Automatic light dimmer circuit
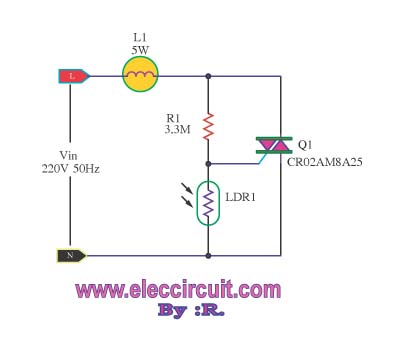
This is an automatic light dimmer circuit. There is no need to manually adjust the brightness of the lights. This circuit is highly convenient, as it utilizes a light-dependent resistor (LDR) to detect external light levels.
The automatic light dimmer circuit operates based on the principle of varying light intensity. The core component, the light-dependent resistor (LDR), changes its resistance according to the amount of ambient light it receives. In bright conditions, the resistance of the LDR decreases, which triggers the circuit to dim the lights. Conversely, in low-light conditions, the resistance increases, prompting the circuit to brighten the lights.
The circuit typically includes a power source, an LDR, a transistor or operational amplifier for signal processing, and a dimming mechanism such as a triac or a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controller. The LDR is connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor, allowing the circuit to produce a voltage signal that corresponds to the light intensity. This voltage is then fed into the base of a transistor, which controls the current flowing to the light source.
In practical applications, the circuit can be integrated into various lighting systems, such as streetlights, indoor lighting, or decorative lights, enhancing energy efficiency and user comfort. The automatic light dimmer circuit is particularly beneficial in settings where lighting needs to adjust based on time of day or occupancy, thereby optimizing power consumption and extending the lifespan of light bulbs.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective solution for automated lighting control, leveraging basic electronic components to achieve functionality that enhances convenience and efficiency in everyday environments.This is an automatic light dimmer circuit. You do not need to dim the lights by yourself. It is so very convenient, because we use the LDR to detect external.. 🔗 External reference
The automatic light dimmer circuit operates based on the principle of varying light intensity. The core component, the light-dependent resistor (LDR), changes its resistance according to the amount of ambient light it receives. In bright conditions, the resistance of the LDR decreases, which triggers the circuit to dim the lights. Conversely, in low-light conditions, the resistance increases, prompting the circuit to brighten the lights.
The circuit typically includes a power source, an LDR, a transistor or operational amplifier for signal processing, and a dimming mechanism such as a triac or a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) controller. The LDR is connected in a voltage divider configuration with a fixed resistor, allowing the circuit to produce a voltage signal that corresponds to the light intensity. This voltage is then fed into the base of a transistor, which controls the current flowing to the light source.
In practical applications, the circuit can be integrated into various lighting systems, such as streetlights, indoor lighting, or decorative lights, enhancing energy efficiency and user comfort. The automatic light dimmer circuit is particularly beneficial in settings where lighting needs to adjust based on time of day or occupancy, thereby optimizing power consumption and extending the lifespan of light bulbs.
Overall, this circuit exemplifies a simple yet effective solution for automated lighting control, leveraging basic electronic components to achieve functionality that enhances convenience and efficiency in everyday environments.This is an automatic light dimmer circuit. You do not need to dim the lights by yourself. It is so very convenient, because we use the LDR to detect external.. 🔗 External reference