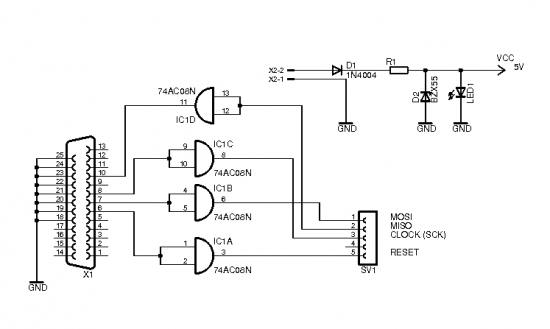
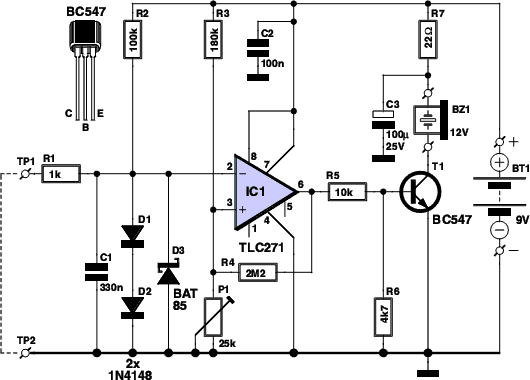
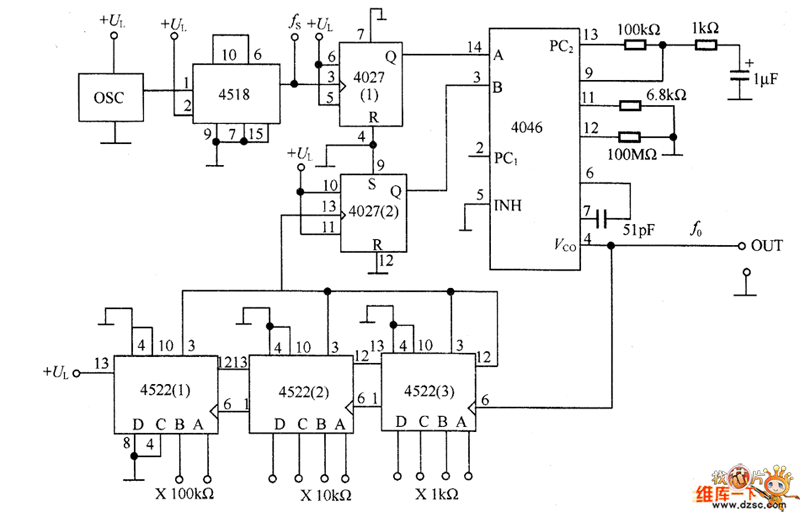
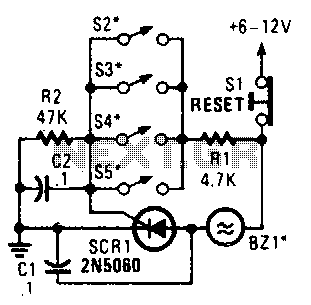
Augmenting a Microcontroller Circuit

To create a versatile and generic microcontroller board, the information provided thus far is sufficient. It covers the essential components needed to achieve this.
The design of a microcontroller board requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure versatility and functionality. The fundamental elements include the microcontroller unit (MCU), power supply, input/output (I/O) interfaces, and communication protocols.
The microcontroller should be selected based on the application requirements, including processing power, memory capacity, and peripheral support. Common choices include ARM Cortex, AVR, or PIC microcontrollers, each offering unique features suited for different tasks.
The power supply circuit must provide stable voltage and current to the microcontroller and any connected peripherals. This can be achieved using a linear or switching regulator, depending on the efficiency requirements and load conditions. It is essential to incorporate decoupling capacitors close to the power pins of the microcontroller to filter out noise and ensure stable operation.
I/O interfaces are critical for interacting with external components such as sensors, actuators, and displays. The board should include a sufficient number of digital and analog pins, as well as support for communication protocols like UART, SPI, and I2C. These protocols enable the microcontroller to communicate with other devices, facilitating data exchange and control.
Additionally, incorporating programming interfaces, such as a USB or JTAG connector, allows for easy firmware updates and debugging. A reset circuit may also be included to ensure the microcontroller can be restarted as needed.
Overall, the schematic design of a generic microcontroller board should emphasize modularity, allowing for easy expansion and integration of additional features as required by specific applications. This flexibility makes it suitable for a wide range of projects, from simple automation tasks to complex embedded systems.If you want to make an ultra-multipurpose, generic microcontroller board, then what I`ve covered already is enough. It`s the bare basics that will get.. 🔗 External reference
The design of a microcontroller board requires careful consideration of various factors to ensure versatility and functionality. The fundamental elements include the microcontroller unit (MCU), power supply, input/output (I/O) interfaces, and communication protocols.
The microcontroller should be selected based on the application requirements, including processing power, memory capacity, and peripheral support. Common choices include ARM Cortex, AVR, or PIC microcontrollers, each offering unique features suited for different tasks.
The power supply circuit must provide stable voltage and current to the microcontroller and any connected peripherals. This can be achieved using a linear or switching regulator, depending on the efficiency requirements and load conditions. It is essential to incorporate decoupling capacitors close to the power pins of the microcontroller to filter out noise and ensure stable operation.
I/O interfaces are critical for interacting with external components such as sensors, actuators, and displays. The board should include a sufficient number of digital and analog pins, as well as support for communication protocols like UART, SPI, and I2C. These protocols enable the microcontroller to communicate with other devices, facilitating data exchange and control.
Additionally, incorporating programming interfaces, such as a USB or JTAG connector, allows for easy firmware updates and debugging. A reset circuit may also be included to ensure the microcontroller can be restarted as needed.
Overall, the schematic design of a generic microcontroller board should emphasize modularity, allowing for easy expansion and integration of additional features as required by specific applications. This flexibility makes it suitable for a wide range of projects, from simple automation tasks to complex embedded systems.If you want to make an ultra-multipurpose, generic microcontroller board, then what I`ve covered already is enough. It`s the bare basics that will get.. 🔗 External reference