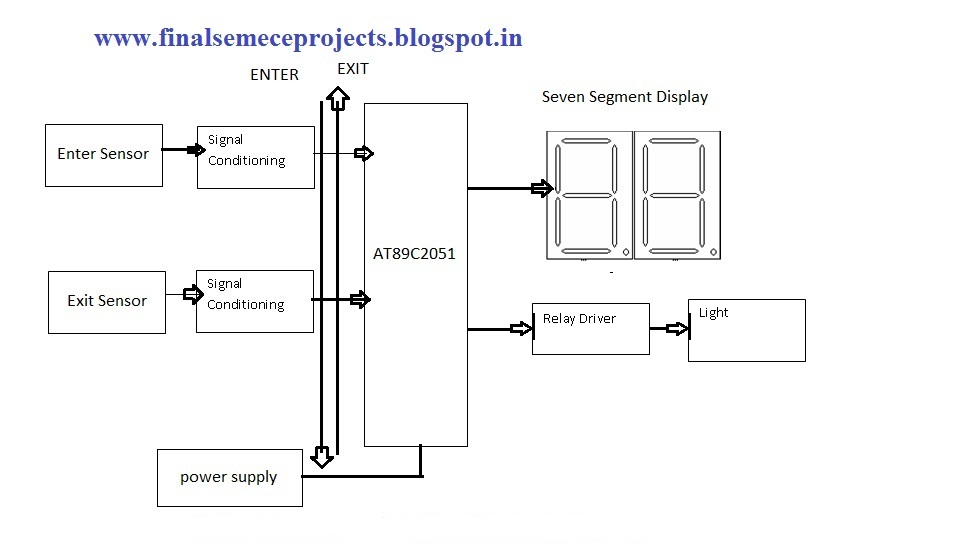
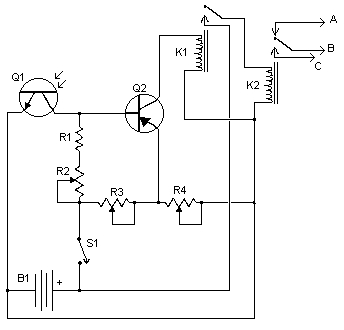
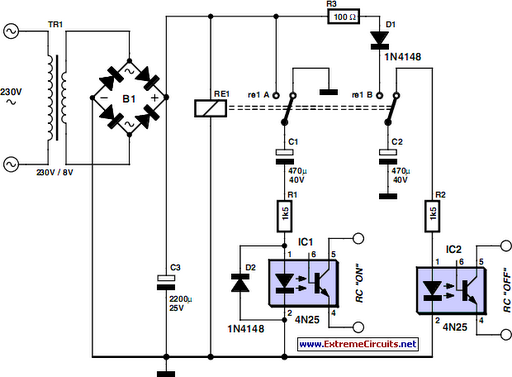
Automatic Mains Disconnect
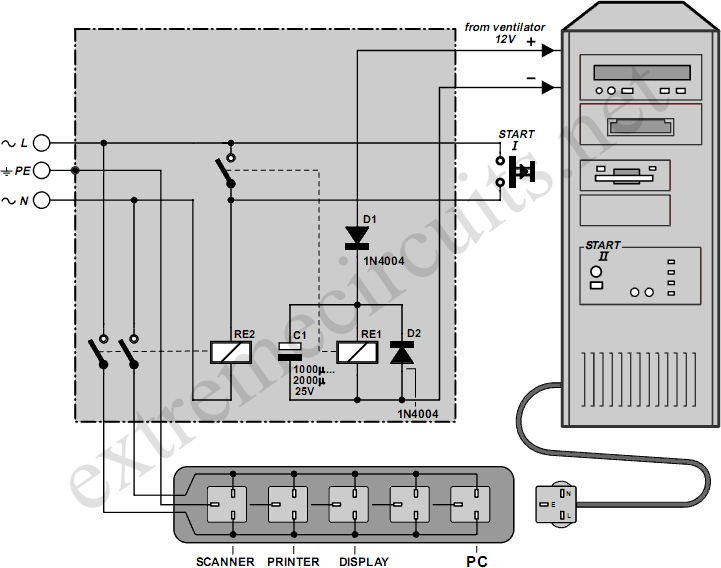
Downloading and CD-burning programs often offer the option to automatically shut down the PC upon completion of their tasks. However, this energy-saving feature is ineffective if all peripheral equipment remains connected to the mains and continues to consume power even after the PC is switched off. The circuit presented here addresses this issue by connecting ahead of the power strip and controlling the mains power for all connected equipment through a power relay. A connection to a 12-V PC fan (which may be the processor fan or the chipset fan, if available) indicates whether the PC is powered on. If it is confirmed that the 12-V power supply voltage turns off during the PC's sleep mode, this connection can be utilized instead. To power everything on, the Start button is pressed, energizing the power relay to supply mains voltage to all equipment. If the PC features an ATX motherboard, the Power switch must be pressed simultaneously to initiate the PC startup. Once the PC fan operates, the low-power relay Re1 engages, taking over the Start switch function, allowing it to be released. This state remains stable. If the PC enters sleep mode, the 12-V voltage drops, and the electrolytic capacitor ensures Re1 remains engaged for a brief period before it disengages, followed by the power relay. Diode D1 prevents the electrolytic capacitor from discharging through the connected fan, while D2 serves as the typical freewheeling diode. The system disconnects from both mains leads, rendering it completely de-energized. It is crucial to select components appropriate for their functions. The contacts of Re2 must be rated to handle the total current drawn by all peripheral equipment and the PC, and the relay coil must be suitable for mains voltage (a minimum separation of 6 mm between coil and contacts is required). A low-power 12-V relay capable of switching mains voltage suffices for Re2. The Start pushbutton switch must be rated for 230-V mains voltage. The circuit board layout and enclosure must adhere to safety regulations, ensuring a separation of at least 6 mm between all components carrying mains voltage and low-voltage components, with the enclosure designed to eliminate any risk of electrical shock. With appropriate skills, the circuit can be integrated into a power strip with a built-in switch, provided the switch is replaced with a pushbutton switch of equivalent mounting dimensions.
