Beginner Circuit question
A newcomer to electronics has questions regarding the interpretation of circuit diagrams. There is uncertainty about the arrangement of wires in these diagrams.
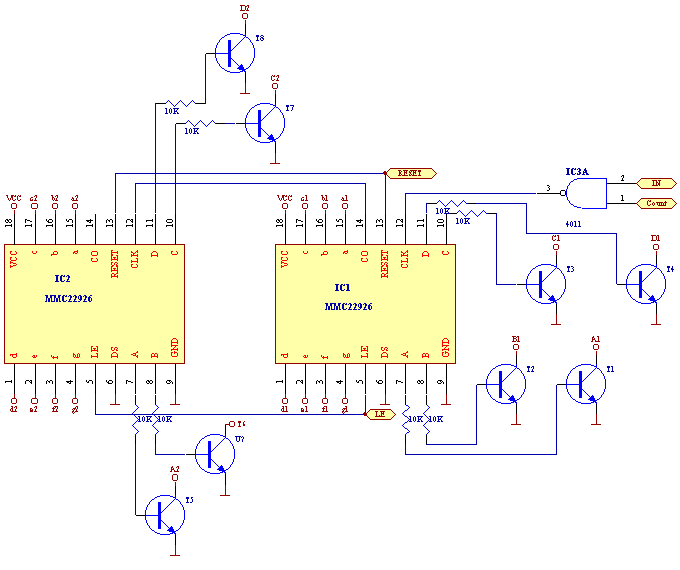
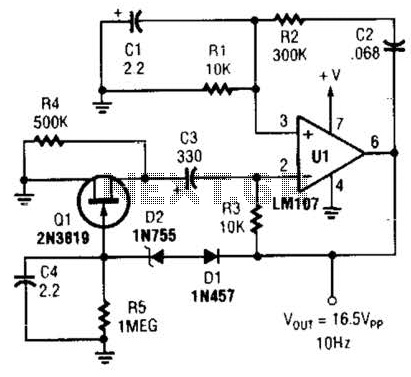
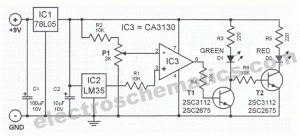
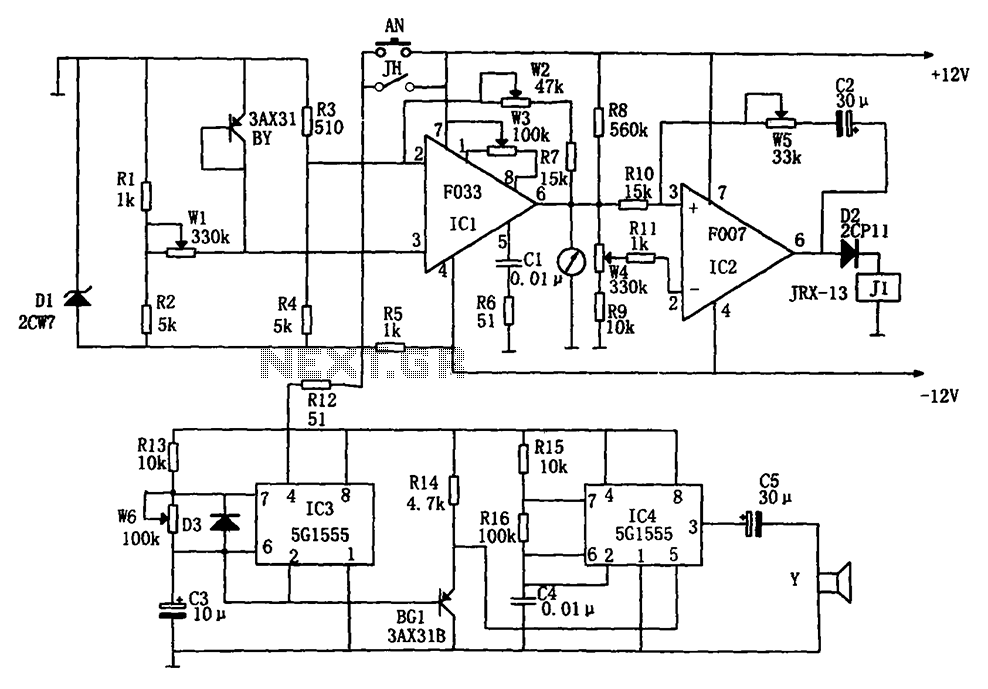
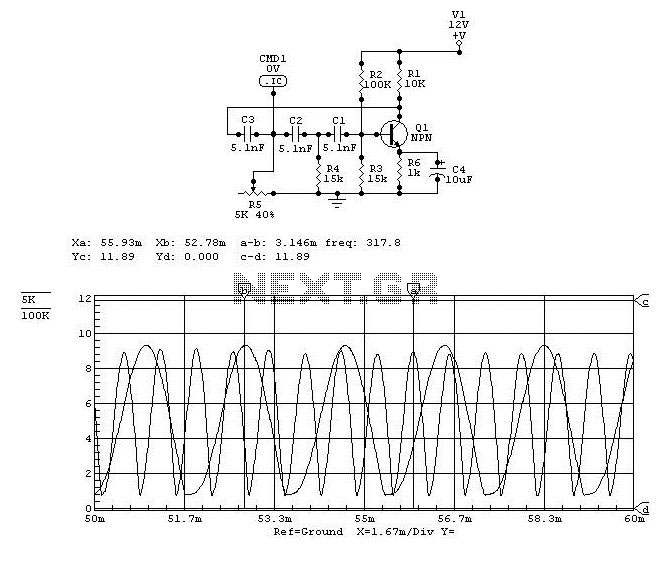
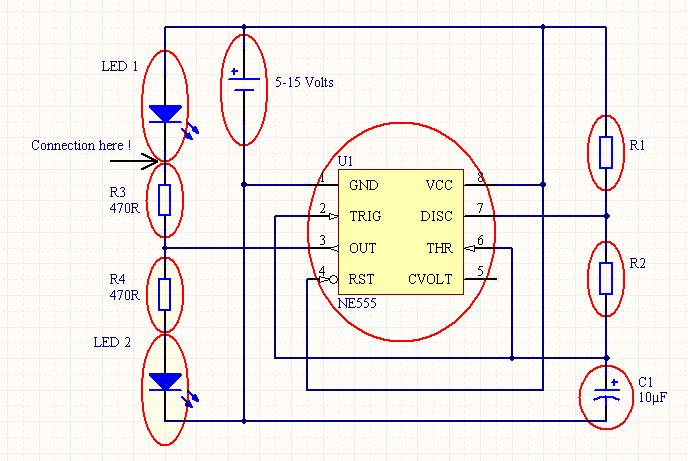
Understanding circuit diagrams is essential for anyone involved in electronics, as they serve as a visual representation of electrical circuits. These diagrams utilize standardized symbols to represent various components, such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, and integrated circuits, along with lines to indicate the connections or paths for electrical current.
To read a circuit diagram effectively, one should first familiarize themselves with the common symbols used in the diagrams. For example, a straight line typically represents a wire, while a zigzag line may denote a resistor. It is also important to understand the flow of current, which is usually indicated by arrows.
The arrangement of wires in a circuit diagram is not necessarily indicative of their physical layout on a circuit board. Instead, the diagram focuses on the functional relationships between components. Therefore, it is crucial to follow the connections as they are depicted, ensuring that the correct components are linked as intended.
To further enhance comprehension, it is advisable to study simple circuit examples, gradually progressing to more complex diagrams. Hands-on practice with building circuits based on these diagrams can also be beneficial. Utilizing simulation software can provide an interactive experience to visualize how the circuit operates without the need for physical components.
