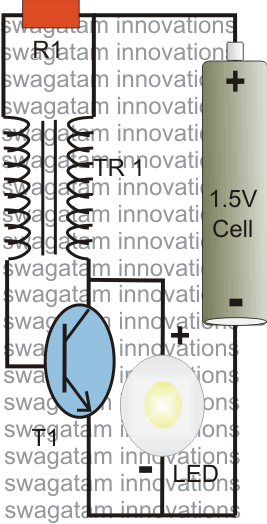
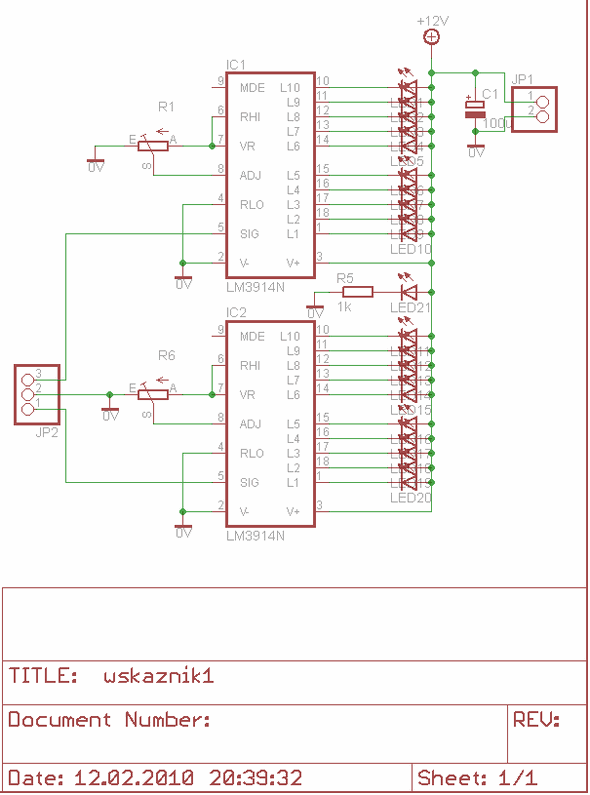
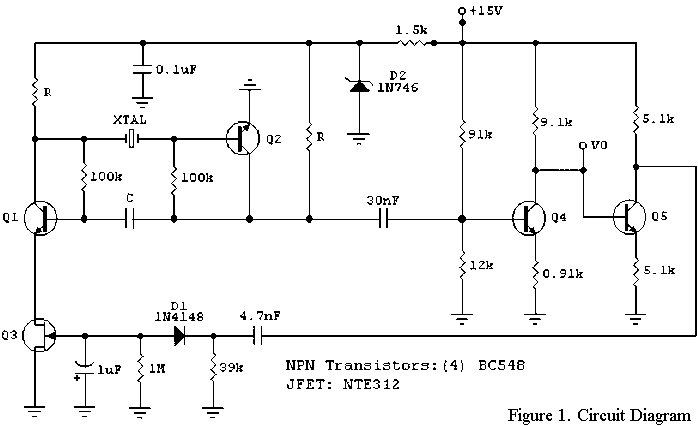
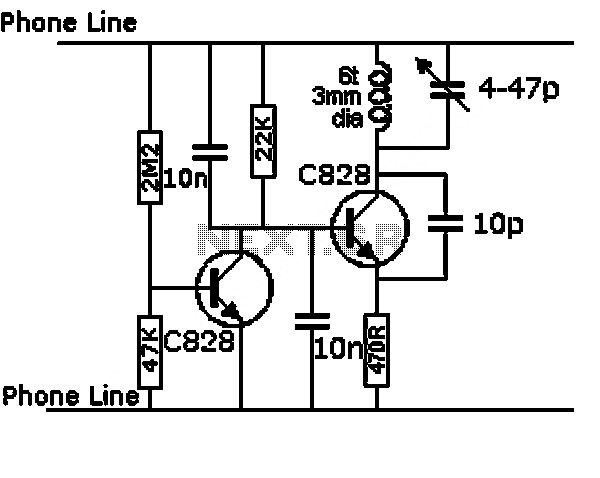
Audiostrobe-compatible LED glasses

Audiostrobe glasses are utilized alongside light and sound machines, as well as certain brainwave entrainment software. The glasses are equipped with built-in LEDs.
Audiostrobe glasses are designed to enhance the sensory experience provided by light and sound machines, which are often employed in therapeutic and recreational settings. These glasses feature integrated light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that synchronize with audio signals to create a multisensory environment. The primary function of the glasses is to facilitate a form of visual stimulation that corresponds to the auditory input, thereby promoting brainwave entrainment.
The circuitry within the audiostrobe glasses typically includes a microcontroller that processes audio signals from the connected device. The microcontroller interprets the audio frequencies and modulates the LED output accordingly. This modulation can vary in intensity and frequency, allowing for a dynamic visual display that complements the sound. The glasses may also incorporate a power management system to ensure efficient operation and extend battery life.
In a typical application, the audiostrobe glasses would connect to a light and sound machine or a compatible software platform through a standard audio jack or Bluetooth connection. Users wear the glasses while listening to specially designed audio tracks that contain embedded signals. These signals are often structured to induce specific brainwave states, such as relaxation or focus, through the combined effects of sound and light.
The design of the glasses must also consider user comfort and safety. Lightweight materials are often employed to ensure prolonged wear without discomfort, and the LEDs are usually shielded to prevent direct eye exposure, ensuring that the experience is both safe and enjoyable.
Overall, audiostrobe glasses represent a sophisticated integration of optics and electronics, providing a unique tool for enhancing cognitive and sensory experiences through the combination of visual and auditory stimuli.Audiostrobe glasses are used in conjunction with light and sound machines, as well as some brainwave entrainment software. The glasses have LEDs buil.. 🔗 External reference
Audiostrobe glasses are designed to enhance the sensory experience provided by light and sound machines, which are often employed in therapeutic and recreational settings. These glasses feature integrated light-emitting diodes (LEDs) that synchronize with audio signals to create a multisensory environment. The primary function of the glasses is to facilitate a form of visual stimulation that corresponds to the auditory input, thereby promoting brainwave entrainment.
The circuitry within the audiostrobe glasses typically includes a microcontroller that processes audio signals from the connected device. The microcontroller interprets the audio frequencies and modulates the LED output accordingly. This modulation can vary in intensity and frequency, allowing for a dynamic visual display that complements the sound. The glasses may also incorporate a power management system to ensure efficient operation and extend battery life.
In a typical application, the audiostrobe glasses would connect to a light and sound machine or a compatible software platform through a standard audio jack or Bluetooth connection. Users wear the glasses while listening to specially designed audio tracks that contain embedded signals. These signals are often structured to induce specific brainwave states, such as relaxation or focus, through the combined effects of sound and light.
The design of the glasses must also consider user comfort and safety. Lightweight materials are often employed to ensure prolonged wear without discomfort, and the LEDs are usually shielded to prevent direct eye exposure, ensuring that the experience is both safe and enjoyable.
Overall, audiostrobe glasses represent a sophisticated integration of optics and electronics, providing a unique tool for enhancing cognitive and sensory experiences through the combination of visual and auditory stimuli.Audiostrobe glasses are used in conjunction with light and sound machines, as well as some brainwave entrainment software. The glasses have LEDs buil.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713