Bionic Ear
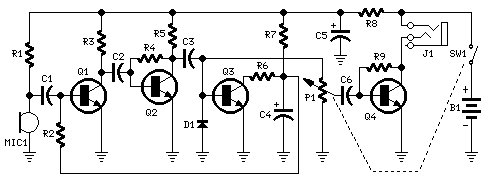
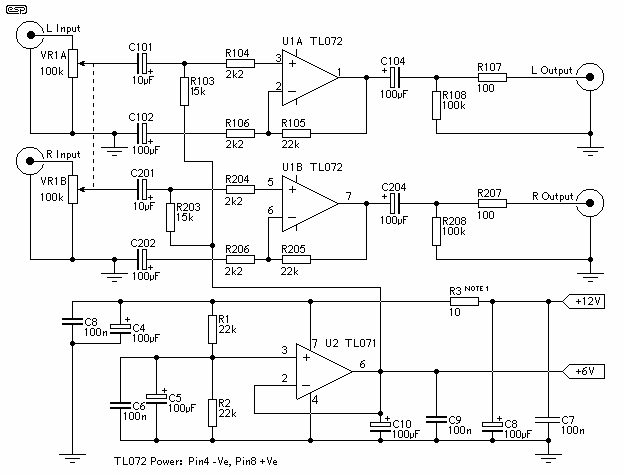
This circuit, connected to 32 Ohm impedance mini-earphones, can detect very remote sounds. Useful for theatre, cinema and lecture goers: every word will be clearly heard. You can also listen to your television set at a very low volume, avoiding to bother relatives and neighbors. Even if you have a faultless hearing, you may discover unexpected sounds using this device: a remote bird twittering will seem very close to you. More: The heart of the circuit is a constant-volume control amplifier. All the signals picked-up by the microphone are amplified at a constant level of about 1 Volt peak to peak. In this manner very low amplitude audio signals are highly amplified and high ampl.
The described circuit is designed to enhance auditory perception, particularly in environments where sound clarity is crucial, such as theaters, cinemas, and lectures. It is optimized for use with 32 Ohm impedance mini-earphones, which are common in portable audio applications, ensuring compatibility and efficient sound delivery.
At the core of the circuit is a constant-volume control amplifier. This amplifier is engineered to maintain a consistent output level, specifically around 1 Volt peak-to-peak, regardless of the input signal's amplitude. This feature is particularly advantageous as it allows the user to hear faint sounds that would typically be inaudible, such as distant conversations or ambient noises, without the risk of sudden loud bursts that could occur with traditional amplifiers.
The microphone serves as the input transducer, capturing sound waves from the environment. It is likely a sensitive electret or condenser type, which is capable of detecting low-level sounds. The audio signals captured by the microphone are routed to the constant-volume control amplifier, where they undergo amplification. The design ensures that while low-amplitude signals are boosted significantly, the overall output remains within a manageable range, preventing distortion or discomfort for the listener.
This circuit can also function as a personal audio enhancement device for television viewing. By connecting the mini-earphones, users can enjoy audio at reduced volumes, thereby minimizing disturbance to others in the vicinity. The application of this circuit extends beyond mere amplification; it enhances the listening experience by revealing subtle sounds that might otherwise go unnoticed, enriching the user's auditory environment.
Overall, the circuit's design prioritizes user comfort and sound clarity, making it a valuable tool for those seeking to improve their auditory experience in various settings.This circuit, connected to 32 Ohm impedance mini-earphones, can detect very remote sounds. Useful for theatre, cinema and lecture goers: every word will be clearly heard. You can also listen to your television set at a very low volume, avoiding to bother relatives and neighbors. Even if you have a faultless hearing, you may discover unexpected sounds using this device: a remote bird twittering will seem very close to you.
The heart of the circuit is a constant-volume control amplifier. All the signals picked-up by the microphone are amplified at a constant level of about 1 Volt peak to peak. In this manner very low amplitude audio signals are highly amplified and high ampl 🔗 External reference
The described circuit is designed to enhance auditory perception, particularly in environments where sound clarity is crucial, such as theaters, cinemas, and lectures. It is optimized for use with 32 Ohm impedance mini-earphones, which are common in portable audio applications, ensuring compatibility and efficient sound delivery.
At the core of the circuit is a constant-volume control amplifier. This amplifier is engineered to maintain a consistent output level, specifically around 1 Volt peak-to-peak, regardless of the input signal's amplitude. This feature is particularly advantageous as it allows the user to hear faint sounds that would typically be inaudible, such as distant conversations or ambient noises, without the risk of sudden loud bursts that could occur with traditional amplifiers.
The microphone serves as the input transducer, capturing sound waves from the environment. It is likely a sensitive electret or condenser type, which is capable of detecting low-level sounds. The audio signals captured by the microphone are routed to the constant-volume control amplifier, where they undergo amplification. The design ensures that while low-amplitude signals are boosted significantly, the overall output remains within a manageable range, preventing distortion or discomfort for the listener.
This circuit can also function as a personal audio enhancement device for television viewing. By connecting the mini-earphones, users can enjoy audio at reduced volumes, thereby minimizing disturbance to others in the vicinity. The application of this circuit extends beyond mere amplification; it enhances the listening experience by revealing subtle sounds that might otherwise go unnoticed, enriching the user's auditory environment.
Overall, the circuit's design prioritizes user comfort and sound clarity, making it a valuable tool for those seeking to improve their auditory experience in various settings.This circuit, connected to 32 Ohm impedance mini-earphones, can detect very remote sounds. Useful for theatre, cinema and lecture goers: every word will be clearly heard. You can also listen to your television set at a very low volume, avoiding to bother relatives and neighbors. Even if you have a faultless hearing, you may discover unexpected sounds using this device: a remote bird twittering will seem very close to you.
The heart of the circuit is a constant-volume control amplifier. All the signals picked-up by the microphone are amplified at a constant level of about 1 Volt peak to peak. In this manner very low amplitude audio signals are highly amplified and high ampl 🔗 External reference