In conclusion, developing proficiency in reading circuit diagrams requires practice and familiarity with electronic symbols and conventions. Engaging with practical examples and simulations can significantly aid in mastering this essential skill in electronics.Hi I am new to electronics and have some questions about reading circuit diagrams. When I look at circuit diagrams I don`t know which order the wires, .. 🔗 External reference
Understanding circuit diagrams is essential for anyone involved in electronics, as they serve as a visual representation of electrical circuits. These diagrams utilize standardized symbols to represent various components, such as resistors, capacitors, diodes, and integrated circuits, along with lines to indicate the connections or paths for electrical current.
To read a circuit diagram effectively, one should first familiarize themselves with the common symbols used in the diagrams. For example, a straight line typically represents a wire, while a zigzag line may denote a resistor. It is also important to understand the flow of current, which is usually indicated by arrows.
The arrangement of wires in a circuit diagram is not necessarily indicative of their physical layout on a circuit board. Instead, the diagram focuses on the functional relationships between components. Therefore, it is crucial to follow the connections as they are depicted, ensuring that the correct components are linked as intended.
To further enhance comprehension, it is advisable to study simple circuit examples, gradually progressing to more complex diagrams. Hands-on practice with building circuits based on these diagrams can also be beneficial. Utilizing simulation software can provide an interactive experience to visualize how the circuit operates without the need for physical components.
In conclusion, developing proficiency in reading circuit diagrams requires practice and familiarity with electronic symbols and conventions. Engaging with practical examples and simulations can significantly aid in mastering this essential skill in electronics.Hi I am new to electronics and have some questions about reading circuit diagrams. When I look at circuit diagrams I don`t know which order the wires, .. 🔗 External reference