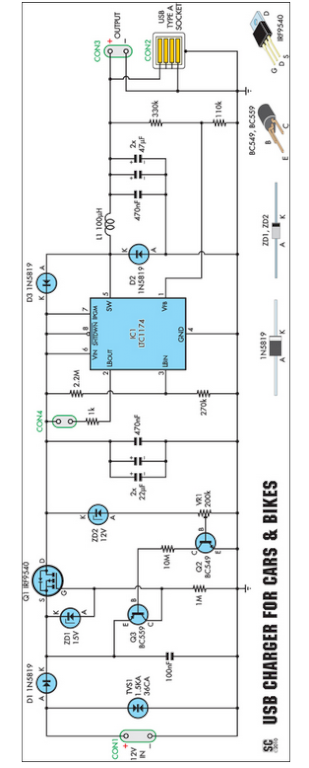
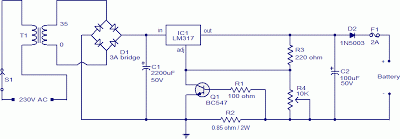
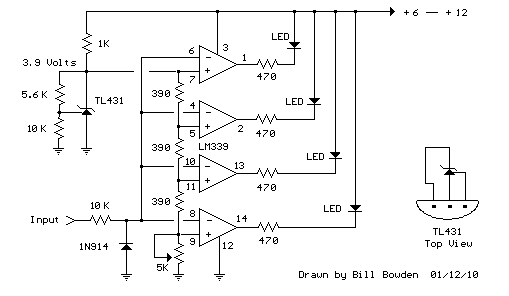
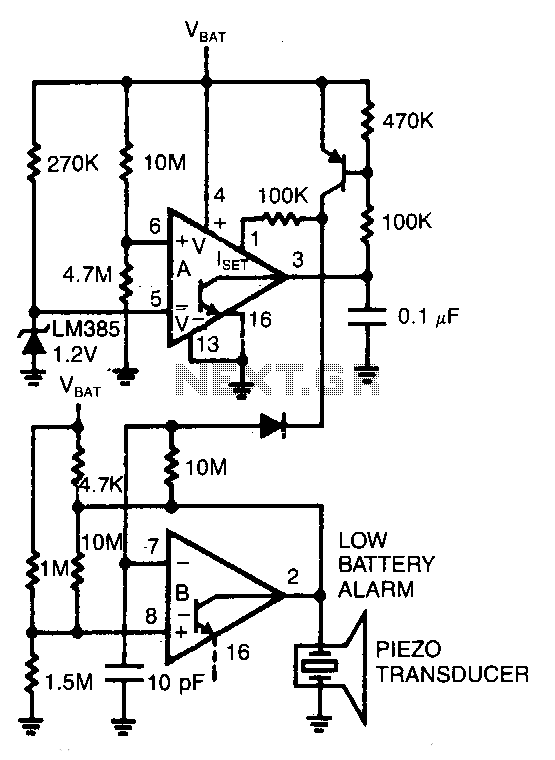
Battery Charger
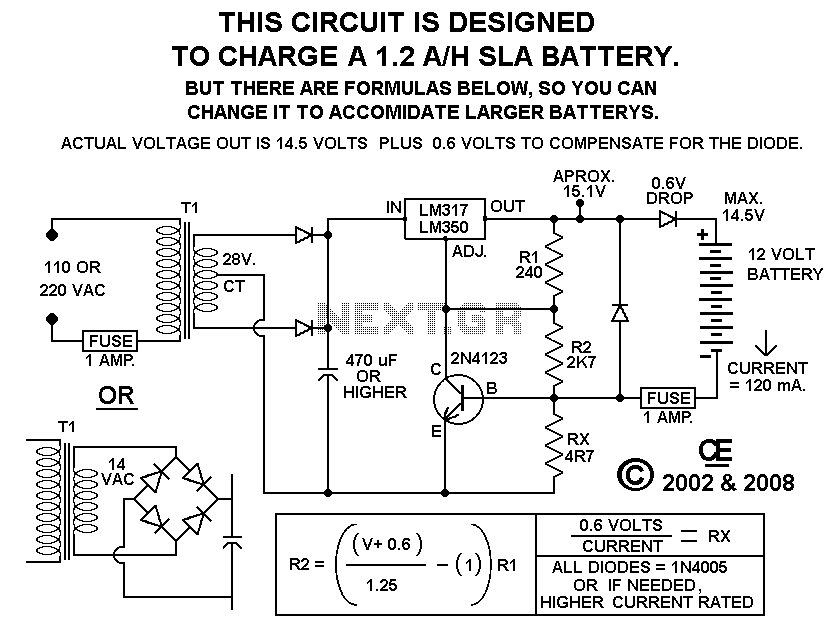
Using this circuit will give good charging results to the gel cell battery used in the metal detector or any other similar and smaller type battery. This charger is both current and voltage regulated. The output is not short circuit protected; however, the current limit is effective if the output is above a 2-volt potential. It is also protected against reversing the battery by a fuse.