The circuit design incorporates a power relay that acts as a switch for the mains supply to peripheral devices. The relay is activated by a 12-V signal from the PC fan, ensuring that power is only supplied when the PC is operational. The use of an electrolytic capacitor allows for a delayed disengagement of the relay, maintaining power to peripherals briefly after the PC enters sleep mode, thus preventing sudden power loss. The inclusion of diodes D1 and D2 serves to protect the circuit from back EMF generated by inductive loads, such as fans, ensuring reliability and longevity of the components.
When designing the circuit, attention must be paid to the ratings of the relays and switches to ensure they can handle the maximum expected load. The separation of high and low voltage components is not only a safety measure but also essential for the circuit's proper functioning, as it minimizes the risk of interference and potential failure. The enclosure should be robust, providing adequate insulation and protection against accidental contact with live parts. This design can be particularly useful in environments where energy conservation is a priority, as it allows for the complete disconnection of power to peripherals when the PC is not in use.Downloading and CD-burning programs usually provide the option of automatically shutting down the PC on completion of their tasks. However, this energy-saving feature is of little benet if even after the PC has been switched off, all of the peripheral equipment remains connected to the mains and happily consumes watt-hours.
The circuit shown he re provides a solution to this dilemma. It is connected ahead of the power strip and connects or disconnects mains power for all of the equipment via a power relay. A connection to a 12-V PC fan (which may be the processor fan or the fan for the chipset, if the latter is present) indicates whether the PC is switched on.
If you are certain that the 12-V power supply voltage is switched off when the PC is in the sleep mode, you can use this connection instead. To switch everything on, press the Start button to cause the power relay to be energized and provide mains voltage to all of the equipment.
If the PC has an ATX board, its Power switch must be pressed at the same time to cause the PC to start up. When the PC fan starts to run, low-power relay Re1 engages and takes over the function of the Start switch, which can then be released.
