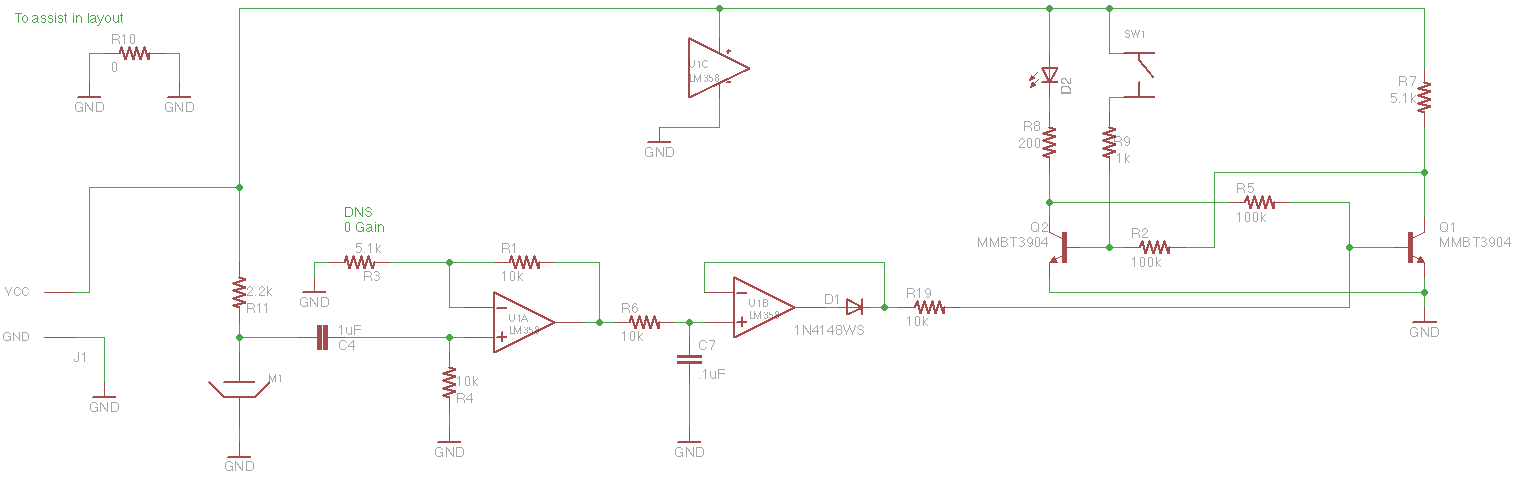
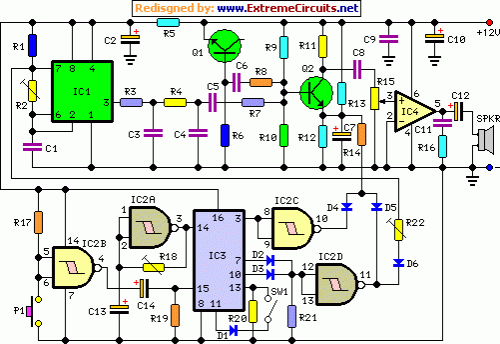
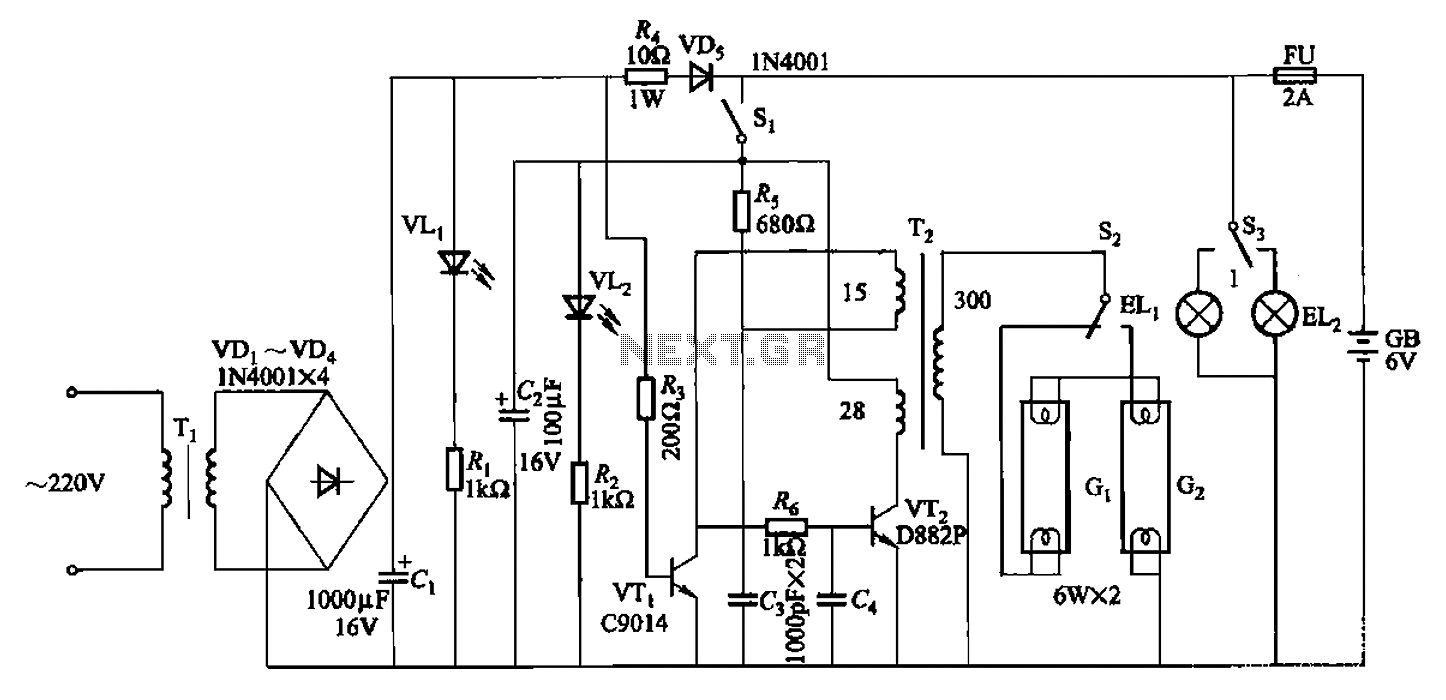
A typical electronic volume control circuit
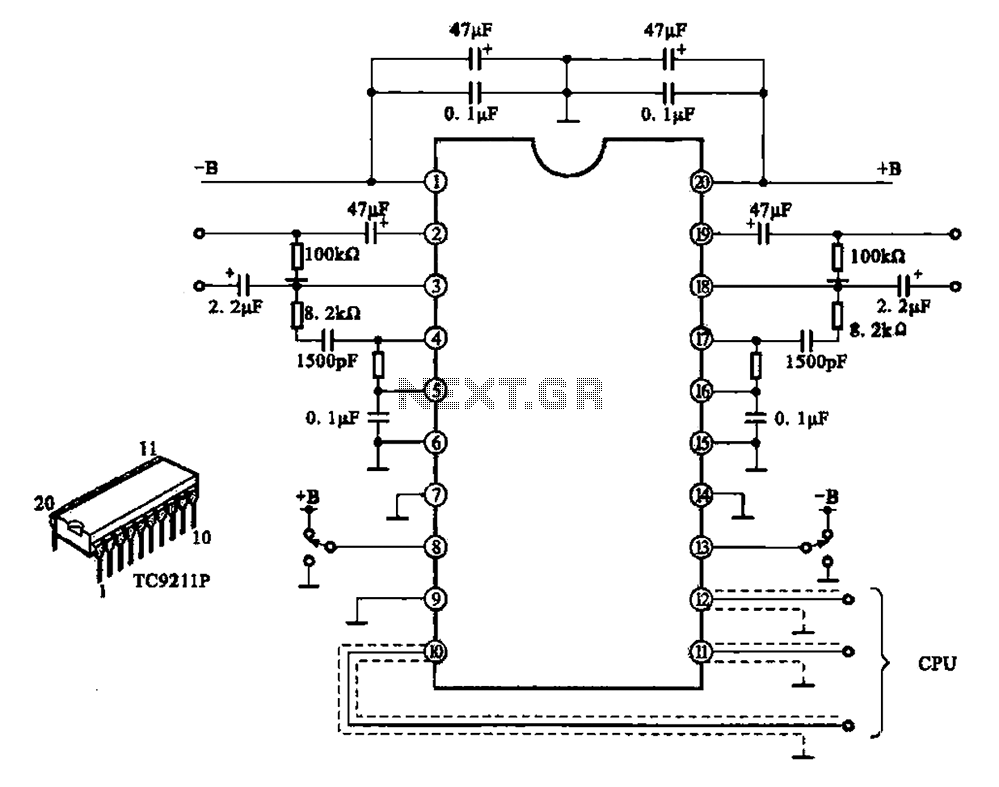
A typical electronic volume control circuit is commonly used in stereo audio devices connected through a computer (CPU). The circuit adjusts the volume of stereo signals via input and output pins. Control signals are sent to the CPU (including clock, data, and standby) through an interface circuit to the TC9211P, which decodes the signals and converts them from digital to analog. This conversion allows for the adjustment of the input signal amplitude, thereby achieving the desired volume control.
