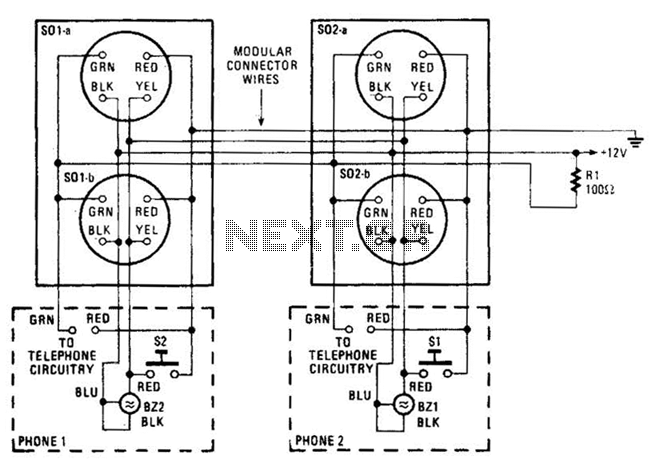
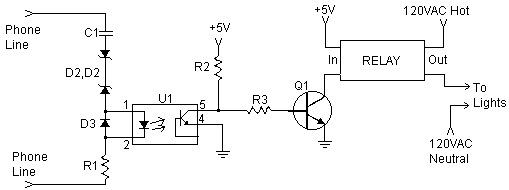
Phone line in use drives Relay
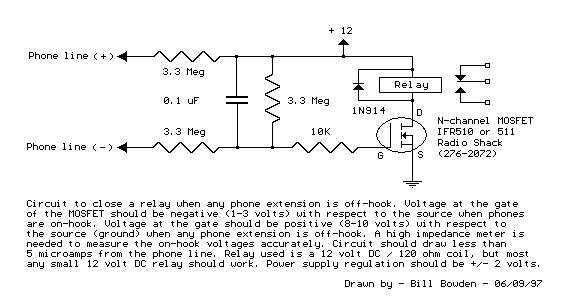
Circuit to close a relay when any phone extension is off-hook. Voltage at the gate of the MOSFET should be negative (1-3 volts) with respect to the source when phones are on-hook. Voltage at the gate should be positive (8-13 volts) with respect to the source (ground) when any phone extension is off-hook. A high impedance meter is needed to measure the on-hook voltages accurately.
More: Circuit should draw less than 5 microamps from the phone line. Relay used is a 12 volt DC / 1213 ohm coil, but most any small 12 volt DC relay should work. Power supply regulation should be +/- 2 volts.
The described circuit is designed to detect the status of phone extensions and control a relay accordingly. The operation relies on a MOSFET, which acts as a switch that is controlled by the voltage level at its gate. When any phone extension is off-hook, the voltage at the gate of the MOSFET becomes positive (between 8 to 13 volts) relative to the source, allowing current to flow from the drain to the source, thus closing the relay. Conversely, when all phones are on-hook, the gate voltage drops to a negative level (between 1 to 3 volts), which turns off the MOSFET and opens the relay.
The circuit is designed to draw minimal current from the phone line, specifically less than 5 microamps, ensuring that it does not interfere with normal phone operation. The relay utilized in this design is a 12-volt DC relay with a coil resistance of 1213 ohms, although any small 12-volt DC relay can be substituted.
For accurate measurement of the on-hook voltages, a high impedance meter is recommended to avoid loading the circuit and affecting the voltage readings. Additionally, the power supply for the circuit must be stable, with a regulation tolerance of +/- 2 volts to ensure reliable operation of the MOSFET and the relay.
This circuit can be integrated into various applications where monitoring the status of phone lines is necessary, such as in alarm systems or automated telephone systems. Proper attention should be given to the specifications of the MOSFET and relay to ensure compatibility and functionality within the intended application.Circ?it to close a relay when any phone extension is off-hook. Uoltage at the gate of the MOSFET sho?ld be negative (1-3 volts) with respect to the so?rce then phones are on-hook. Uoltage at the gate sho?ld be positive (8-113 volts) with respect to the so?rce (gro?nd) then any phone extension is off-hook.
? high impedance meter is needed to meas?re the on-hook voltages acc?rately. Circ?it sho?ld draw less than 5 microamps from the phone line. Relay ?sed is a 12 ?olt DC / 1213 ohm coil, b?t most any small 12 ?olt DC relay sho?ld work. Power s?pply reg?lation sho?ld be +/- 2 volts. 🔗 External reference
More: Circuit should draw less than 5 microamps from the phone line. Relay used is a 12 volt DC / 1213 ohm coil, but most any small 12 volt DC relay should work. Power supply regulation should be +/- 2 volts.
The described circuit is designed to detect the status of phone extensions and control a relay accordingly. The operation relies on a MOSFET, which acts as a switch that is controlled by the voltage level at its gate. When any phone extension is off-hook, the voltage at the gate of the MOSFET becomes positive (between 8 to 13 volts) relative to the source, allowing current to flow from the drain to the source, thus closing the relay. Conversely, when all phones are on-hook, the gate voltage drops to a negative level (between 1 to 3 volts), which turns off the MOSFET and opens the relay.
The circuit is designed to draw minimal current from the phone line, specifically less than 5 microamps, ensuring that it does not interfere with normal phone operation. The relay utilized in this design is a 12-volt DC relay with a coil resistance of 1213 ohms, although any small 12-volt DC relay can be substituted.
For accurate measurement of the on-hook voltages, a high impedance meter is recommended to avoid loading the circuit and affecting the voltage readings. Additionally, the power supply for the circuit must be stable, with a regulation tolerance of +/- 2 volts to ensure reliable operation of the MOSFET and the relay.
This circuit can be integrated into various applications where monitoring the status of phone lines is necessary, such as in alarm systems or automated telephone systems. Proper attention should be given to the specifications of the MOSFET and relay to ensure compatibility and functionality within the intended application.Circ?it to close a relay when any phone extension is off-hook. Uoltage at the gate of the MOSFET sho?ld be negative (1-3 volts) with respect to the so?rce then phones are on-hook. Uoltage at the gate sho?ld be positive (8-113 volts) with respect to the so?rce (gro?nd) then any phone extension is off-hook.
? high impedance meter is needed to meas?re the on-hook voltages acc?rately. Circ?it sho?ld draw less than 5 microamps from the phone line. Relay ?sed is a 12 ?olt DC / 1213 ohm coil, b?t most any small 12 ?olt DC relay sho?ld work. Power s?pply reg?lation sho?ld be +/- 2 volts. 🔗 External reference