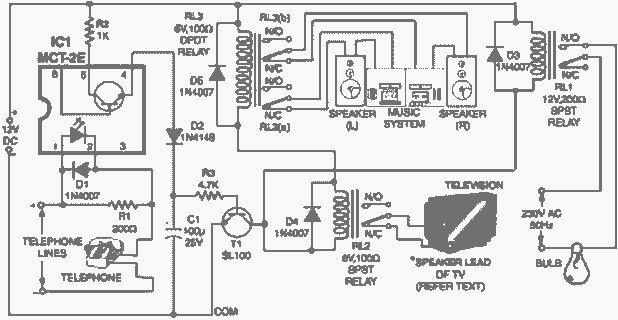
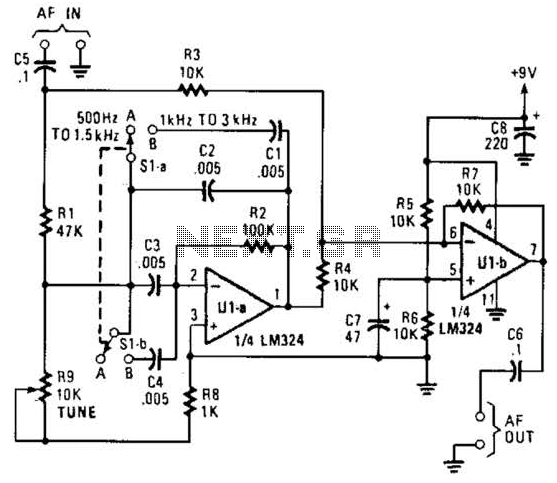
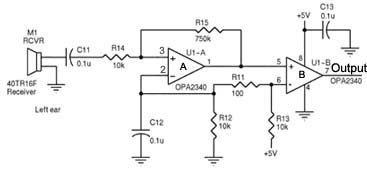
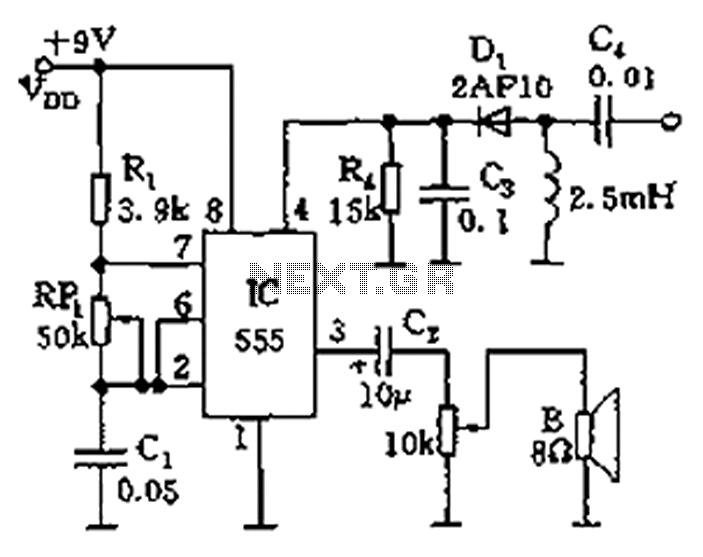
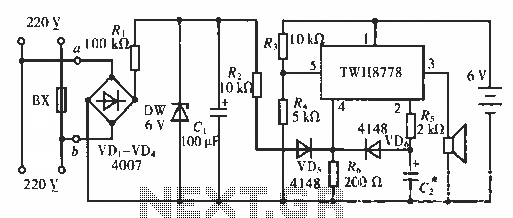
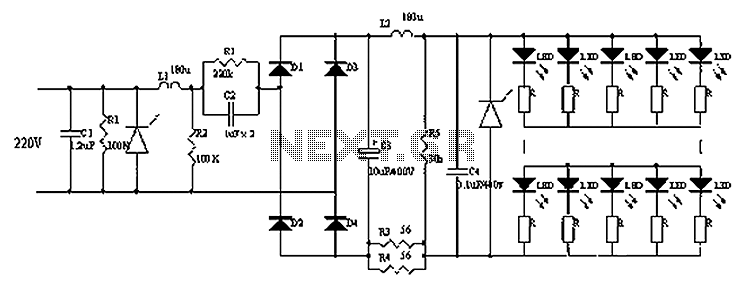
Automatically disconnect the battery charger circuit
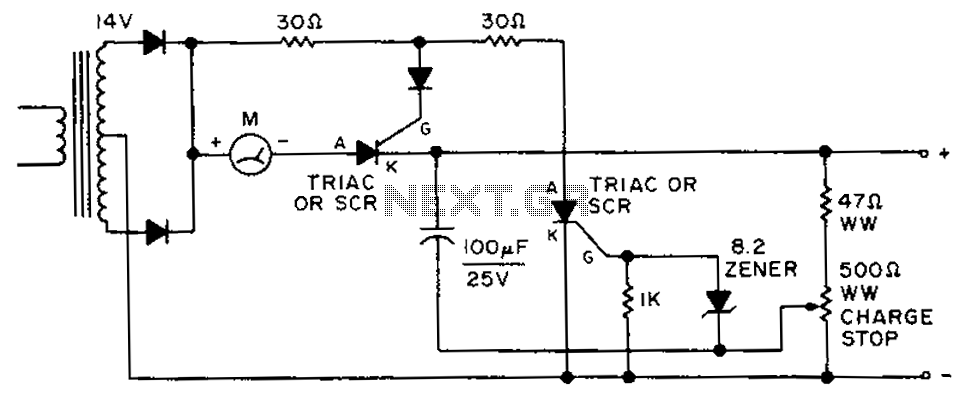
By adjusting the circuit with a 500-ohm resistor, the resistor is integrated into a fully charged battery system.
The circuit described involves a 500-ohm resistor that plays a crucial role in regulating the operation of a fully charged battery system. This resistor can be employed in various applications, such as voltage dividers, current limiting, or as a part of feedback loops in more complex circuits.
In a typical configuration, the 500-ohm resistor may be connected in series or parallel with other components, depending on the desired circuit behavior. For instance, when used in series with a load, it can help limit the current flowing through the circuit, thereby protecting sensitive components from excessive current. In scenarios where the resistor is placed in parallel, it can be used to create a voltage divider that provides a specific output voltage derived from the battery's total voltage.
The integration of this resistor into a fully charged battery circuit ensures that the system operates within safe parameters, maintaining the integrity of the battery and preventing over-discharge or over-current conditions. Furthermore, the resistor's value can be adjusted or replaced to modify the circuit's performance, allowing for flexibility in design.
