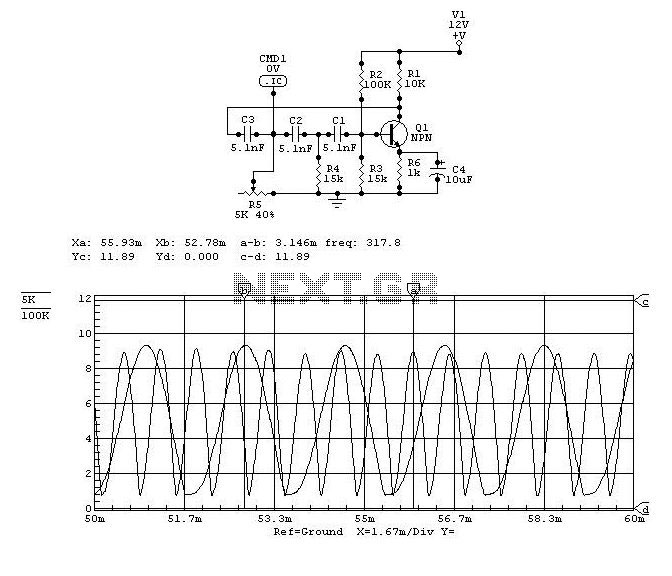
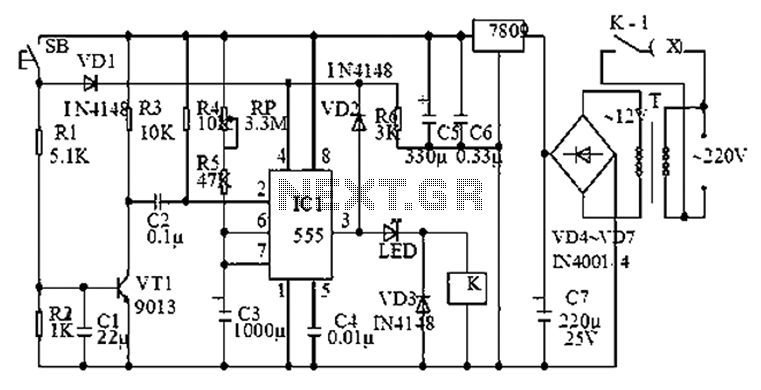
230volt led circuit
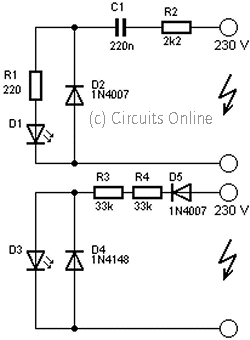
This circuit is used to power an LED with a voltage of 230V. The 230V must be reduced to meet the LED's voltage requirements. To achieve this, a circuit is necessary as described below.
The circuit designed to power an LED from a 230V AC supply typically involves a step-down transformer or a resistor-capacitor (RC) network to reduce the high voltage to a safe level suitable for the LED.
In a basic configuration, the circuit may include the following components:
1. **Transformer**: A step-down transformer can be used to convert the 230V AC to a lower AC voltage, typically around 12V or 24V, depending on the LED specifications. The transformer should be rated for the required output current to ensure safe operation.
2. **Rectifier**: After stepping down the voltage, a rectifier circuit is necessary to convert the AC voltage to DC. A bridge rectifier configuration using four diodes is commonly employed to ensure that both halves of the AC waveform are utilized.
3. **Smoothing Capacitor**: Following the rectification process, a smoothing capacitor is used to reduce voltage ripple and provide a steady DC voltage to the LED. The size of the capacitor will depend on the load current and the acceptable ripple voltage.
4. **Current Limiting Resistor**: LEDs require current limiting to prevent damage. A resistor can be placed in series with the LED to limit the current to the desired level. The value of the resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law, taking into account the forward voltage drop of the LED and the supply voltage.
5. **LED**: The LED operates at a specific forward voltage and current, which must be matched with the output of the circuit. Depending on the application, multiple LEDs can be connected in series or parallel configurations to achieve the desired brightness and voltage rating.
6. **Heat Sink**: If the circuit operates at higher currents, a heat sink may be necessary to dissipate heat generated by the LED and other components, ensuring reliability and longevity.
This circuit design ensures that the LED operates safely and efficiently while utilizing a standard 230V AC supply. Proper attention to component ratings and circuit layout will enhance performance and safety.This is a circuit that is used to menhidupkan LED with voltage 230Volt, 230Volt it so that the voltage must be lowered in accordance with the needs of the LED itself. To lower it even necessary circuit as below. 🔗 External reference
The circuit designed to power an LED from a 230V AC supply typically involves a step-down transformer or a resistor-capacitor (RC) network to reduce the high voltage to a safe level suitable for the LED.
In a basic configuration, the circuit may include the following components:
1. **Transformer**: A step-down transformer can be used to convert the 230V AC to a lower AC voltage, typically around 12V or 24V, depending on the LED specifications. The transformer should be rated for the required output current to ensure safe operation.
2. **Rectifier**: After stepping down the voltage, a rectifier circuit is necessary to convert the AC voltage to DC. A bridge rectifier configuration using four diodes is commonly employed to ensure that both halves of the AC waveform are utilized.
3. **Smoothing Capacitor**: Following the rectification process, a smoothing capacitor is used to reduce voltage ripple and provide a steady DC voltage to the LED. The size of the capacitor will depend on the load current and the acceptable ripple voltage.
4. **Current Limiting Resistor**: LEDs require current limiting to prevent damage. A resistor can be placed in series with the LED to limit the current to the desired level. The value of the resistor can be calculated using Ohm's law, taking into account the forward voltage drop of the LED and the supply voltage.
5. **LED**: The LED operates at a specific forward voltage and current, which must be matched with the output of the circuit. Depending on the application, multiple LEDs can be connected in series or parallel configurations to achieve the desired brightness and voltage rating.
6. **Heat Sink**: If the circuit operates at higher currents, a heat sink may be necessary to dissipate heat generated by the LED and other components, ensuring reliability and longevity.
This circuit design ensures that the LED operates safely and efficiently while utilizing a standard 230V AC supply. Proper attention to component ratings and circuit layout will enhance performance and safety.This is a circuit that is used to menhidupkan LED with voltage 230Volt, 230Volt it so that the voltage must be lowered in accordance with the needs of the LED itself. To lower it even necessary circuit as below. 🔗 External reference