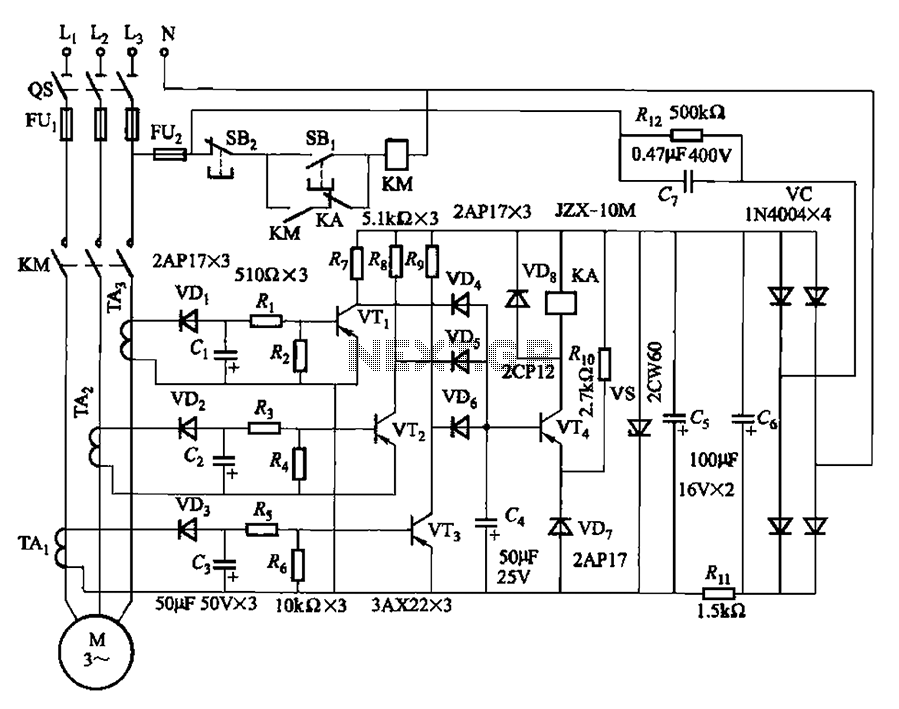
Brushless DC motor control circuit
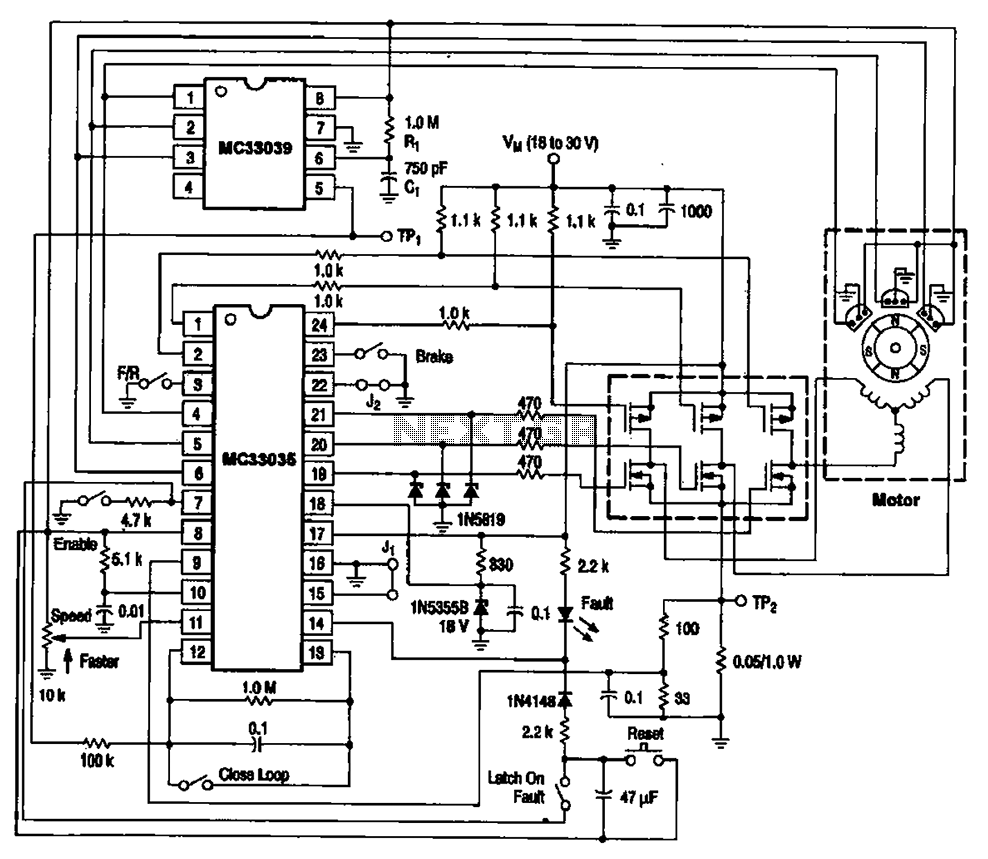
The brushless DC motor control circuit utilizing the MC33035 and MC33039 chips employs a combination of control circuits as illustrated in the figure. The primary components include the MC33035 motor control chip, the MC33039 brushless motor adapter, field effect transistors, and other elements forming the drive circuit. During operation, the MC33035 generates six I-WM signals to drive the motor control circuit through six field effect transistors. This configuration forms a bridge circuit where the outputs are connected to the three-phase motor windings. The three-phase current in the windings changes sequentially according to a specific pattern, creating a rotating magnetic field that causes the rotor of the motor to rotate continuously.
