Before power is in the release state holding brake circuit
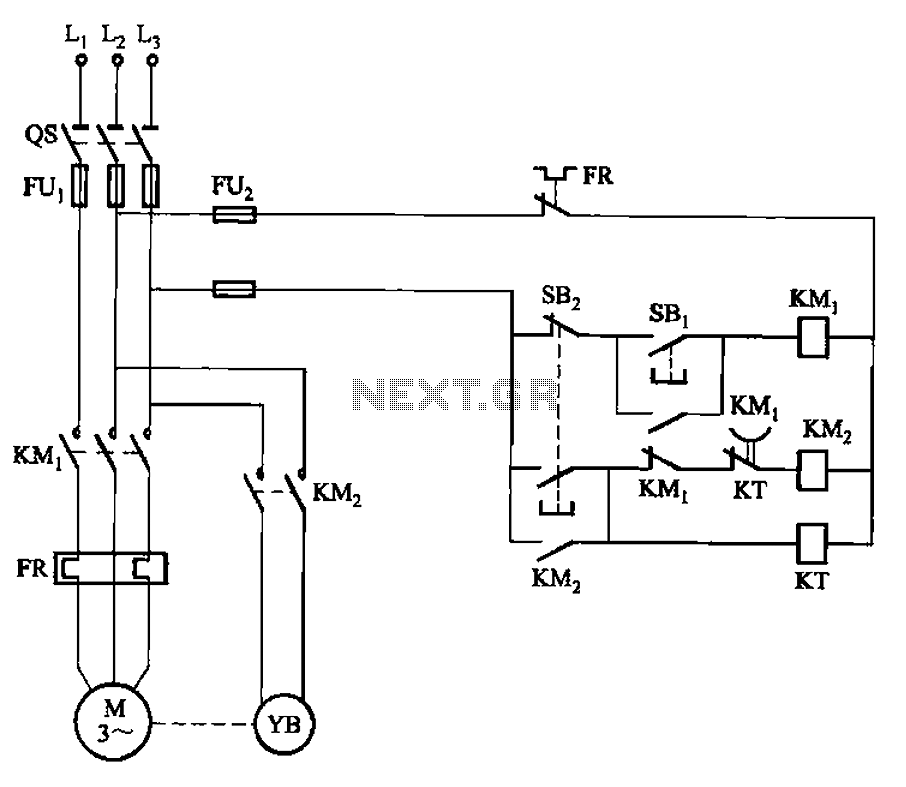
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-123 operates as follows: When the stop button SBz is pressed, contact KMi releases, cutting off power to the motor. Simultaneously, KMz is activated, engaging the electromagnetic brake YB to hold the motor in place. After a predetermined time delay, the time delay relay KT closes its normally closed contacts, which disconnects and releases KM2, returning the circuit to its initial state before starting.
The circuit described operates through a sequence of interconnected components designed to manage the motor's operation effectively. The stop button SBz serves as the primary control input, initiating the shutdown sequence when pressed. Upon activation, contact KMi opens, severing the power supply to the motor, which halts its operation. The simultaneous engagement of KMz activates the electromagnetic brake YB, ensuring that the motor does not inadvertently restart or move during the shutdown process.
The time delay relay KT introduces a critical timing function into the circuit. It is configured to maintain its normally closed contacts in the initial state, allowing current to flow in the circuit. Once the stop button is pressed, KT begins its timing cycle. After the designated delay period elapses, KT closes its contacts, which causes KM2 to release. This action restores the circuit to its pre-operation state, allowing for a safe and controlled restart of the motor when ready.
This circuit design is particularly useful in applications where motor control and safety are paramount, such as in industrial machinery or automated systems. The integration of a time delay relay adds an essential layer of safety, preventing immediate re-engagement of the motor and allowing for any necessary maintenance or checks to be performed before the system is reactivated. Circuit shown in Figure 3-123. When you press the stop button SBz, contact KMi release, cut off the power to the motor, at the same time, KMz pull, turn the electromagnetic bra ke YB power supply, the motor hold Brake. After a period of time delay, time delay relay KT close the normally closed contacts disconnect, KM2 release, the circuit before starting the recovery state.
The circuit described operates through a sequence of interconnected components designed to manage the motor's operation effectively. The stop button SBz serves as the primary control input, initiating the shutdown sequence when pressed. Upon activation, contact KMi opens, severing the power supply to the motor, which halts its operation. The simultaneous engagement of KMz activates the electromagnetic brake YB, ensuring that the motor does not inadvertently restart or move during the shutdown process.
The time delay relay KT introduces a critical timing function into the circuit. It is configured to maintain its normally closed contacts in the initial state, allowing current to flow in the circuit. Once the stop button is pressed, KT begins its timing cycle. After the designated delay period elapses, KT closes its contacts, which causes KM2 to release. This action restores the circuit to its pre-operation state, allowing for a safe and controlled restart of the motor when ready.
This circuit design is particularly useful in applications where motor control and safety are paramount, such as in industrial machinery or automated systems. The integration of a time delay relay adds an essential layer of safety, preventing immediate re-engagement of the motor and allowing for any necessary maintenance or checks to be performed before the system is reactivated. Circuit shown in Figure 3-123. When you press the stop button SBz, contact KMi release, cut off the power to the motor, at the same time, KMz pull, turn the electromagnetic bra ke YB power supply, the motor hold Brake. After a period of time delay, time delay relay KT close the normally closed contacts disconnect, KM2 release, the circuit before starting the recovery state.