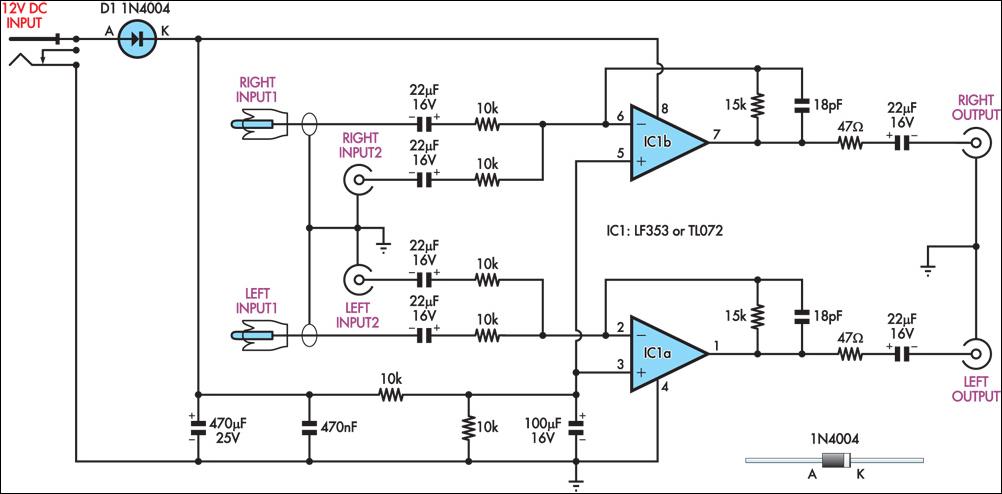
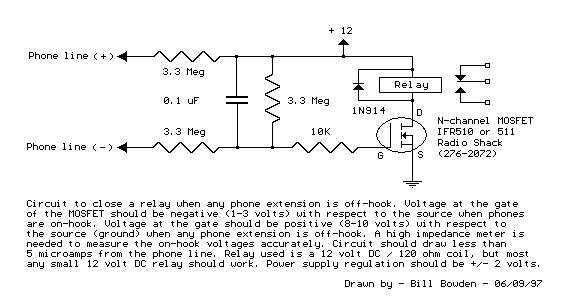
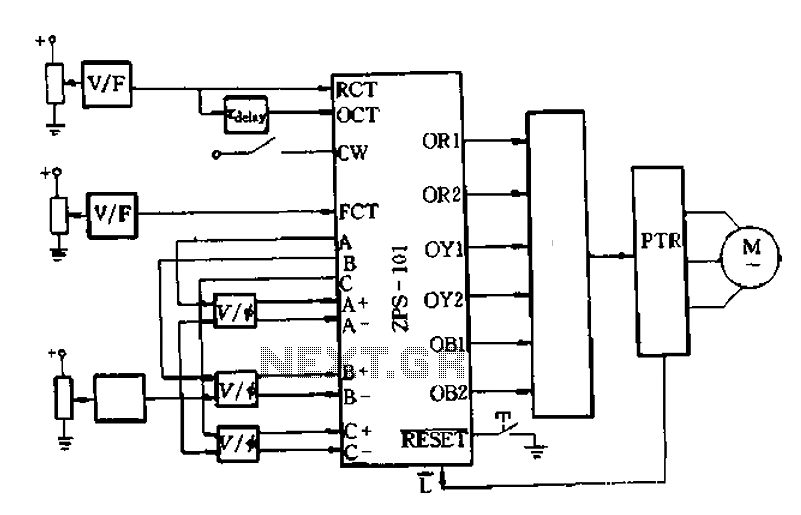
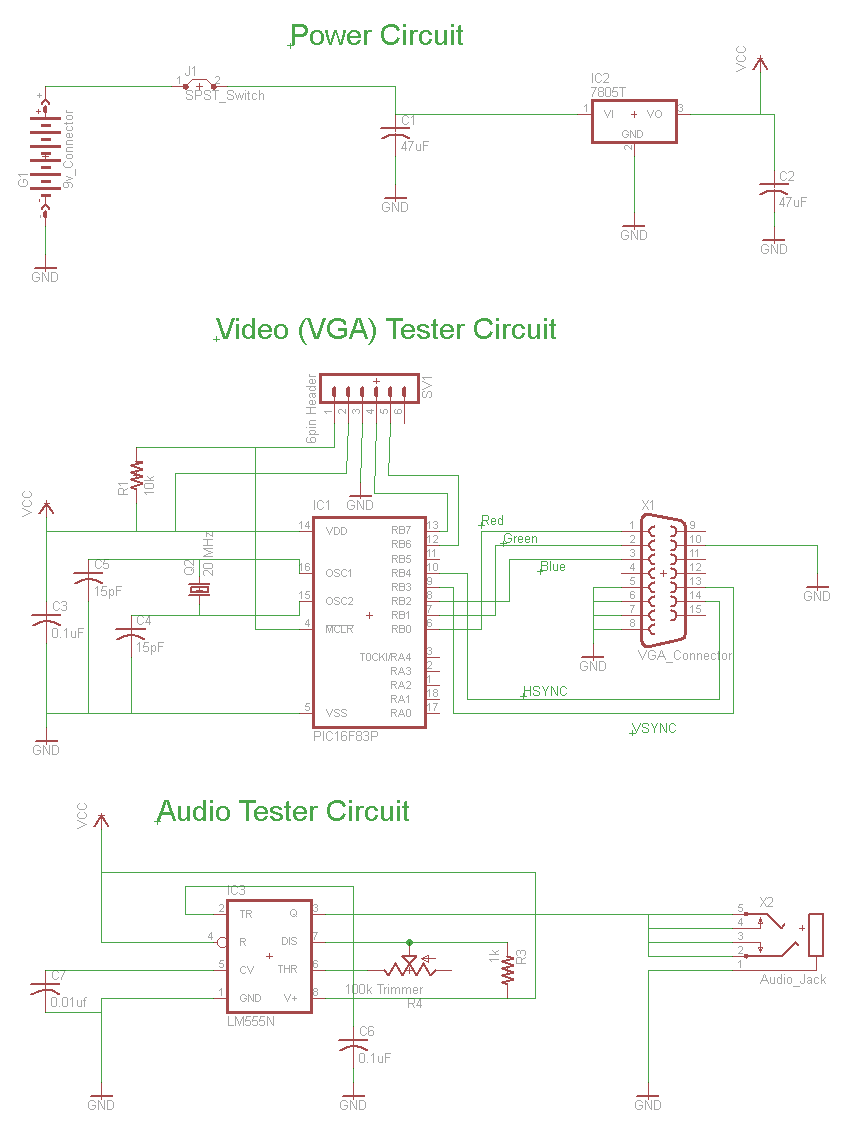
Autopatch telephone line interface
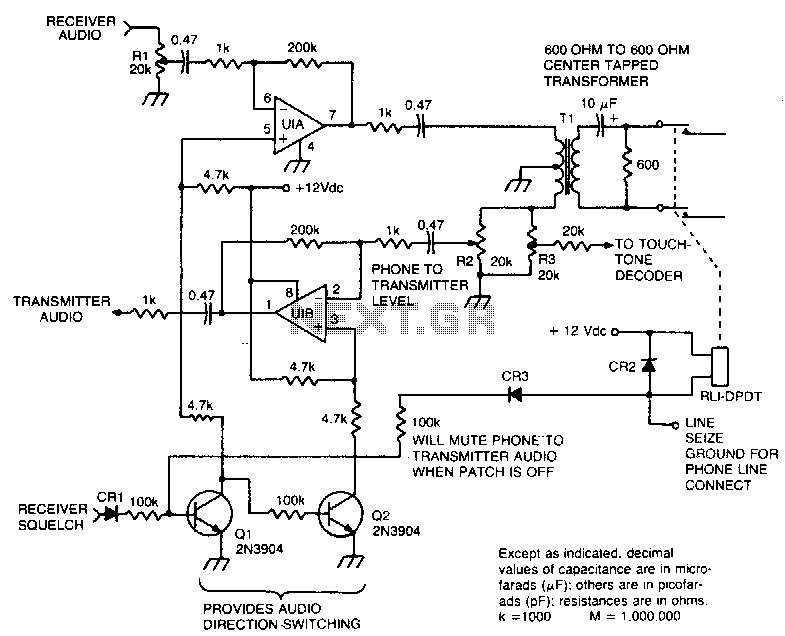
This circuit facilitates the communication link between the receiver and the phone line, as well as the phone line and the transmitter, utilizing an operational amplifier (op-amp) for signal amplification.
The described circuit connects a receiver to a phone line and a phone line to a transmitter, ensuring effective signal transmission and reception. The operational amplifier plays a critical role in this configuration, providing necessary gain to the signals being processed.
In this application, the op-amp is typically configured in a non-inverting mode to amplify the weak signals received from the transducer or sensor. The input from the receiver is fed into the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp, while the output is taken from the op-amp's output terminal, which then connects to the phone line. The gain of the op-amp can be adjusted using feedback resistors, allowing for optimal signal strength based on the specific requirements of the communication system.
For the phone line to transmitter link, a similar configuration can be employed. The output from the phone line can be fed into another op-amp stage, which ensures that the signal is sufficiently amplified before it reaches the transmitter. This stage is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the signal over longer distances, minimizing the effects of noise and attenuation that may occur along the transmission path.
In addition to the op-amps, the circuit may also include passive components such as resistors and capacitors for filtering and stability purposes. Properly designed power supply circuitry is essential to ensure that the op-amps operate within their specified voltage range, which is critical for maintaining performance and preventing distortion.