In summary, the 500-ohm resistor is a vital component within a fully charged battery system, serving to regulate current and voltage, thereby enhancing the overall reliability and functionality of the circuit. By setting the 500 ohm resistor to adjust the circuit, the resistor is part of a fully charged battery.
The circuit described involves a 500-ohm resistor that plays a crucial role in regulating the operation of a fully charged battery system. This resistor can be employed in various applications, such as voltage dividers, current limiting, or as a part of feedback loops in more complex circuits.
In a typical configuration, the 500-ohm resistor may be connected in series or parallel with other components, depending on the desired circuit behavior. For instance, when used in series with a load, it can help limit the current flowing through the circuit, thereby protecting sensitive components from excessive current. In scenarios where the resistor is placed in parallel, it can be used to create a voltage divider that provides a specific output voltage derived from the battery's total voltage.
The integration of this resistor into a fully charged battery circuit ensures that the system operates within safe parameters, maintaining the integrity of the battery and preventing over-discharge or over-current conditions. Furthermore, the resistor's value can be adjusted or replaced to modify the circuit's performance, allowing for flexibility in design.
In summary, the 500-ohm resistor is a vital component within a fully charged battery system, serving to regulate current and voltage, thereby enhancing the overall reliability and functionality of the circuit. By setting the 500 ohm resistor to adjust the circuit, the resistor is part of a fully charged battery.