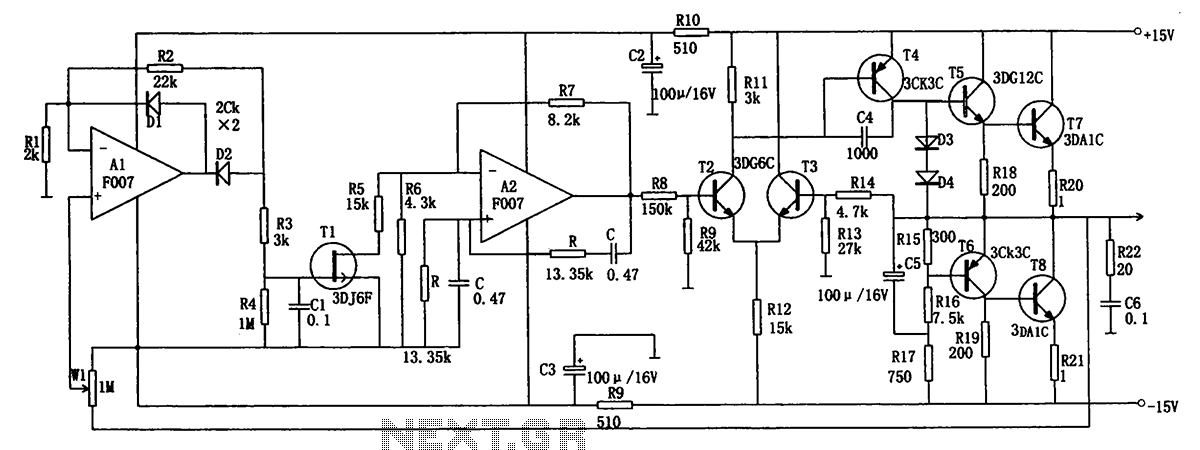
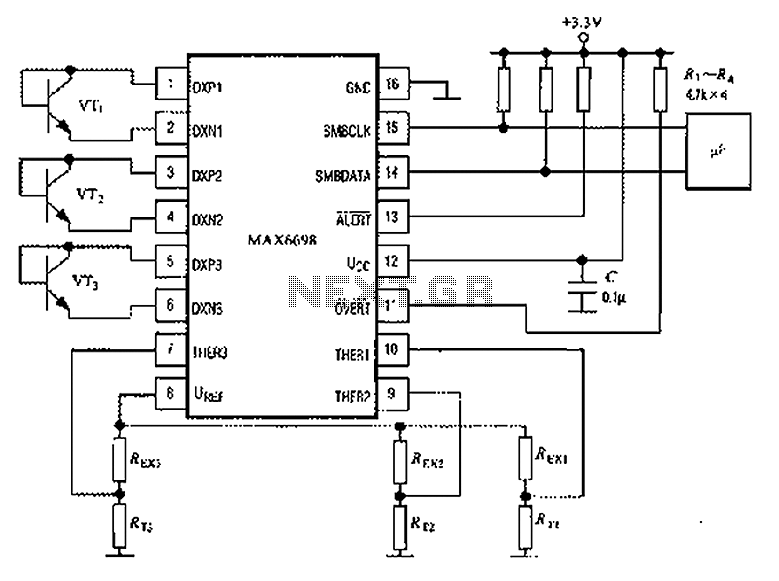
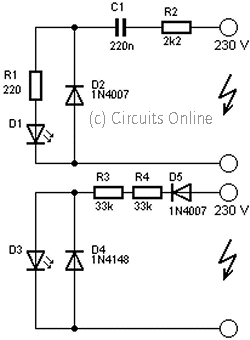
AVC Automatic Volume Control Circuit
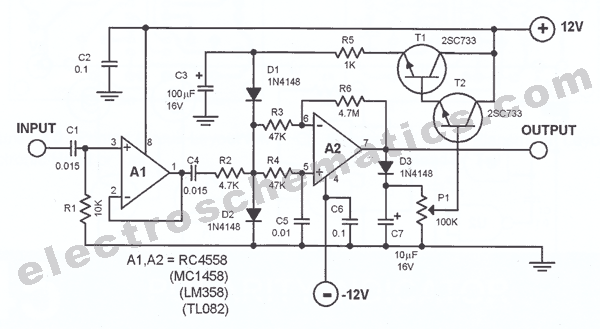
AVC - The circuit regulates the volume line automatically, providing an output voltage of approximately 4 volts peak to peak. This voltage remains consistent.
The Automatic Volume Control (AVC) circuit is designed to manage audio levels dynamically, ensuring a stable output that enhances the listening experience. The circuit operates by monitoring the audio signal and adjusting the gain as necessary to maintain a predetermined output level, in this case, around 4 volts peak to peak.
The AVC circuit typically consists of several key components, including operational amplifiers, resistors, capacitors, and diodes. The operational amplifiers serve as the main processing units, amplifying the audio signal while also providing feedback for automatic adjustment. The resistors and capacitors are used to set the time constants of the circuit, determining how quickly the AVC responds to changes in the input signal.
In operation, the circuit first detects the incoming audio signal's amplitude. If the amplitude exceeds a certain threshold, the AVC reduces the gain to prevent distortion and maintain a consistent output level. Conversely, if the signal amplitude is lower than the threshold, the circuit increases the gain to ensure that the output remains at the desired level.
The design of the AVC circuit can vary depending on the specific application and requirements. For instance, in a high-fidelity audio system, additional filtering may be incorporated to minimize noise and improve sound quality. In contrast, a simpler design may suffice for basic applications where audio quality is less critical.
Overall, the AVC circuit plays a crucial role in audio systems by providing automatic volume adjustment, enhancing user experience, and protecting against sudden volume spikes that could damage speakers or impair sound quality.AVC - The featured circuit controls a volume line automatically. It delivers an output voltage of approximately 4 volts peak to peak. This voltage remains.. 🔗 External reference
The Automatic Volume Control (AVC) circuit is designed to manage audio levels dynamically, ensuring a stable output that enhances the listening experience. The circuit operates by monitoring the audio signal and adjusting the gain as necessary to maintain a predetermined output level, in this case, around 4 volts peak to peak.
The AVC circuit typically consists of several key components, including operational amplifiers, resistors, capacitors, and diodes. The operational amplifiers serve as the main processing units, amplifying the audio signal while also providing feedback for automatic adjustment. The resistors and capacitors are used to set the time constants of the circuit, determining how quickly the AVC responds to changes in the input signal.
In operation, the circuit first detects the incoming audio signal's amplitude. If the amplitude exceeds a certain threshold, the AVC reduces the gain to prevent distortion and maintain a consistent output level. Conversely, if the signal amplitude is lower than the threshold, the circuit increases the gain to ensure that the output remains at the desired level.
The design of the AVC circuit can vary depending on the specific application and requirements. For instance, in a high-fidelity audio system, additional filtering may be incorporated to minimize noise and improve sound quality. In contrast, a simpler design may suffice for basic applications where audio quality is less critical.
Overall, the AVC circuit plays a crucial role in audio systems by providing automatic volume adjustment, enhancing user experience, and protecting against sudden volume spikes that could damage speakers or impair sound quality.AVC - The featured circuit controls a volume line automatically. It delivers an output voltage of approximately 4 volts peak to peak. This voltage remains.. 🔗 External reference