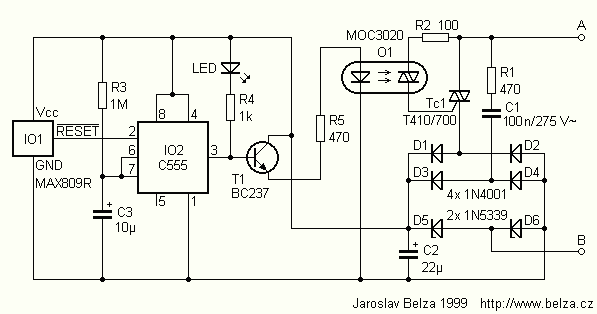
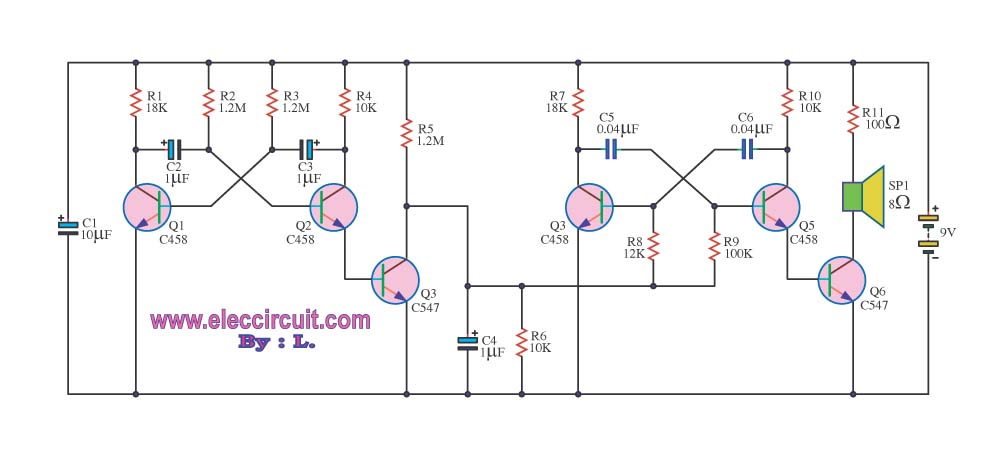
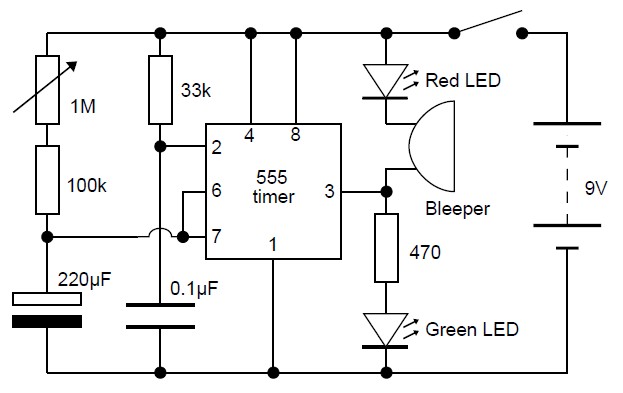
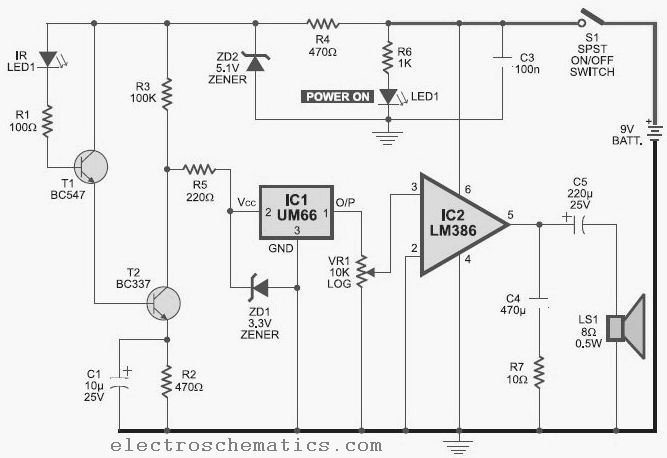
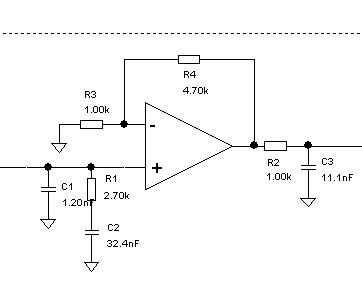
bass booster circuit
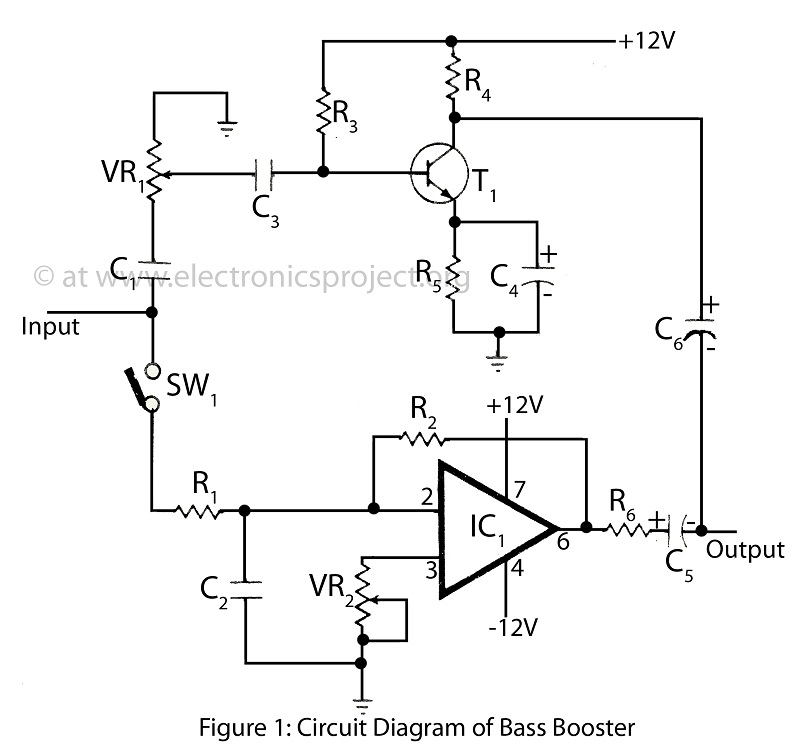
The bass booster featured on this website enhances the beat frequency while maintaining the integrity of the high-frequency response. The circuit diagram for the bass booster, along with various radio circuits, is also provided.
The bass booster circuit operates by selectively amplifying the lower frequency range, typically between 20 Hz to 200 Hz, which corresponds to the bass frequencies in audio signals. This enhancement is achieved through the use of operational amplifiers (op-amps) and passive components such as resistors and capacitors.
The core of the bass booster circuit involves a low-pass filter configuration that allows the desired bass frequencies to pass while attenuating higher frequencies. The cutoff frequency is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors in the filter. Typically, a gain stage is added to amplify the filtered signal, ensuring that the output level is sufficient for driving speakers or headphones.
In addition to the basic low-pass filter design, the circuit may include features such as adjustable gain, which can be implemented using a variable resistor (potentiometer). This allows users to control the level of bass enhancement according to their preferences.
The output stage of the circuit is crucial, as it must be capable of driving the load without distortion. Depending on the application, the output can be connected directly to a speaker or to a power amplifier. Proper power supply decoupling is also essential to prevent noise from affecting the performance of the bass booster.