The circuit described functions as a regulated charger specifically designed for gel cell batteries, which are commonly used in portable devices like metal detectors. The charger incorporates both current and voltage regulation to ensure that the battery is charged efficiently and safely, minimizing the risk of overcharging.
The primary components of this circuit include a transformer, a rectifier, a voltage regulator, and a current limiting circuit. The transformer steps down the AC mains voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging the battery. The rectifier, typically a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage to a pulsating DC voltage.
Following the rectification, the voltage regulator ensures that the output voltage remains stable, regardless of variations in input voltage or load conditions. This is crucial for gel cell batteries, which can be sensitive to overvoltage conditions. The current limiting feature is implemented using a resistor or a more sophisticated current sensing circuit, which restricts the charging current to a safe level, particularly when the output voltage exceeds 2 volts.
The lack of short circuit protection means that if a short occurs at the output, the circuit may not automatically shut down. However, the current limiting mechanism will still function to prevent excessive current flow, thereby offering some level of protection.
To safeguard against reverse polarity connections, a fuse is included in the circuit. This fuse will blow if the battery is connected incorrectly, preventing damage to the charger and the battery.
Overall, this circuit design is effective for charging gel cell batteries in various applications, providing essential features such as voltage regulation, current limiting, and reverse polarity protection, making it suitable for use in metal detectors and other similar devices.Using this circuit will give Good Charging results to the Gell Cell Battery used in the Metal Detector, or any other simular and smaller type battery. This charger is both Current and Voltage Regulated. The Output is NOT short circuit protected, However the current limit is effective if the output is above a 2 volt potential. It is also protected against reversing the battery, by a fuse. 🔗 External reference
The circuit described functions as a regulated charger specifically designed for gel cell batteries, which are commonly used in portable devices like metal detectors. The charger incorporates both current and voltage regulation to ensure that the battery is charged efficiently and safely, minimizing the risk of overcharging.
The primary components of this circuit include a transformer, a rectifier, a voltage regulator, and a current limiting circuit. The transformer steps down the AC mains voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging the battery. The rectifier, typically a bridge rectifier configuration, converts the AC voltage to a pulsating DC voltage.
Following the rectification, the voltage regulator ensures that the output voltage remains stable, regardless of variations in input voltage or load conditions. This is crucial for gel cell batteries, which can be sensitive to overvoltage conditions. The current limiting feature is implemented using a resistor or a more sophisticated current sensing circuit, which restricts the charging current to a safe level, particularly when the output voltage exceeds 2 volts.
The lack of short circuit protection means that if a short occurs at the output, the circuit may not automatically shut down. However, the current limiting mechanism will still function to prevent excessive current flow, thereby offering some level of protection.
To safeguard against reverse polarity connections, a fuse is included in the circuit. This fuse will blow if the battery is connected incorrectly, preventing damage to the charger and the battery.
Overall, this circuit design is effective for charging gel cell batteries in various applications, providing essential features such as voltage regulation, current limiting, and reverse polarity protection, making it suitable for use in metal detectors and other similar devices.Using this circuit will give Good Charging results to the Gell Cell Battery used in the Metal Detector, or any other simular and smaller type battery. This charger is both Current and Voltage Regulated. The Output is NOT short circuit protected, However the current limit is effective if the output is above a 2 volt potential. It is also protected against reversing the battery, by a fuse. 🔗 External reference