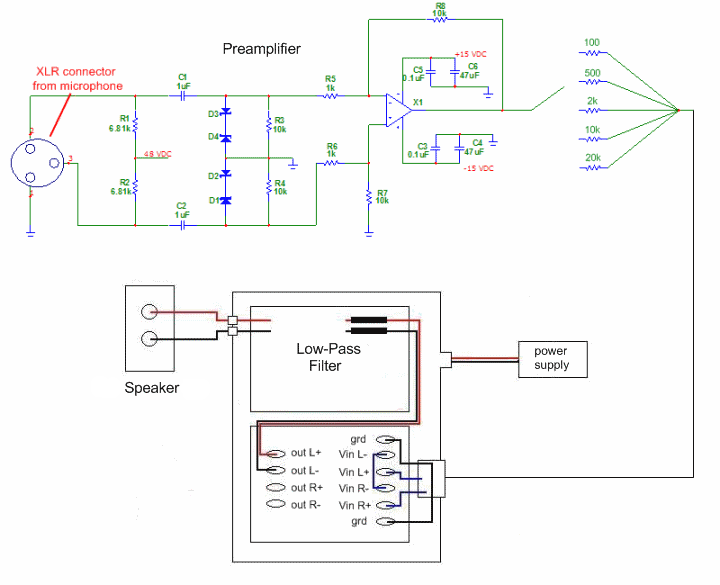
Simple Hybrid Audio Amplifier

The debate continues regarding whether valves or transistors are superior. This discussion will not be addressed here. However, if one cannot make their…
The comparison between valves (vacuum tubes) and transistors has been a longstanding topic in the field of electronics, each having its unique advantages and applications. Valves are known for their warm sound quality and high voltage handling capabilities, making them popular in audio amplification and vintage equipment. Conversely, transistors offer advantages such as compact size, lower power consumption, and greater reliability, which have led to their dominance in modern electronic devices.
In a comprehensive electronic schematic, the choice between using valves or transistors can significantly influence the design parameters. For instance, a valve-based amplifier circuit would typically include components such as high-voltage power supplies, filament transformers for heating the cathodes, and output transformers to match the impedance of speakers. These circuits often require careful layout considerations to manage heat dissipation and electromagnetic interference.
On the other hand, a transistor-based amplifier circuit would utilize low-voltage power supplies and include biasing resistors to set the operating point of the transistors. The schematic would also incorporate capacitors for coupling and decoupling signals, ensuring that the audio fidelity remains intact while preventing DC bias from affecting subsequent stages.
When designing a circuit, it is essential to evaluate the intended application, desired sound characteristics, and physical constraints. This evaluation will guide the selection of either valves or transistors, ultimately influencing the performance, reliability, and user experience of the electronic device. Each technology presents distinct challenges and benefits that must be carefully considered during the design process.The debate still goes on as to which are better, valves or transistors. We don t intend to get involved in that argument here. But if you can t make your.. 🔗 External reference
The comparison between valves (vacuum tubes) and transistors has been a longstanding topic in the field of electronics, each having its unique advantages and applications. Valves are known for their warm sound quality and high voltage handling capabilities, making them popular in audio amplification and vintage equipment. Conversely, transistors offer advantages such as compact size, lower power consumption, and greater reliability, which have led to their dominance in modern electronic devices.
In a comprehensive electronic schematic, the choice between using valves or transistors can significantly influence the design parameters. For instance, a valve-based amplifier circuit would typically include components such as high-voltage power supplies, filament transformers for heating the cathodes, and output transformers to match the impedance of speakers. These circuits often require careful layout considerations to manage heat dissipation and electromagnetic interference.
On the other hand, a transistor-based amplifier circuit would utilize low-voltage power supplies and include biasing resistors to set the operating point of the transistors. The schematic would also incorporate capacitors for coupling and decoupling signals, ensuring that the audio fidelity remains intact while preventing DC bias from affecting subsequent stages.
When designing a circuit, it is essential to evaluate the intended application, desired sound characteristics, and physical constraints. This evaluation will guide the selection of either valves or transistors, ultimately influencing the performance, reliability, and user experience of the electronic device. Each technology presents distinct challenges and benefits that must be carefully considered during the design process.The debate still goes on as to which are better, valves or transistors. We don t intend to get involved in that argument here. But if you can t make your.. 🔗 External reference