The brushless DC motor control circuit is designed to efficiently manage the operation of brushless motors, which are known for their high efficiency and reliability. The MC33035 serves as the primary control unit, generating pulse-width modulation (PWM) signals that regulate the speed and torque of the motor. The MC33039 complements this functionality by providing additional control features, such as over-current protection and thermal shutdown.
In the circuit, the six field effect transistors (FETs) are configured in a three-phase bridge arrangement, allowing for precise control of the current flowing through each motor winding. The sequential activation of the FETs is crucial for generating a rotating magnetic field. This field interacts with permanent magnets on the rotor, resulting in continuous rotation.
The design of this circuit is particularly beneficial for applications requiring precise speed control and high torque at low speeds. Furthermore, the integration of the MC33035 and MC33039 offers a compact solution that minimizes component count while maximizing performance. The use of FETs ensures rapid switching times and high efficiency, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the motor control system.
In summary, the brushless DC motor control circuit utilizing the MC33035 and MC33039 chips provides a sophisticated solution for controlling brushless motors, ensuring efficient operation and precise control through a well-designed arrangement of power electronics. Brushless DC motor control circuit MC33035 and MC33039 uses a combination of the control circuit is shown in Figure A typical brushless DC motor control circuit, which is mainl y driven by the motor control chip MC33035 and MC33039 brushless motor adapter and field effect transistors and other parts of the drive circuit. At work. MC33035 output channel 6 I-WM signals to drive the motor driving circuit 6 by a field effect transistor.
It is seen from six field effect transistor bridge circuit. Outputs are connected to the three-phase motor winding. Three-phase current in the windings sequentially changed according to the law, to form a rotating magnetic field, the rotor of the drive motor continuously rotates.
The brushless DC motor control circuit is designed to efficiently manage the operation of brushless motors, which are known for their high efficiency and reliability. The MC33035 serves as the primary control unit, generating pulse-width modulation (PWM) signals that regulate the speed and torque of the motor. The MC33039 complements this functionality by providing additional control features, such as over-current protection and thermal shutdown.
In the circuit, the six field effect transistors (FETs) are configured in a three-phase bridge arrangement, allowing for precise control of the current flowing through each motor winding. The sequential activation of the FETs is crucial for generating a rotating magnetic field. This field interacts with permanent magnets on the rotor, resulting in continuous rotation.
The design of this circuit is particularly beneficial for applications requiring precise speed control and high torque at low speeds. Furthermore, the integration of the MC33035 and MC33039 offers a compact solution that minimizes component count while maximizing performance. The use of FETs ensures rapid switching times and high efficiency, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the motor control system.
In summary, the brushless DC motor control circuit utilizing the MC33035 and MC33039 chips provides a sophisticated solution for controlling brushless motors, ensuring efficient operation and precise control through a well-designed arrangement of power electronics. Brushless DC motor control circuit MC33035 and MC33039 uses a combination of the control circuit is shown in Figure A typical brushless DC motor control circuit, which is mainl y driven by the motor control chip MC33035 and MC33039 brushless motor adapter and field effect transistors and other parts of the drive circuit. At work. MC33035 output channel 6 I-WM signals to drive the motor driving circuit 6 by a field effect transistor.
It is seen from six field effect transistor bridge circuit. Outputs are connected to the three-phase motor winding. Three-phase current in the windings sequentially changed according to the law, to form a rotating magnetic field, the rotor of the drive motor continuously rotates.