This state is stable. If the PC switches to the sleep state, the 12-V voltage drops out. The electrolytic capacitor ensures that Re1 remains engaged for a short time, after which it drops out, followed by the power relay. D1 prevents the electrolytic capacitor from discharging through the connected fan, and D2 is the usual freewheeling diode.
The system is disconnected from both mains leads and is thus completely de-energized. Be sure to select components that are suitable for their tasks. Naturally, the contacts of Re2 should be rated to handle the total current drawn by all of the peripheral equipment and the PC, and the relay coil must be suitable for use with mains voltage (6 mm minimum separation between coil and contacts). A low-power 12-V relay that can switch mains voltage is adequate for Re2. The Start pushbutton switch is connected to the mains voltage, so a 230-V type must be used. The circuit board layout and enclosure must also be designed in accordance with safety regulations. A separation of at least 6 mm must be maintained between all components carrying mains voltage and the low-voltage components, and the enclosure must be completely free of risk of electrical shock.
With a bit of skill, the circuit can betted into a power bar with a built-in switch, if the switch is replaced by a pushbutton switch having the same mounting dimensions. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design incorporates a power relay that acts as a switch for the mains supply to peripheral devices. The relay is activated by a 12-V signal from the PC fan, ensuring that power is only supplied when the PC is operational. The use of an electrolytic capacitor allows for a delayed disengagement of the relay, maintaining power to peripherals briefly after the PC enters sleep mode, thus preventing sudden power loss. The inclusion of diodes D1 and D2 serves to protect the circuit from back EMF generated by inductive loads, such as fans, ensuring reliability and longevity of the components.
When designing the circuit, attention must be paid to the ratings of the relays and switches to ensure they can handle the maximum expected load. The separation of high and low voltage components is not only a safety measure but also essential for the circuit's proper functioning, as it minimizes the risk of interference and potential failure. The enclosure should be robust, providing adequate insulation and protection against accidental contact with live parts. This design can be particularly useful in environments where energy conservation is a priority, as it allows for the complete disconnection of power to peripherals when the PC is not in use.Downloading and CD-burning programs usually provide the option of automatically shutting down the PC on completion of their tasks. However, this energy-saving feature is of little benet if even after the PC has been switched off, all of the peripheral equipment remains connected to the mains and happily consumes watt-hours.
The circuit shown he re provides a solution to this dilemma. It is connected ahead of the power strip and connects or disconnects mains power for all of the equipment via a power relay. A connection to a 12-V PC fan (which may be the processor fan or the fan for the chipset, if the latter is present) indicates whether the PC is switched on.
If you are certain that the 12-V power supply voltage is switched off when the PC is in the sleep mode, you can use this connection instead. To switch everything on, press the Start button to cause the power relay to be energized and provide mains voltage to all of the equipment.
If the PC has an ATX board, its Power switch must be pressed at the same time to cause the PC to start up. When the PC fan starts to run, low-power relay Re1 engages and takes over the function of the Start switch, which can then be released.
This state is stable. If the PC switches to the sleep state, the 12-V voltage drops out. The electrolytic capacitor ensures that Re1 remains engaged for a short time, after which it drops out, followed by the power relay. D1 prevents the electrolytic capacitor from discharging through the connected fan, and D2 is the usual freewheeling diode.
The system is disconnected from both mains leads and is thus completely de-energized. Be sure to select components that are suitable for their tasks. Naturally, the contacts of Re2 should be rated to handle the total current drawn by all of the peripheral equipment and the PC, and the relay coil must be suitable for use with mains voltage (6 mm minimum separation between coil and contacts). A low-power 12-V relay that can switch mains voltage is adequate for Re2. The Start pushbutton switch is connected to the mains voltage, so a 230-V type must be used. The circuit board layout and enclosure must also be designed in accordance with safety regulations. A separation of at least 6 mm must be maintained between all components carrying mains voltage and the low-voltage components, and the enclosure must be completely free of risk of electrical shock.
With a bit of skill, the circuit can betted into a power bar with a built-in switch, if the switch is replaced by a pushbutton switch having the same mounting dimensions. 🔗 External reference