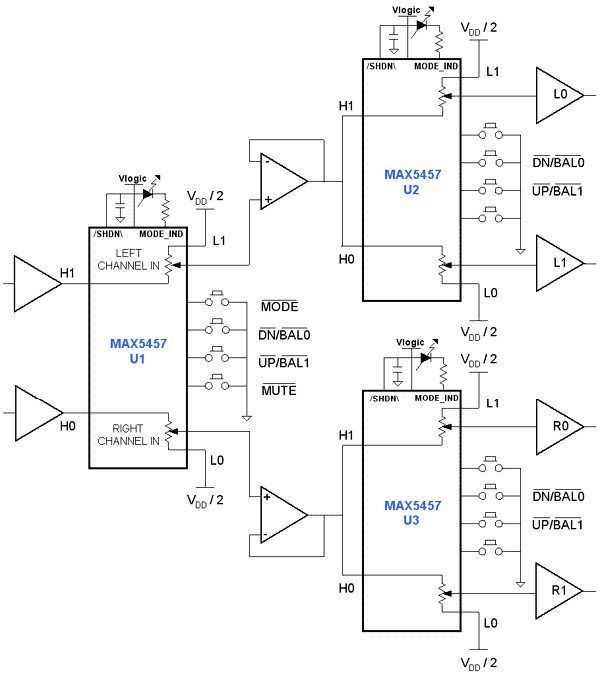
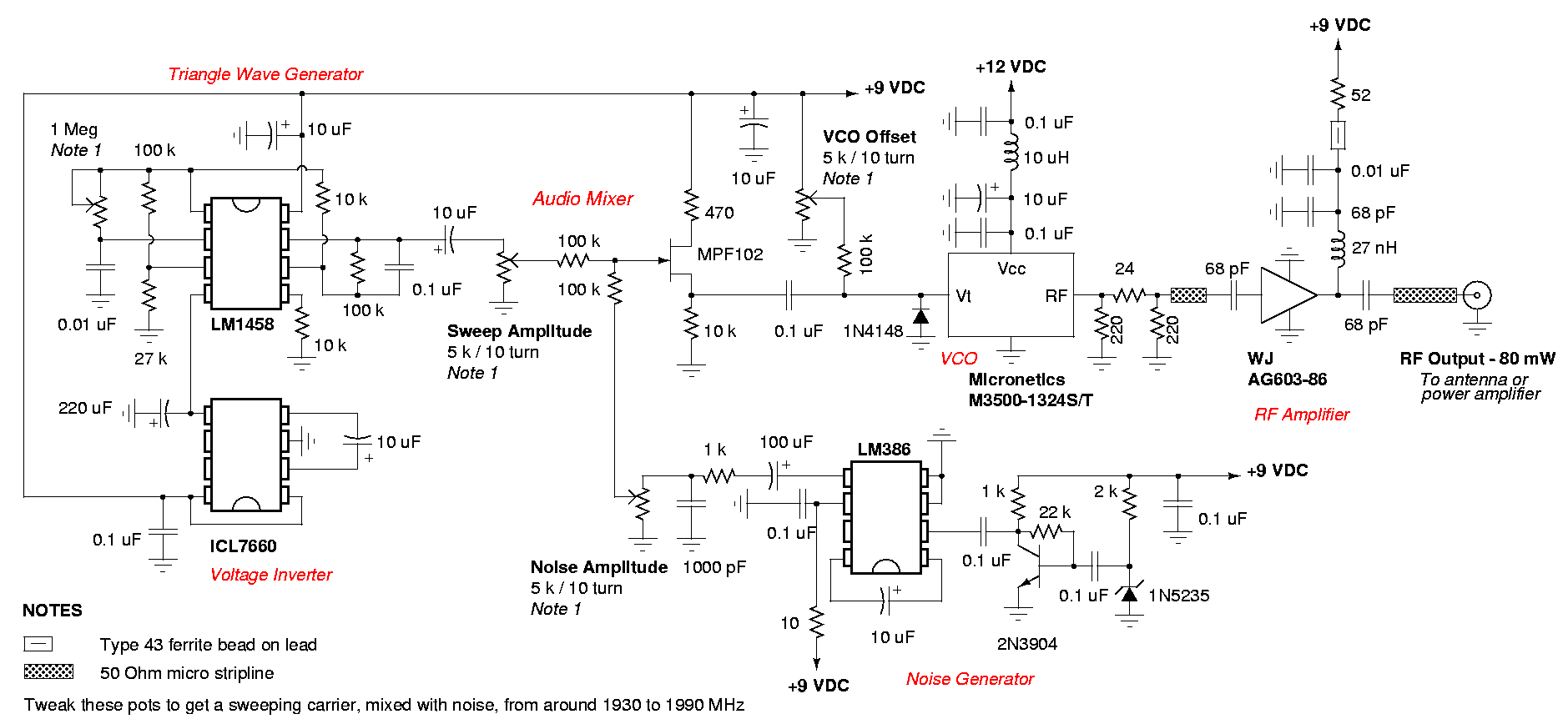
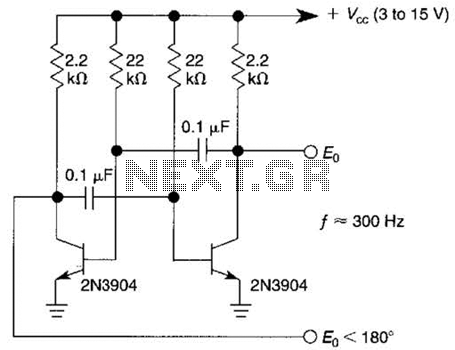
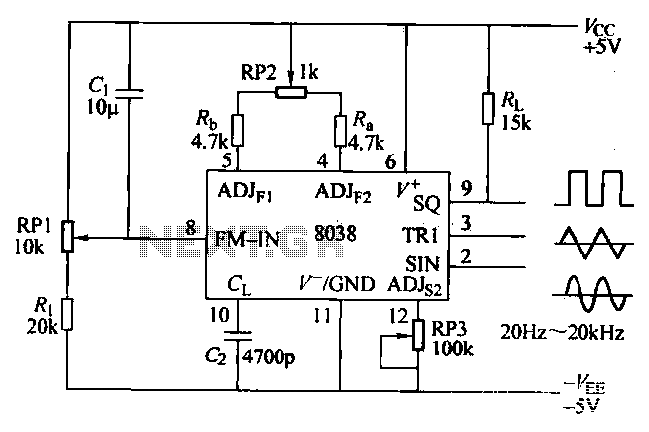
Build Own RFID circuit
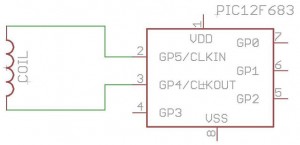
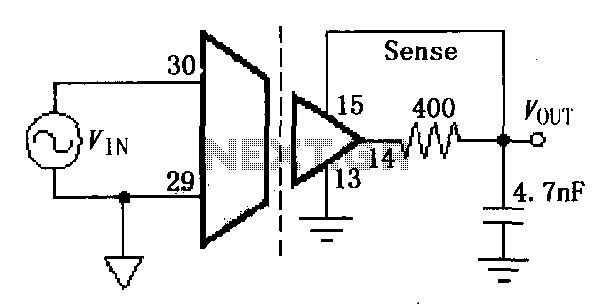
How to build your own RFID system using a microcontroller. This schematic is very simple.
Building a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system using a microcontroller involves several key components and a straightforward schematic design. The essential elements of an RFID system include an RFID reader, an RFID tag, and a microcontroller that processes the data from the reader.
The RFID reader is responsible for emitting radio waves that power the RFID tag and receive the information transmitted back. The microcontroller serves as the central processing unit, interfacing with the RFID reader to interpret the data received from the tags.
The typical schematic for a basic RFID system includes the following components:
1. **Microcontroller**: Select a suitable microcontroller, such as an Arduino or PIC, that has adequate I/O pins and supports the necessary communication protocols (e.g., SPI, I2C, UART).
2. **RFID Reader Module**: This module is connected to the microcontroller. Common examples include the RC522 or PN532 modules. The connections typically involve power (VCC and GND), and communication pins (MOSI, MISO, SCK, and SS for SPI communication).
3. **Power Supply**: Ensure that the power supply meets the voltage and current requirements of the microcontroller and the RFID reader. This may involve using a battery or an external power source.
4. **RFID Tags**: These tags can be passive or active. Passive tags are powered by the RFID reader's signal, while active tags have their own power source. The choice of tags will depend on the application requirements.
5. **Connecting Wires**: Use appropriate gauge wires to connect the microcontroller to the RFID reader and other components, ensuring reliable connections.
The schematic will typically illustrate the connections between the microcontroller and the RFID reader, including any necessary pull-up resistors and capacitors to stabilize the power supply and communication lines.
Programming the microcontroller involves writing code to initialize the RFID reader, continuously poll for tags, and process the data received. This can include reading unique identifiers (UIDs) from the tags and executing specific actions based on the tag data, such as logging information or triggering other devices.
