DC Motor Reversing Circuit
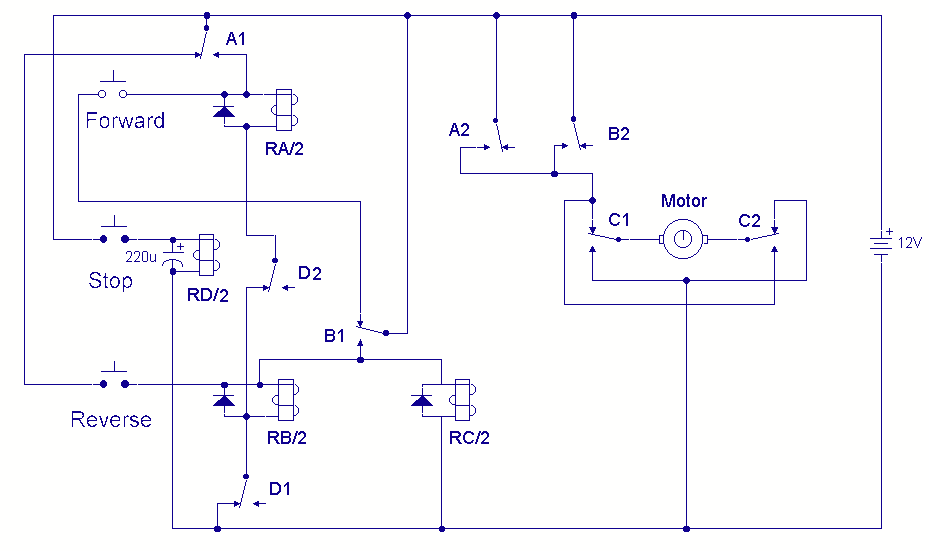
A DC motor reversing circuit using non-latching push button switches. Relays control forward, stop, and reverse action, and the motor cannot be switched from forward to reverse unless the stop switch is pressed first.
The described circuit employs a system of non-latching push button switches to control the direction of a DC motor. The primary components consist of two relays, which are utilized to manage the motor's operation modes: forward, stop, and reverse. The non-latching nature of the push buttons ensures that the circuit remains in a specific state only while the button is pressed, thereby enhancing safety and preventing accidental activation.
In this configuration, the circuit includes two push buttons labeled as "Forward" and "Reverse," as well as a "Stop" button. When the "Forward" button is pressed, the corresponding relay is activated, allowing current to flow to the motor in one direction, thereby driving it forward. The relay remains engaged as long as the button is held down. Upon releasing the button, the relay deactivates, cutting off power to the motor.
To reverse the motor's direction, the "Stop" button must be pressed first. This action deactivates the forward relay, ensuring that the motor comes to a complete stop before any directional change occurs. Once the motor is stopped, pressing the "Reverse" button activates the reverse relay, which allows current to flow in the opposite direction, thereby reversing the motor's rotation.
This design is critical for applications where rapid switching between forward and reverse operation is required, as it prevents potential damage to the motor and associated circuitry. Additionally, the use of relays provides isolation between the control circuit and the motor circuit, enhancing safety and reliability. The circuit can be further protected with diodes across the relay coils to prevent back EMF from damaging the control components when the relays are deactivated.
Overall, this circuit design is effective for simple DC motor control applications requiring directional reversal with built-in safety mechanisms.A DC motor reversing circuit using non latching push button switches. Relays control forward, stop and reverse action, and the motor cannot be switched from forward to reverse unless the stop switch is pressed first. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs a system of non-latching push button switches to control the direction of a DC motor. The primary components consist of two relays, which are utilized to manage the motor's operation modes: forward, stop, and reverse. The non-latching nature of the push buttons ensures that the circuit remains in a specific state only while the button is pressed, thereby enhancing safety and preventing accidental activation.
In this configuration, the circuit includes two push buttons labeled as "Forward" and "Reverse," as well as a "Stop" button. When the "Forward" button is pressed, the corresponding relay is activated, allowing current to flow to the motor in one direction, thereby driving it forward. The relay remains engaged as long as the button is held down. Upon releasing the button, the relay deactivates, cutting off power to the motor.
To reverse the motor's direction, the "Stop" button must be pressed first. This action deactivates the forward relay, ensuring that the motor comes to a complete stop before any directional change occurs. Once the motor is stopped, pressing the "Reverse" button activates the reverse relay, which allows current to flow in the opposite direction, thereby reversing the motor's rotation.
This design is critical for applications where rapid switching between forward and reverse operation is required, as it prevents potential damage to the motor and associated circuitry. Additionally, the use of relays provides isolation between the control circuit and the motor circuit, enhancing safety and reliability. The circuit can be further protected with diodes across the relay coils to prevent back EMF from damaging the control components when the relays are deactivated.
Overall, this circuit design is effective for simple DC motor control applications requiring directional reversal with built-in safety mechanisms.A DC motor reversing circuit using non latching push button switches. Relays control forward, stop and reverse action, and the motor cannot be switched from forward to reverse unless the stop switch is pressed first. 🔗 External reference