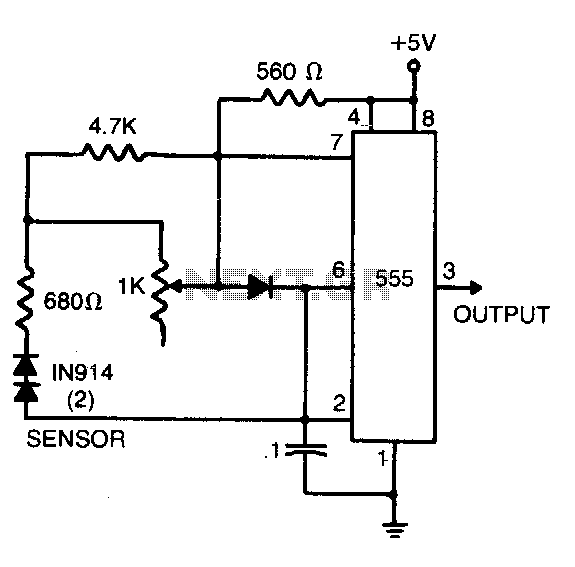
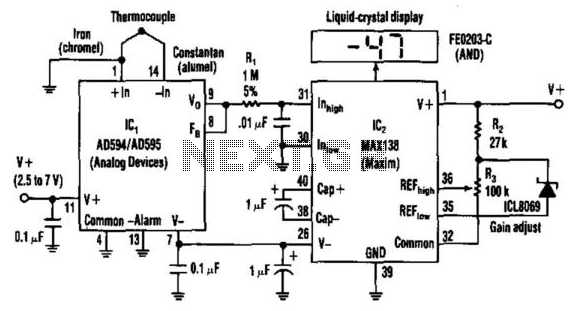
Differential thermometer
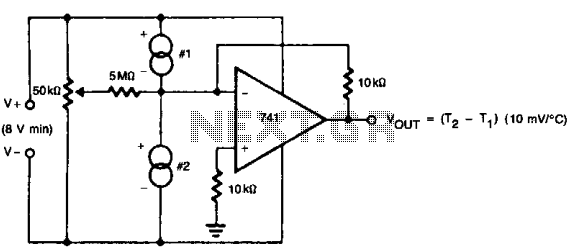
The 50 k ohm potentiometer adjusts offsets in devices, whether internal or external, allowing for the setting of the difference interval size. This feature makes it suitable for liquid-level detection, particularly in scenarios where a measurable temperature difference exists.
The 50 k ohm potentiometer serves as a critical component in various electronic circuits, particularly in applications requiring precision adjustments of voltage levels or signal offsets. Its primary function is to provide a variable resistance that can be used to fine-tune the performance of a circuit. In the context of liquid-level detection, this potentiometer can be employed to calibrate the sensitivity of sensors that measure liquid levels, ensuring accurate readings even in the presence of temperature variations.
In practical applications, the potentiometer can be connected in a voltage divider configuration, allowing it to adjust the reference voltage fed to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or a microcontroller input. This adjustment can help mitigate the effects of temperature-induced voltage drift, which is crucial in maintaining reliable operation of the liquid-level detection system.
Furthermore, the use of a 50 k ohm potentiometer is advantageous due to its balance between resolution and power consumption. Higher resistance values reduce current draw, which is particularly important in battery-operated devices. The ability to fine-tune the offset allows for greater flexibility in circuit design, enabling engineers to adapt the system to various environmental conditions without the need for extensive recalibration.
In summary, the 50 k ohm potentiometer is an essential tool in electronic design, particularly for applications involving liquid-level detection and temperature-sensitive measurements, where precise offset adjustments are necessary for optimal performance.The 50 k ohm pot trims offsets in the devices whether internal or external, so it can be used to set the size of the difference interval. This also makes it useful for liquid-level detection. (where there will be a measurable temperature difference)
The 50 k ohm potentiometer serves as a critical component in various electronic circuits, particularly in applications requiring precision adjustments of voltage levels or signal offsets. Its primary function is to provide a variable resistance that can be used to fine-tune the performance of a circuit. In the context of liquid-level detection, this potentiometer can be employed to calibrate the sensitivity of sensors that measure liquid levels, ensuring accurate readings even in the presence of temperature variations.
In practical applications, the potentiometer can be connected in a voltage divider configuration, allowing it to adjust the reference voltage fed to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) or a microcontroller input. This adjustment can help mitigate the effects of temperature-induced voltage drift, which is crucial in maintaining reliable operation of the liquid-level detection system.
Furthermore, the use of a 50 k ohm potentiometer is advantageous due to its balance between resolution and power consumption. Higher resistance values reduce current draw, which is particularly important in battery-operated devices. The ability to fine-tune the offset allows for greater flexibility in circuit design, enabling engineers to adapt the system to various environmental conditions without the need for extensive recalibration.
In summary, the 50 k ohm potentiometer is an essential tool in electronic design, particularly for applications involving liquid-level detection and temperature-sensitive measurements, where precise offset adjustments are necessary for optimal performance.The 50 k ohm pot trims offsets in the devices whether internal or external, so it can be used to set the size of the difference interval. This also makes it useful for liquid-level detection. (where there will be a measurable temperature difference)