The electronic volume control circuit typically involves several key components that work together to manage audio levels effectively. At its core is the TC9211P integrated circuit, which serves as the digital-to-analog converter (DAC) and the volume control processor. This IC receives digital control signals from the CPU, which dictate the desired volume level. The control signals include clock, data, and standby signals that are essential for the operation of the TC9211P.
The interface circuit plays a crucial role in facilitating communication between the CPU and the TC9211P. It ensures that the digital signals are correctly formatted and transmitted, allowing for accurate decoding. The input pins of the circuit receive stereo audio signals, which are typically in the form of differential signals to minimize noise and interference. These signals are then processed by the TC9211P, which adjusts the amplitude of the audio signals based on the control signals received.
The output pins deliver the adjusted analog audio signals to the audio amplification stage or directly to the speakers. This allows the user to experience varying audio levels based on their preferences. The circuit may also incorporate additional features such as mute functionality and a standby mode to enhance usability and energy efficiency.
Overall, the electronic volume control circuit is an essential component in modern audio systems, providing precise and reliable control over sound levels in stereo applications. Its integration with digital systems, such as CPUs, reflects the increasing convergence of analog and digital technologies in audio processing.A typical electronic volume control circuit It shows a typical electronic volume control circuit. The circuit is often used in stereo audio devices through the computer (CPU) i nto the line and adjust the volume control. Stereo signals by the, ? pin input by, pin output adjusted. The control signal to the CPU (clock, data and standby) from ? ~ foot into TC9211P in via an interface circuit for decoding and D/A converter into an analog signal control input signal amplitude number, so as to achieve the purpose of controlling the volume .
The electronic volume control circuit typically involves several key components that work together to manage audio levels effectively. At its core is the TC9211P integrated circuit, which serves as the digital-to-analog converter (DAC) and the volume control processor. This IC receives digital control signals from the CPU, which dictate the desired volume level. The control signals include clock, data, and standby signals that are essential for the operation of the TC9211P.
The interface circuit plays a crucial role in facilitating communication between the CPU and the TC9211P. It ensures that the digital signals are correctly formatted and transmitted, allowing for accurate decoding. The input pins of the circuit receive stereo audio signals, which are typically in the form of differential signals to minimize noise and interference. These signals are then processed by the TC9211P, which adjusts the amplitude of the audio signals based on the control signals received.
The output pins deliver the adjusted analog audio signals to the audio amplification stage or directly to the speakers. This allows the user to experience varying audio levels based on their preferences. The circuit may also incorporate additional features such as mute functionality and a standby mode to enhance usability and energy efficiency.
Overall, the electronic volume control circuit is an essential component in modern audio systems, providing precise and reliable control over sound levels in stereo applications. Its integration with digital systems, such as CPUs, reflects the increasing convergence of analog and digital technologies in audio processing.A typical electronic volume control circuit It shows a typical electronic volume control circuit. The circuit is often used in stereo audio devices through the computer (CPU) i nto the line and adjust the volume control. Stereo signals by the, ? pin input by, pin output adjusted. The control signal to the CPU (clock, data and standby) from ? ~ foot into TC9211P in via an interface circuit for decoding and D/A converter into an analog signal control input signal amplitude number, so as to achieve the purpose of controlling the volume .