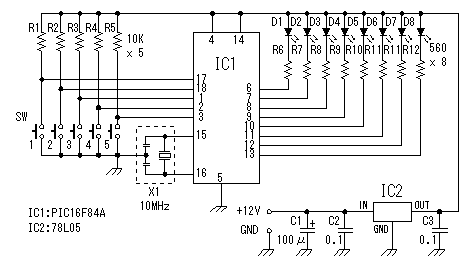
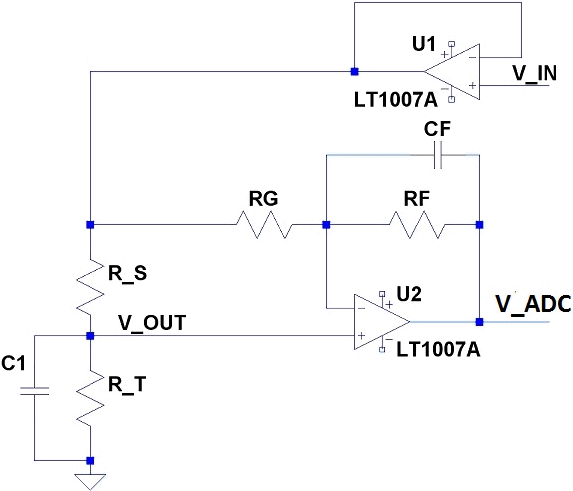
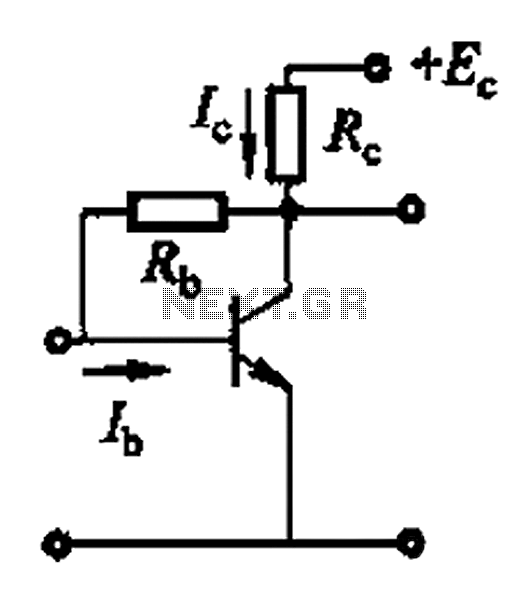
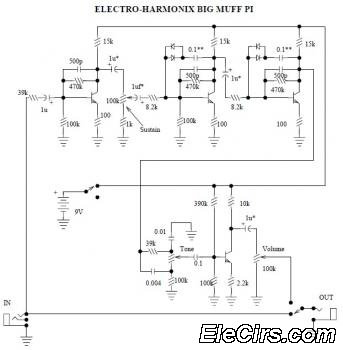
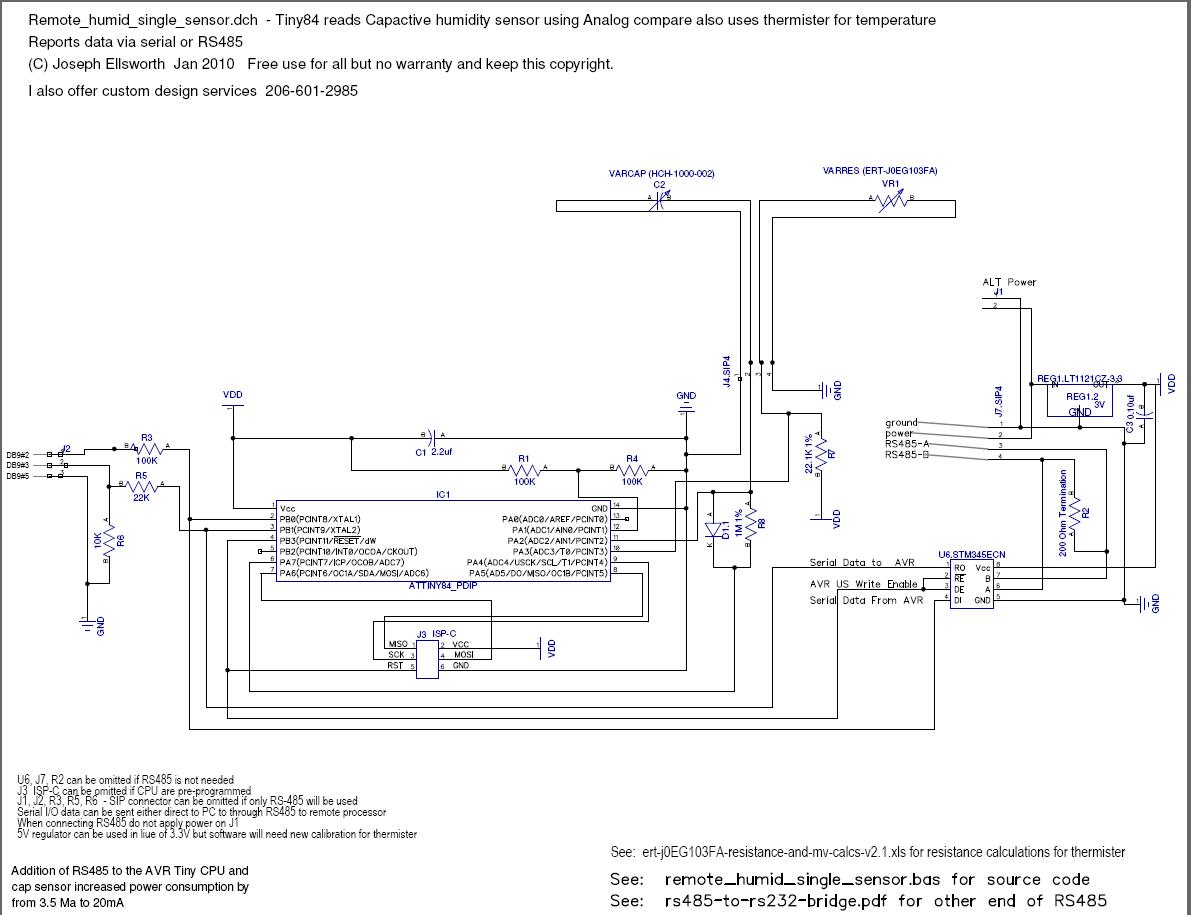
Basic Hall Effect Sensor IC
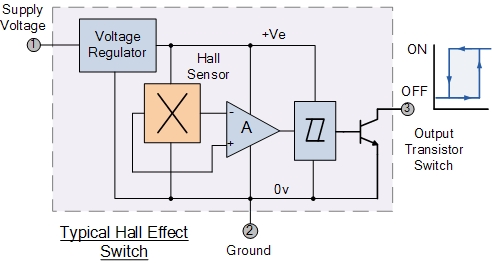
This tutorial covers the Hall Effect Sensor and Magnetic Hall Effect Switch, which are output transducers utilized for detecting magnetic fields.
The Hall Effect Sensor operates based on the principle that a voltage is generated across a conductor when it is exposed to a magnetic field perpendicular to the current flow. This phenomenon, known as the Hall Effect, allows for the detection of magnetic fields with high sensitivity and accuracy. Hall Effect Sensors are commonly used in various applications, including automotive systems, industrial automation, and consumer electronics.
The Magnetic Hall Effect Switch, a specific type of Hall Effect Sensor, functions as a binary output device that activates or deactivates based on the presence or absence of a magnetic field. When a magnetic field is applied, the switch closes, allowing current to flow through the circuit. Conversely, when the magnetic field is removed, the switch opens, interrupting the current. This characteristic makes it ideal for applications such as position sensing, speed detection, and contactless switching.
In terms of circuit design, a typical Hall Effect Sensor circuit includes the sensor itself, a power supply, and a load. The sensor is connected to a voltage source, often in the range of 5V to 15V, depending on the specific sensor model. The output can be configured to provide either an analog voltage that varies with the magnetic field strength or a digital output that toggles between high and low states.
To enhance the performance of the Hall Effect Sensor, additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be included in the circuit. Resistors can be used for current limiting and signal conditioning, while capacitors may serve to filter noise and stabilize the output signal. Proper layout and grounding techniques are also crucial to minimize interference and ensure reliable operation.
