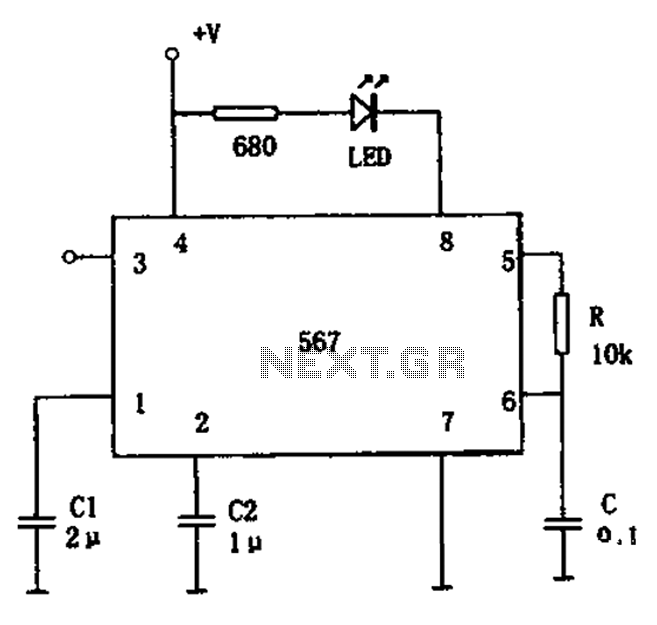
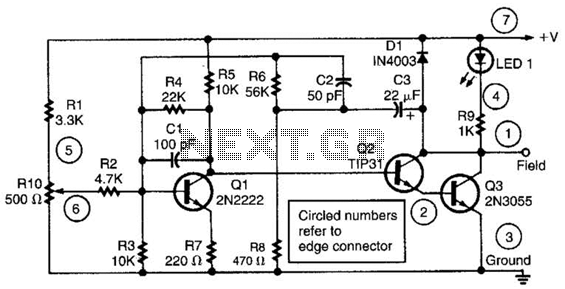
Battery state of charge indicator circuit
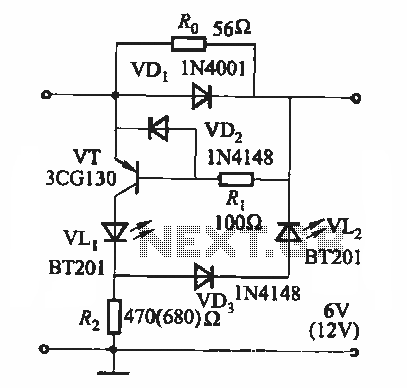
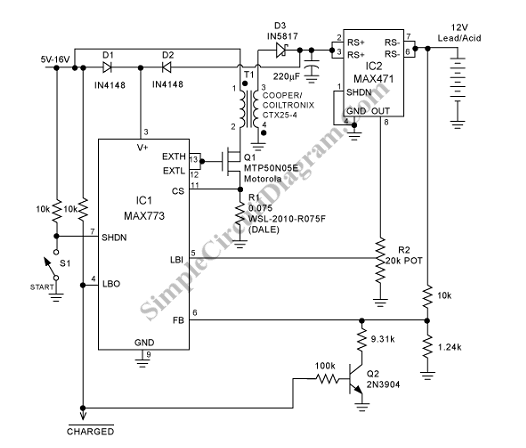
During the charging process, the green light-emitting diode (LED) VLi indicates that the battery is sufficiently charged, while the red light-emitting diode (LED) VLz illuminates when the battery is low.
The circuit involves two light-emitting diodes (LEDs) serving as indicators for the battery charging status. The green LED (VLi) is connected in parallel with the battery and is configured to light up when the battery voltage reaches a predetermined threshold, indicating that the battery is adequately charged. This is typically achieved through a voltage divider or a comparator circuit that senses the battery voltage and activates the green LED accordingly.
Conversely, the red LED (VLz) functions as a low battery indicator. It is also connected to the same battery circuit but is designed to illuminate when the battery voltage falls below a certain level. This can be implemented using a similar voltage sensing mechanism, where the circuit detects insufficient voltage and triggers the red LED to signal that the battery requires charging.
Both LEDs can be connected to a common ground, and appropriate current-limiting resistors should be included in series with each LED to prevent excessive current flow, which could damage the diodes. The use of these indicators enhances user experience by providing clear visual feedback regarding the battery status during operation and charging, ensuring that the user is informed about the battery's condition at all times.When charging, the green light-emitting diode VLi; the battery is sufficient, red light-emitting diode tube VLz bright.
The circuit involves two light-emitting diodes (LEDs) serving as indicators for the battery charging status. The green LED (VLi) is connected in parallel with the battery and is configured to light up when the battery voltage reaches a predetermined threshold, indicating that the battery is adequately charged. This is typically achieved through a voltage divider or a comparator circuit that senses the battery voltage and activates the green LED accordingly.
Conversely, the red LED (VLz) functions as a low battery indicator. It is also connected to the same battery circuit but is designed to illuminate when the battery voltage falls below a certain level. This can be implemented using a similar voltage sensing mechanism, where the circuit detects insufficient voltage and triggers the red LED to signal that the battery requires charging.
Both LEDs can be connected to a common ground, and appropriate current-limiting resistors should be included in series with each LED to prevent excessive current flow, which could damage the diodes. The use of these indicators enhances user experience by providing clear visual feedback regarding the battery status during operation and charging, ensuring that the user is informed about the battery's condition at all times.When charging, the green light-emitting diode VLi; the battery is sufficient, red light-emitting diode tube VLz bright.