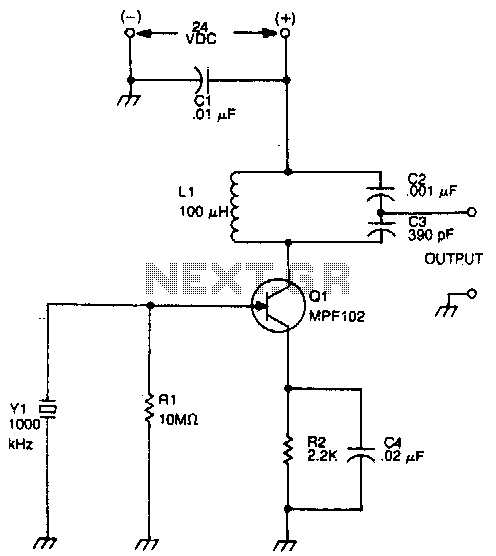
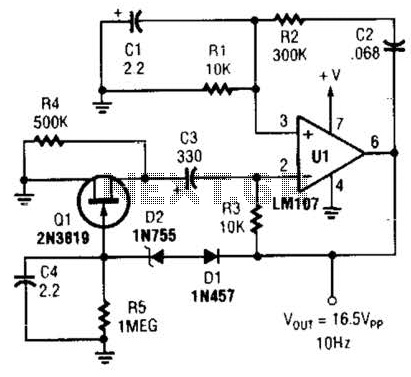
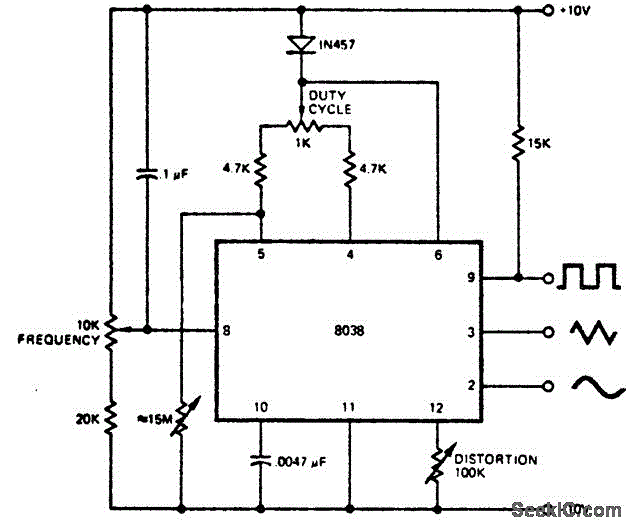
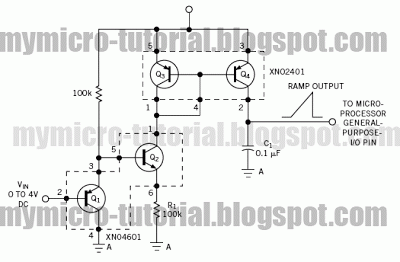
Crystal-controlled oscillator
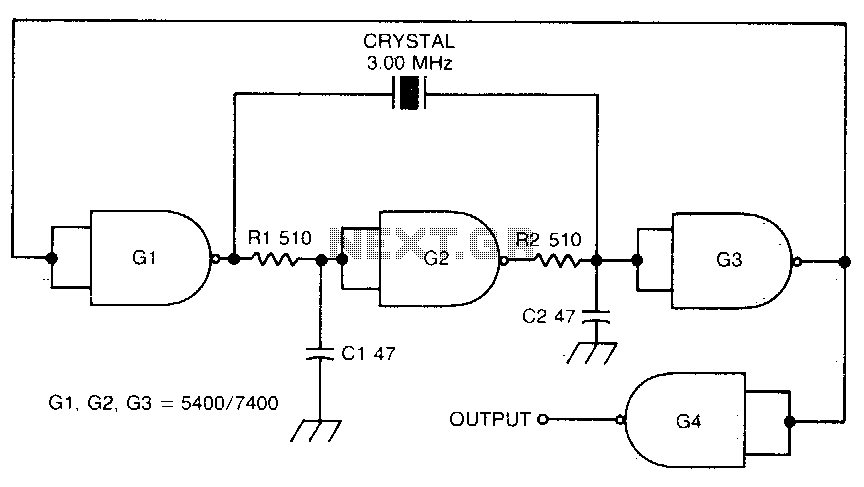
This circuit oscillates without the crystal. When the crystal is included in the circuit, the frequency will match that of the crystal. The circuit exhibits good starting characteristics even with low-quality crystals.
This circuit design features a basic oscillator configuration that can operate independently of a crystal oscillator, allowing it to generate oscillations based on its intrinsic properties. When a crystal is introduced into the circuit, it stabilizes the oscillation frequency to that of the crystal's resonant frequency, ensuring more precise control over the output frequency.
The oscillator typically comprises an active component, such as a transistor or an operational amplifier, configured in a feedback loop to sustain oscillations. The feedback network may include passive components like resistors and capacitors, which determine the oscillation frequency when no crystal is present. The inclusion of a crystal enhances the circuit's frequency stability and accuracy, making it suitable for applications requiring precise timing signals.
One notable aspect of this circuit is its ability to start oscillating reliably, even when utilizing low-quality crystals. This characteristic can be attributed to the design's robust feedback mechanism, which compensates for variations in the crystal's performance. Consequently, the circuit can maintain functionality across a range of crystal qualities, making it versatile for various electronic applications.
In summary, this oscillator circuit offers flexibility in operation, allowing it to function without a crystal while achieving enhanced frequency stability when one is used. Its effective starting characteristics ensure reliable performance, even with suboptimal crystal components.This circuit oscillates without the crystal. With the crystal in the circuit, the frequency will be that of the crystal The circuit has good starting characteristics even with the poorest crystals.
This circuit design features a basic oscillator configuration that can operate independently of a crystal oscillator, allowing it to generate oscillations based on its intrinsic properties. When a crystal is introduced into the circuit, it stabilizes the oscillation frequency to that of the crystal's resonant frequency, ensuring more precise control over the output frequency.
The oscillator typically comprises an active component, such as a transistor or an operational amplifier, configured in a feedback loop to sustain oscillations. The feedback network may include passive components like resistors and capacitors, which determine the oscillation frequency when no crystal is present. The inclusion of a crystal enhances the circuit's frequency stability and accuracy, making it suitable for applications requiring precise timing signals.
One notable aspect of this circuit is its ability to start oscillating reliably, even when utilizing low-quality crystals. This characteristic can be attributed to the design's robust feedback mechanism, which compensates for variations in the crystal's performance. Consequently, the circuit can maintain functionality across a range of crystal qualities, making it versatile for various electronic applications.
In summary, this oscillator circuit offers flexibility in operation, allowing it to function without a crystal while achieving enhanced frequency stability when one is used. Its effective starting characteristics ensure reliable performance, even with suboptimal crystal components.This circuit oscillates without the crystal. With the crystal in the circuit, the frequency will be that of the crystal The circuit has good starting characteristics even with the poorest crystals.