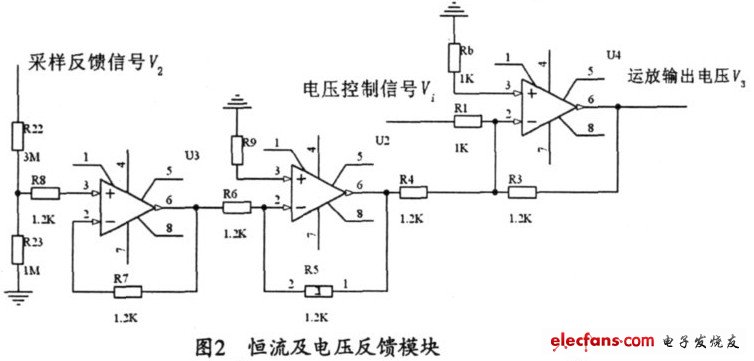
Brushless DC electric motor control by CPLD
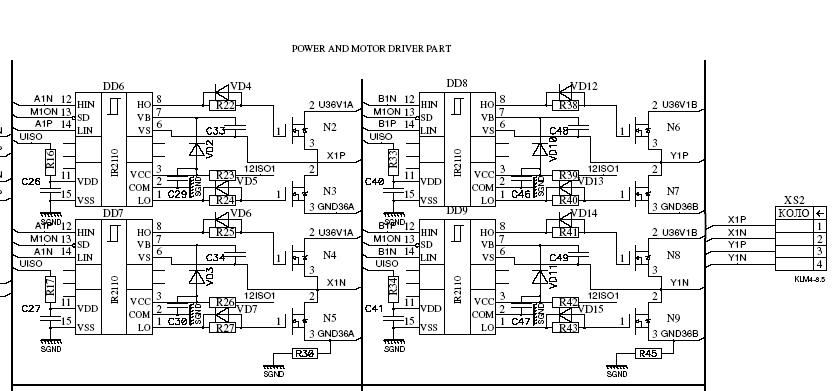
The primary application area for brushless direct current motors (BLDC) is in positioning systems.
Brushless Direct Current (BLDC) motors are widely utilized in various positioning applications due to their high efficiency, reliability, and precise control capabilities. These motors operate without brushes, which minimizes mechanical wear and enhances longevity. The primary function of BLDC motors in positioning systems includes precise angular positioning, speed control, and torque management.
In a typical positioning system, a BLDC motor is paired with a feedback mechanism, such as an encoder or a resolver, to provide real-time positional data. This feedback loop is essential for maintaining accuracy and ensuring that the motor responds appropriately to control signals. The motor driver circuit, which typically includes a microcontroller or a dedicated driver IC, interprets the feedback signals and adjusts the motor's operation accordingly.
The control strategy for BLDC motors often employs techniques such as Field-Oriented Control (FOC) or trapezoidal control, which optimize performance across a range of speeds and load conditions. Additionally, BLDC motors are favored in applications requiring high dynamic response, such as robotics, CNC machinery, and automated assembly systems, where precise positioning is critical.
In summary, the application of BLDC motors in positioning systems is characterized by their efficiency, durability, and ability to deliver accurate control, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial and consumer applications.The main area for application of brushless direct current motors (BLDC) is positioning 🔗 External reference
Brushless Direct Current (BLDC) motors are widely utilized in various positioning applications due to their high efficiency, reliability, and precise control capabilities. These motors operate without brushes, which minimizes mechanical wear and enhances longevity. The primary function of BLDC motors in positioning systems includes precise angular positioning, speed control, and torque management.
In a typical positioning system, a BLDC motor is paired with a feedback mechanism, such as an encoder or a resolver, to provide real-time positional data. This feedback loop is essential for maintaining accuracy and ensuring that the motor responds appropriately to control signals. The motor driver circuit, which typically includes a microcontroller or a dedicated driver IC, interprets the feedback signals and adjusts the motor's operation accordingly.
The control strategy for BLDC motors often employs techniques such as Field-Oriented Control (FOC) or trapezoidal control, which optimize performance across a range of speeds and load conditions. Additionally, BLDC motors are favored in applications requiring high dynamic response, such as robotics, CNC machinery, and automated assembly systems, where precise positioning is critical.
In summary, the application of BLDC motors in positioning systems is characterized by their efficiency, durability, and ability to deliver accurate control, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial and consumer applications.The main area for application of brushless direct current motors (BLDC) is positioning 🔗 External reference