In conclusion, building a simple RFID system with a microcontroller is achievable with basic electronic components and programming knowledge, making it a suitable project for educational purposes or hobbyist applications.how to build own RIFD, use one Microcontroller we can build it. This schematics is Very Simple 🔗 External reference
Building a Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) system using a microcontroller involves several key components and a straightforward schematic design. The essential elements of an RFID system include an RFID reader, an RFID tag, and a microcontroller that processes the data from the reader.
The RFID reader is responsible for emitting radio waves that power the RFID tag and receive the information transmitted back. The microcontroller serves as the central processing unit, interfacing with the RFID reader to interpret the data received from the tags.
The typical schematic for a basic RFID system includes the following components:
1. **Microcontroller**: Select a suitable microcontroller, such as an Arduino or PIC, that has adequate I/O pins and supports the necessary communication protocols (e.g., SPI, I2C, UART).
2. **RFID Reader Module**: This module is connected to the microcontroller. Common examples include the RC522 or PN532 modules. The connections typically involve power (VCC and GND), and communication pins (MOSI, MISO, SCK, and SS for SPI communication).
3. **Power Supply**: Ensure that the power supply meets the voltage and current requirements of the microcontroller and the RFID reader. This may involve using a battery or an external power source.
4. **RFID Tags**: These tags can be passive or active. Passive tags are powered by the RFID reader's signal, while active tags have their own power source. The choice of tags will depend on the application requirements.
5. **Connecting Wires**: Use appropriate gauge wires to connect the microcontroller to the RFID reader and other components, ensuring reliable connections.
The schematic will typically illustrate the connections between the microcontroller and the RFID reader, including any necessary pull-up resistors and capacitors to stabilize the power supply and communication lines.
Programming the microcontroller involves writing code to initialize the RFID reader, continuously poll for tags, and process the data received. This can include reading unique identifiers (UIDs) from the tags and executing specific actions based on the tag data, such as logging information or triggering other devices.
In conclusion, building a simple RFID system with a microcontroller is achievable with basic electronic components and programming knowledge, making it a suitable project for educational purposes or hobbyist applications.how to build own RIFD, use one Microcontroller we can build it. This schematics is Very Simple 🔗 External reference