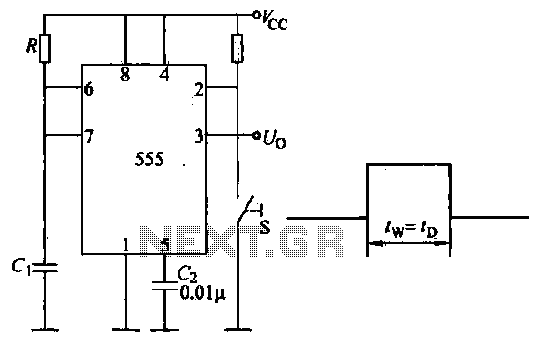
Birds singing analog signal generator circuit
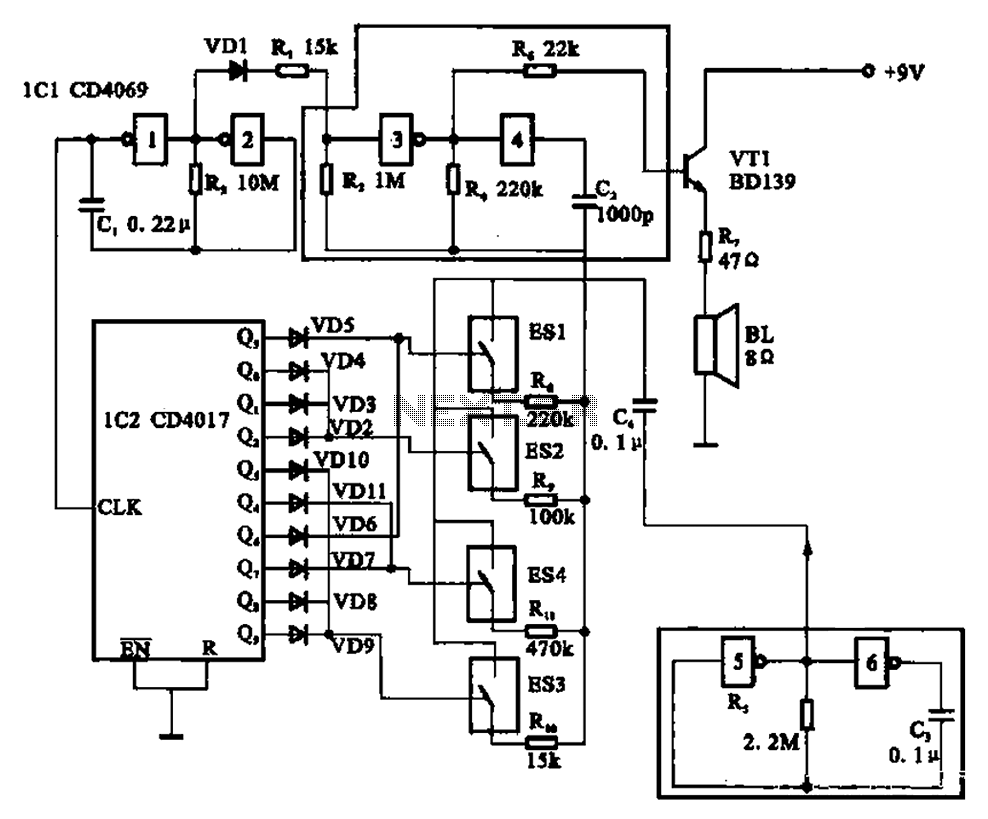
The circuit illustrated is an analog signal generator designed to produce a chirping sound, simulating birds singing. It employs six CD4069 inverters to create three oscillators, with two of them functioning as ultra-low frequency oscillators. The oscillation frequency is in the fraction of hertz range, and the generated signal acts as a clock signal for the counting device IC2 at its CLK terminal. The output from IC2, based on the number of input pulses, controls the configuration of outputs Q1-Q9, which in turn regulates the subsequent pole tube matrix. The audio oscillator is composed of inverters 3 and 4, while IC1, utilizing inverters 5 and 6, forms a low-frequency oscillator. The audio signal generated by the audio oscillator is modulated by the low-frequency oscillator's output. The low-frequency oscillation signal is output through capacitor C4 and is routed through resistors R1 and R11, with the connection determined by the analog switches ES1 to ES4. Additionally, these switches control the operation of diodes VD2 to VD9.
