Bi-Stable Multivibrator (RS Flip-FLop) with Op-Amp
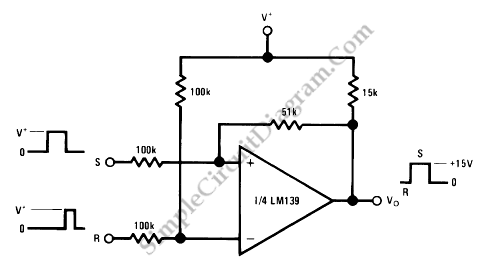
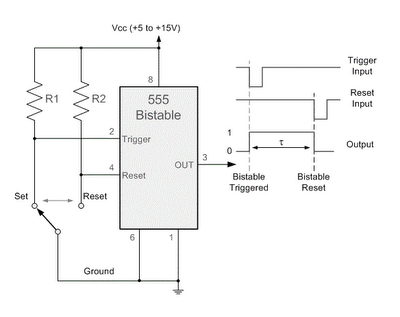
This bi-stable circuit utilizes an operational amplifier and functions similarly to an RS flip-flop. A bi-stable circuit is characterized by having two stable states: low and high, remaining in the low state until it is set to high.
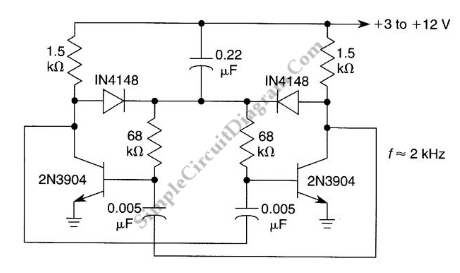
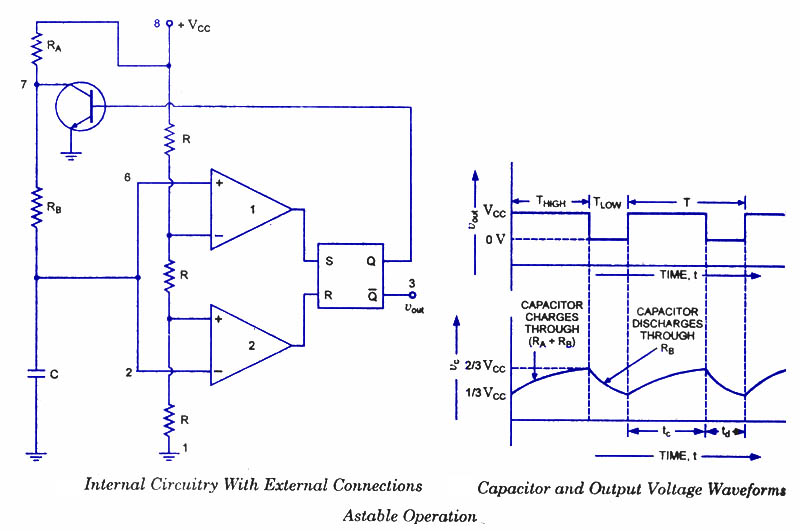
The bi-stable circuit described operates using an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured to function as a flip-flop. The two stable states of the circuit are maintained through positive feedback, allowing the circuit to retain its output state until an external input triggers a change. The circuit consists of an op-amp, resistors, and capacitors arranged in such a way that the output voltage can switch between two distinct levels, typically representing binary states.
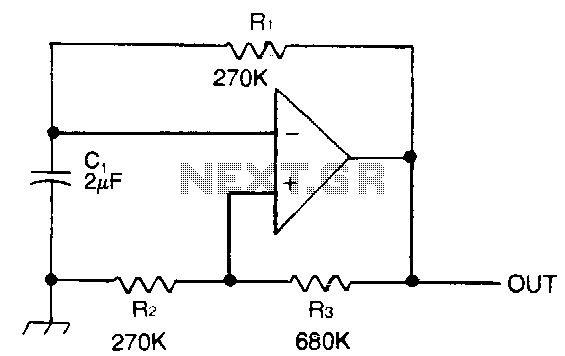
In this configuration, the non-inverting input of the op-amp is connected to a voltage divider formed by two resistors. The inverting input is connected to the output through a feedback resistor, creating a loop that reinforces the current state of the output. When a trigger signal is applied to the non-inverting input, the op-amp responds by changing its output state, which in turn affects the feedback loop and stabilizes the new state.
The circuit can be reset or set by applying appropriate signals to designated inputs, allowing for versatile applications in digital electronics, such as memory storage, frequency division, and signal conditioning. The response time and stability of the circuit can be adjusted through the selection of resistor and capacitor values, enabling fine-tuning for specific applications. The bi-stable nature of this circuit makes it ideal for use in applications requiring memory elements or state retention without continuous power supply.This bi-stable circuit uses an op-amp, acts similar with RS flip-flop. Bi-stable circuit is a circuit with two stable states, low and remain low until set is.. 🔗 External reference
The bi-stable circuit described operates using an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured to function as a flip-flop. The two stable states of the circuit are maintained through positive feedback, allowing the circuit to retain its output state until an external input triggers a change. The circuit consists of an op-amp, resistors, and capacitors arranged in such a way that the output voltage can switch between two distinct levels, typically representing binary states.
In this configuration, the non-inverting input of the op-amp is connected to a voltage divider formed by two resistors. The inverting input is connected to the output through a feedback resistor, creating a loop that reinforces the current state of the output. When a trigger signal is applied to the non-inverting input, the op-amp responds by changing its output state, which in turn affects the feedback loop and stabilizes the new state.
The circuit can be reset or set by applying appropriate signals to designated inputs, allowing for versatile applications in digital electronics, such as memory storage, frequency division, and signal conditioning. The response time and stability of the circuit can be adjusted through the selection of resistor and capacitor values, enabling fine-tuning for specific applications. The bi-stable nature of this circuit makes it ideal for use in applications requiring memory elements or state retention without continuous power supply.This bi-stable circuit uses an op-amp, acts similar with RS flip-flop. Bi-stable circuit is a circuit with two stable states, low and remain low until set is.. 🔗 External reference