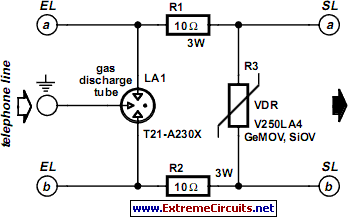
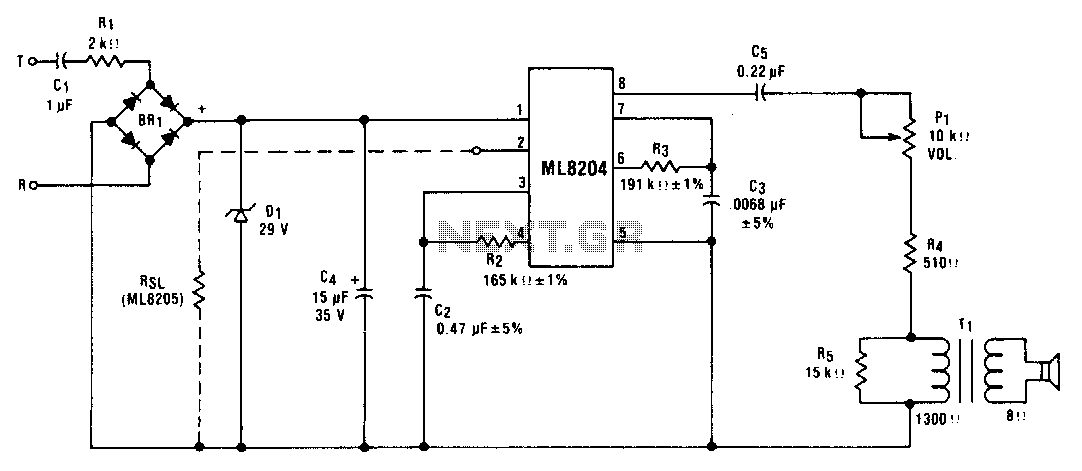
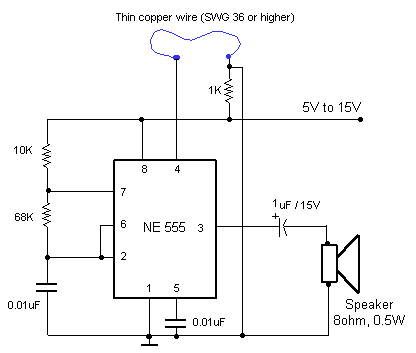
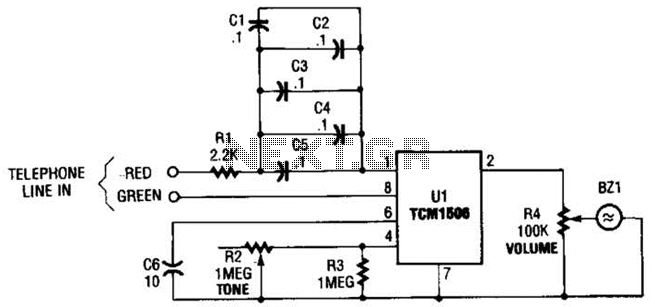
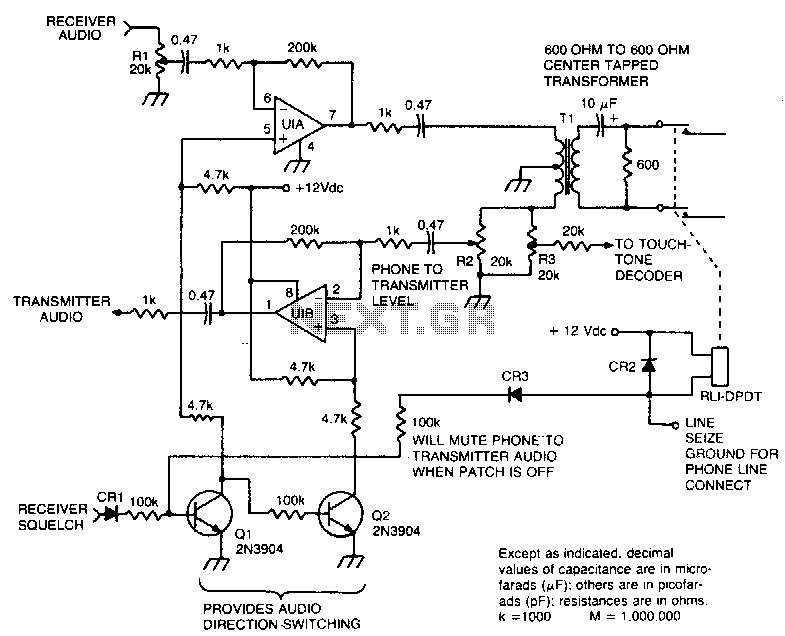
FM Telephone Bugs
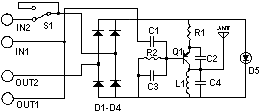
Small telephone bug. It listens to the telephone line on an FM receiver. It is self-powered and has a small part count. Circuit diagram, schematics, electronics project.
The small telephone bug is a compact and efficient device designed to intercept audio signals from a telephone line and transmit them wirelessly to an FM receiver. This device operates independently using its own power source, eliminating the need for external power supplies. The simplicity of the design is reflected in its low component count, making it an accessible project for electronics enthusiasts.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a microphone to capture audio signals, an amplifier to boost the microphone's output, and an FM transmitter circuit to modulate the audio signals onto a radio frequency. The FM transmitter may utilize a simple oscillator circuit, often based on a transistor, to generate the necessary frequency for transmission.
The microphone is usually connected to the amplifier, which enhances the audio signal before it is fed into the FM modulator. The modulator converts the audio signal into an FM signal that can be picked up by standard FM receivers. The entire circuit is designed to operate with minimal power consumption, allowing for prolonged use without frequent battery replacements.
A schematic diagram of the circuit would typically illustrate the connections between these components, highlighting the power supply configuration, signal flow, and any necessary tuning elements to adjust the transmission frequency. This project provides an excellent opportunity to learn about analog audio processing and radio frequency transmission in a hands-on manner.Small telephone bug. Listen telephone line on your FM receiver. It is self powered. Small part count. Circuit diagram, schematics, electronics project.. 🔗 External reference
The small telephone bug is a compact and efficient device designed to intercept audio signals from a telephone line and transmit them wirelessly to an FM receiver. This device operates independently using its own power source, eliminating the need for external power supplies. The simplicity of the design is reflected in its low component count, making it an accessible project for electronics enthusiasts.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a microphone to capture audio signals, an amplifier to boost the microphone's output, and an FM transmitter circuit to modulate the audio signals onto a radio frequency. The FM transmitter may utilize a simple oscillator circuit, often based on a transistor, to generate the necessary frequency for transmission.
The microphone is usually connected to the amplifier, which enhances the audio signal before it is fed into the FM modulator. The modulator converts the audio signal into an FM signal that can be picked up by standard FM receivers. The entire circuit is designed to operate with minimal power consumption, allowing for prolonged use without frequent battery replacements.
A schematic diagram of the circuit would typically illustrate the connections between these components, highlighting the power supply configuration, signal flow, and any necessary tuning elements to adjust the transmission frequency. This project provides an excellent opportunity to learn about analog audio processing and radio frequency transmission in a hands-on manner.Small telephone bug. Listen telephone line on your FM receiver. It is self powered. Small part count. Circuit diagram, schematics, electronics project.. 🔗 External reference