The described circuit serves as a versatile analog signal generator, capable of producing low-frequency chirp sounds reminiscent of birds. It incorporates multiple CD4069 inverters, which are utilized to create oscillators that generate the necessary frequencies for both the low-frequency and audio signals. The use of ultra-low frequency oscillators allows for the generation of signals that can produce very slow oscillations, which are essential for mimicking the natural rhythm of bird songs.
The clock signal produced by the low-frequency oscillators is fed into the counting device IC2, which counts the pulses and determines the output based on its configuration. This output is essential for controlling the pole tube matrix, which shapes the audio output further. The design allows for flexibility in configuring the output signals through the various Q outputs, which can be adjusted to create different chirp patterns.
The audio oscillator, formed by inverters 3 and 4, works in conjunction with the low-frequency oscillator to modulate the audio output. The modulation is achieved by varying the amplitude or frequency of the audio signal based on the low-frequency oscillation, resulting in a dynamic sound output that can change over time, mimicking the natural variability of bird calls.
The inclusion of analog switches ES1 to ES4 adds a layer of control to the circuit, allowing for selective activation of certain components within the circuit. This feature enhances the circuit's functionality, enabling the user to tailor the sound output by engaging or disengaging specific diodes (VD2 to VD9) and resistors (R1 and R11). This modular approach allows for experimentation and customization of the chirping sounds produced, making it suitable for various applications in sound synthesis and educational projects. Birds singing analog signal generator circuit Shown is an analog chirp signal generator circuit. The inverter circuit consists of six CD4069 composed of three oscillators, two inverters lcl l, 2 ultra-low frequency oscillator composition, the oscillation frequency is a fraction of hertz, the signal as a clock signal into the counting device IC2 of the CLK terminal, depending on the number of input pulse, Q1-Q9 in different configuration output of IC2 to control subsequent fftj- pole tube matrix. ICI inverters 3,4 composed audio oscillator for generating an audio signal. IC1 non-inverter S, 6 composed of low-frequency oscillator. Audio oscillator control signal output by the low-frequency oscillator, so the audio output of the oscillator is modulated by an audio signal.
Low frequency oscillation signal output by C4, by B-RII to one or more of the audio oscillator, 8 ~ Rl1 whether the access depends on the analog switch ES1 ~ ES4 on and off, but also by ES1-ES4 control in VD2-VD9.
The described circuit serves as a versatile analog signal generator, capable of producing low-frequency chirp sounds reminiscent of birds. It incorporates multiple CD4069 inverters, which are utilized to create oscillators that generate the necessary frequencies for both the low-frequency and audio signals. The use of ultra-low frequency oscillators allows for the generation of signals that can produce very slow oscillations, which are essential for mimicking the natural rhythm of bird songs.
The clock signal produced by the low-frequency oscillators is fed into the counting device IC2, which counts the pulses and determines the output based on its configuration. This output is essential for controlling the pole tube matrix, which shapes the audio output further. The design allows for flexibility in configuring the output signals through the various Q outputs, which can be adjusted to create different chirp patterns.
The audio oscillator, formed by inverters 3 and 4, works in conjunction with the low-frequency oscillator to modulate the audio output. The modulation is achieved by varying the amplitude or frequency of the audio signal based on the low-frequency oscillation, resulting in a dynamic sound output that can change over time, mimicking the natural variability of bird calls.
The inclusion of analog switches ES1 to ES4 adds a layer of control to the circuit, allowing for selective activation of certain components within the circuit. This feature enhances the circuit's functionality, enabling the user to tailor the sound output by engaging or disengaging specific diodes (VD2 to VD9) and resistors (R1 and R11). This modular approach allows for experimentation and customization of the chirping sounds produced, making it suitable for various applications in sound synthesis and educational projects. Birds singing analog signal generator circuit Shown is an analog chirp signal generator circuit. The inverter circuit consists of six CD4069 composed of three oscillators, two inverters lcl l, 2 ultra-low frequency oscillator composition, the oscillation frequency is a fraction of hertz, the signal as a clock signal into the counting device IC2 of the CLK terminal, depending on the number of input pulse, Q1-Q9 in different configuration output of IC2 to control subsequent fftj- pole tube matrix. ICI inverters 3,4 composed audio oscillator for generating an audio signal. IC1 non-inverter S, 6 composed of low-frequency oscillator. Audio oscillator control signal output by the low-frequency oscillator, so the audio output of the oscillator is modulated by an audio signal.
Low frequency oscillation signal output by C4, by B-RII to one or more of the audio oscillator, 8 ~ Rl1 whether the access depends on the analog switch ES1 ~ ES4 on and off, but also by ES1-ES4 control in VD2-VD9.