Overall, the Hall Effect Sensor and Magnetic Hall Effect Switch are essential components in modern electronic systems, providing efficient and reliable methods for magnetic field detection and control.Electronics Tutorial about the Hall Effect Sensor and Magnetic Hall Effect Switch which is an Output Transducer used to detect Magnetic Fields.. 🔗 External reference
The Hall Effect Sensor operates based on the principle that a voltage is generated across a conductor when it is exposed to a magnetic field perpendicular to the current flow. This phenomenon, known as the Hall Effect, allows for the detection of magnetic fields with high sensitivity and accuracy. Hall Effect Sensors are commonly used in various applications, including automotive systems, industrial automation, and consumer electronics.
The Magnetic Hall Effect Switch, a specific type of Hall Effect Sensor, functions as a binary output device that activates or deactivates based on the presence or absence of a magnetic field. When a magnetic field is applied, the switch closes, allowing current to flow through the circuit. Conversely, when the magnetic field is removed, the switch opens, interrupting the current. This characteristic makes it ideal for applications such as position sensing, speed detection, and contactless switching.
In terms of circuit design, a typical Hall Effect Sensor circuit includes the sensor itself, a power supply, and a load. The sensor is connected to a voltage source, often in the range of 5V to 15V, depending on the specific sensor model. The output can be configured to provide either an analog voltage that varies with the magnetic field strength or a digital output that toggles between high and low states.
To enhance the performance of the Hall Effect Sensor, additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be included in the circuit. Resistors can be used for current limiting and signal conditioning, while capacitors may serve to filter noise and stabilize the output signal. Proper layout and grounding techniques are also crucial to minimize interference and ensure reliable operation.
Overall, the Hall Effect Sensor and Magnetic Hall Effect Switch are essential components in modern electronic systems, providing efficient and reliable methods for magnetic field detection and control.Electronics Tutorial about the Hall Effect Sensor and Magnetic Hall Effect Switch which is an Output Transducer used to detect Magnetic Fields.. 🔗 External reference