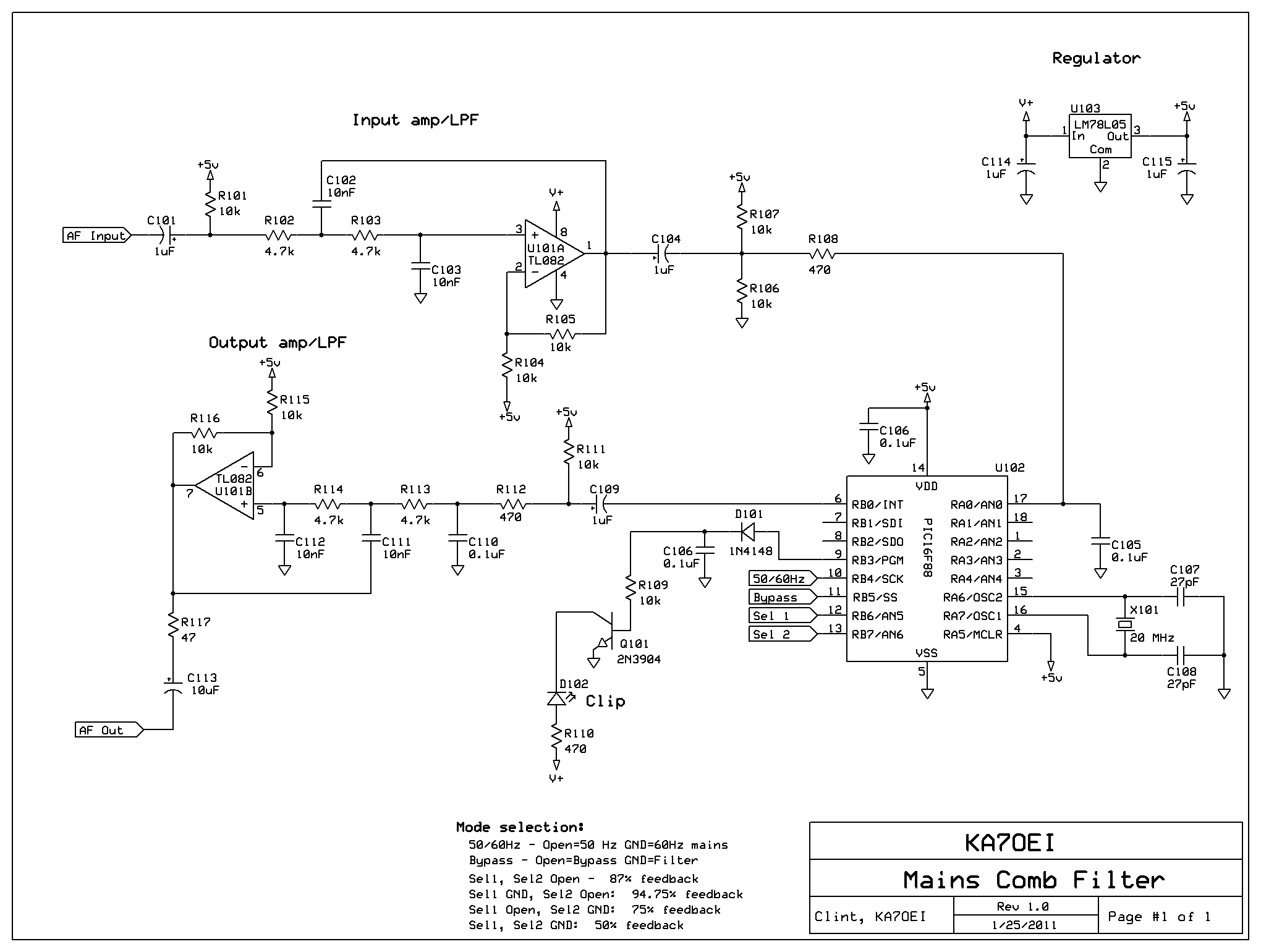
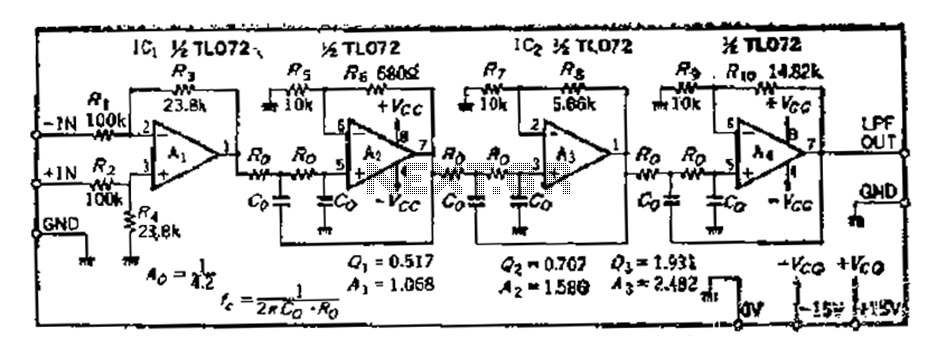
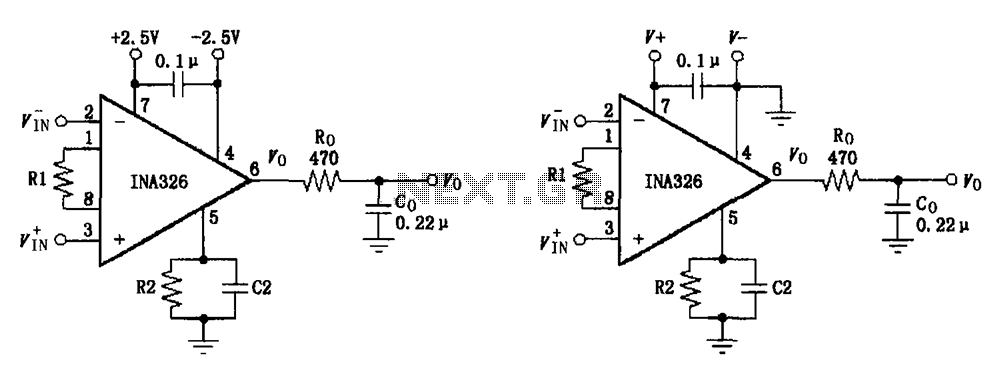
Basic Differential BiQuad Filter
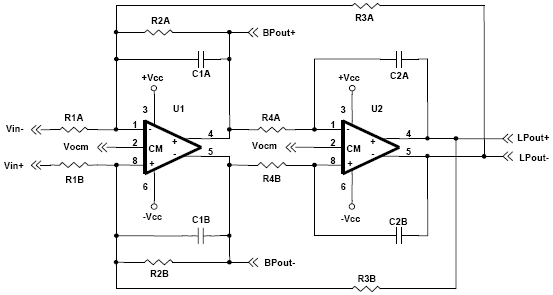
A biquad filter is a type of linear filter that implements a transfer function which is the ratio of two quadratic functions. It is available in low pass, high pass, band pass, and notch configurations.
A biquad filter is characterized by its ability to provide precise control over the frequency response due to its second-order nature. This filter can be implemented using active or passive components and is often utilized in audio processing, communication systems, and various signal processing applications.
The transfer function of a biquad filter can be expressed in the standard form:
H(s) = (b0 + b1*s + b2*s^2) / (1 + a1*s + a2*s^2)
where:
- H(s) is the transfer function,
- b0, b1, b2 are the coefficients of the numerator, defining the filter's behavior,
- a1, a2 are the coefficients of the denominator, which affect stability and frequency response.
In practical applications, the design of a biquad filter involves selecting appropriate coefficients to achieve the desired filter characteristics, such as cutoff frequency, gain, and quality factor (Q). The Q factor is particularly important as it determines the bandwidth of the filter's response; a higher Q results in a narrower bandwidth.
Biquad filters can be implemented using operational amplifiers (op-amps) in active configurations, where feedback and gain can be easily adjusted. The design can be realized using various topologies, including Sallen-Key and multiple feedback configurations, each offering unique advantages in terms of component count, performance, and complexity.
In digital signal processing (DSP), biquad filters are often implemented in software or hardware using digital algorithms. The coefficients can be computed based on the desired specifications, and the filter can be executed in real-time to process audio signals or other data streams.