Overall, this circuit design effectively enables communication between various components in a telecommunication system, leveraging the capabilities of operational amplifiers to enhance signal quality and reliability.This circuit provides for the receiver-to-phone line and phone line-to-transmitter link with both using an op amp for gain.
The described circuit connects a receiver to a phone line and a phone line to a transmitter, ensuring effective signal transmission and reception. The operational amplifier plays a critical role in this configuration, providing necessary gain to the signals being processed.
In this application, the op-amp is typically configured in a non-inverting mode to amplify the weak signals received from the transducer or sensor. The input from the receiver is fed into the non-inverting terminal of the op-amp, while the output is taken from the op-amp's output terminal, which then connects to the phone line. The gain of the op-amp can be adjusted using feedback resistors, allowing for optimal signal strength based on the specific requirements of the communication system.
For the phone line to transmitter link, a similar configuration can be employed. The output from the phone line can be fed into another op-amp stage, which ensures that the signal is sufficiently amplified before it reaches the transmitter. This stage is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the signal over longer distances, minimizing the effects of noise and attenuation that may occur along the transmission path.
In addition to the op-amps, the circuit may also include passive components such as resistors and capacitors for filtering and stability purposes. Properly designed power supply circuitry is essential to ensure that the op-amps operate within their specified voltage range, which is critical for maintaining performance and preventing distortion.
Overall, this circuit design effectively enables communication between various components in a telecommunication system, leveraging the capabilities of operational amplifiers to enhance signal quality and reliability.This circuit provides for the receiver-to-phone line and phone line-to-transmitter link with both using an op amp for gain.