Overall, this bass booster circuit design provides a straightforward and effective means of enhancing low-frequency audio signals, making it suitable for various audio applications, including home audio systems, car audio, and portable speakers.Bass booster of this website is used to boosts the beat frequency without effect the high frequency circuit diagram of bass booster bass booster and different radio circuit. 🔗 External reference
The bass booster circuit operates by selectively amplifying the lower frequency range, typically between 20 Hz to 200 Hz, which corresponds to the bass frequencies in audio signals. This enhancement is achieved through the use of operational amplifiers (op-amps) and passive components such as resistors and capacitors.
The core of the bass booster circuit involves a low-pass filter configuration that allows the desired bass frequencies to pass while attenuating higher frequencies. The cutoff frequency is determined by the values of the resistors and capacitors in the filter. Typically, a gain stage is added to amplify the filtered signal, ensuring that the output level is sufficient for driving speakers or headphones.
In addition to the basic low-pass filter design, the circuit may include features such as adjustable gain, which can be implemented using a variable resistor (potentiometer). This allows users to control the level of bass enhancement according to their preferences.
The output stage of the circuit is crucial, as it must be capable of driving the load without distortion. Depending on the application, the output can be connected directly to a speaker or to a power amplifier. Proper power supply decoupling is also essential to prevent noise from affecting the performance of the bass booster.
Overall, this bass booster circuit design provides a straightforward and effective means of enhancing low-frequency audio signals, making it suitable for various audio applications, including home audio systems, car audio, and portable speakers.Bass booster of this website is used to boosts the beat frequency without effect the high frequency circuit diagram of bass booster bass booster and different radio circuit. 🔗 External reference