bugs
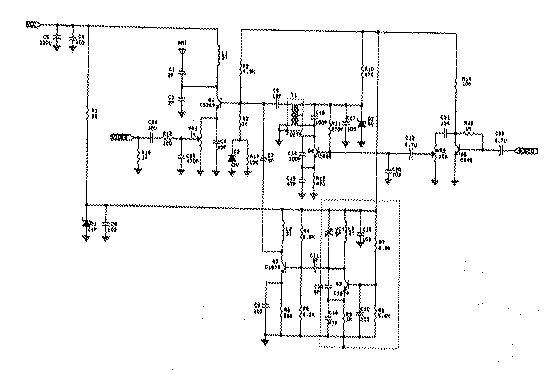
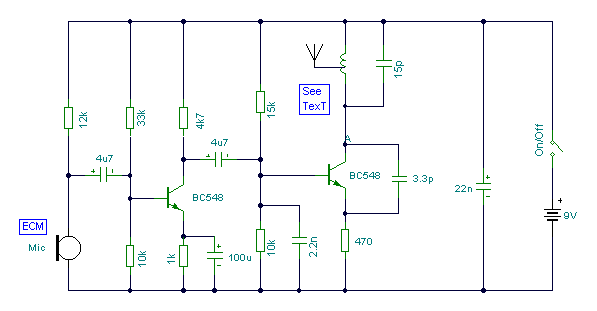
Radio transmitters for eavesdropping on private conversations and sending video pictures, battery-operated.
Radio transmitters designed for eavesdropping applications typically operate within specific frequency ranges to capture audio and video signals discreetly. These devices often utilize low-power RF (radio frequency) technology to ensure prolonged battery life, allowing for extended periods of surveillance without the need for frequent recharging or battery replacement.
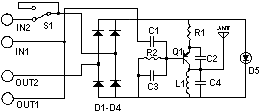
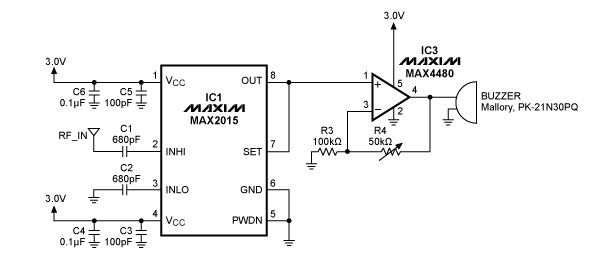
The circuit design of such a transmitter generally includes several key components: an audio/video input stage, a modulator, a power amplifier, and an antenna. The audio/video input stage captures the desired signals, which can be sourced from microphones or cameras integrated into the device. This stage may include preamplifiers to enhance the quality of the input signals before modulation.
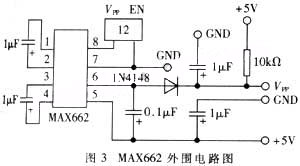
The modulator converts the audio and video signals into radio frequency signals suitable for transmission. Common modulation techniques include amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM), with FM often preferred for its resistance to noise and interference. The modulated signal is then amplified by the power amplifier to ensure it can travel the desired distance before being transmitted via the antenna.
The antenna design is critical for optimizing transmission range and quality. It must be tuned to the operating frequency of the transmitter and can vary in size and shape depending on the frequency band used. Additionally, the device may include a battery management system to monitor battery levels and optimize power consumption.
Such radio transmitters must comply with local regulations regarding radio frequency emissions and privacy laws, as unauthorized eavesdropping is illegal in many jurisdictions. Therefore, careful consideration of legal implications is essential when designing and deploying these devices.radio transmitters for evesdropping on private conversations and sending video pictures, battery operated.. 🔗 External reference
Radio transmitters designed for eavesdropping applications typically operate within specific frequency ranges to capture audio and video signals discreetly. These devices often utilize low-power RF (radio frequency) technology to ensure prolonged battery life, allowing for extended periods of surveillance without the need for frequent recharging or battery replacement.
The circuit design of such a transmitter generally includes several key components: an audio/video input stage, a modulator, a power amplifier, and an antenna. The audio/video input stage captures the desired signals, which can be sourced from microphones or cameras integrated into the device. This stage may include preamplifiers to enhance the quality of the input signals before modulation.
The modulator converts the audio and video signals into radio frequency signals suitable for transmission. Common modulation techniques include amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM), with FM often preferred for its resistance to noise and interference. The modulated signal is then amplified by the power amplifier to ensure it can travel the desired distance before being transmitted via the antenna.
The antenna design is critical for optimizing transmission range and quality. It must be tuned to the operating frequency of the transmitter and can vary in size and shape depending on the frequency band used. Additionally, the device may include a battery management system to monitor battery levels and optimize power consumption.
Such radio transmitters must comply with local regulations regarding radio frequency emissions and privacy laws, as unauthorized eavesdropping is illegal in many jurisdictions. Therefore, careful consideration of legal implications is essential when designing and deploying these devices.radio transmitters for evesdropping on private conversations and sending video pictures, battery operated.. 🔗 External reference