Overall, the versatility and effectiveness of biquad filters make them a fundamental building block in both analog and digital signal processing applications.A biquad filter is a type of linear filter that implements a transfer function that is the ratio of two quadratic functions. It is available in low pass, high.. 🔗 External reference
A biquad filter is characterized by its ability to provide precise control over the frequency response due to its second-order nature. This filter can be implemented using active or passive components and is often utilized in audio processing, communication systems, and various signal processing applications.
The transfer function of a biquad filter can be expressed in the standard form:
H(s) = (b0 + b1*s + b2*s^2) / (1 + a1*s + a2*s^2)
where:
- H(s) is the transfer function,
- b0, b1, b2 are the coefficients of the numerator, defining the filter's behavior,
- a1, a2 are the coefficients of the denominator, which affect stability and frequency response.
In practical applications, the design of a biquad filter involves selecting appropriate coefficients to achieve the desired filter characteristics, such as cutoff frequency, gain, and quality factor (Q). The Q factor is particularly important as it determines the bandwidth of the filter's response; a higher Q results in a narrower bandwidth.
Biquad filters can be implemented using operational amplifiers (op-amps) in active configurations, where feedback and gain can be easily adjusted. The design can be realized using various topologies, including Sallen-Key and multiple feedback configurations, each offering unique advantages in terms of component count, performance, and complexity.
In digital signal processing (DSP), biquad filters are often implemented in software or hardware using digital algorithms. The coefficients can be computed based on the desired specifications, and the filter can be executed in real-time to process audio signals or other data streams.
Overall, the versatility and effectiveness of biquad filters make them a fundamental building block in both analog and digital signal processing applications.A biquad filter is a type of linear filter that implements a transfer function that is the ratio of two quadratic functions. It is available in low pass, high.. 🔗 External reference