Capacitor in parallel with resistor on xoscope amplifier schematic
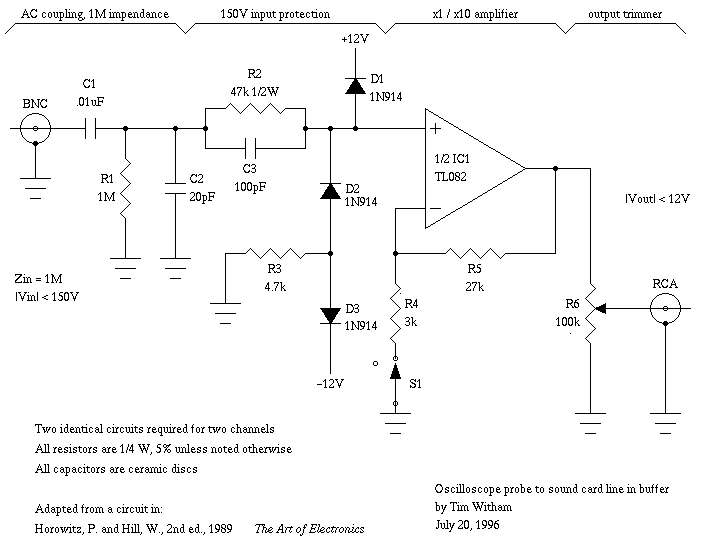
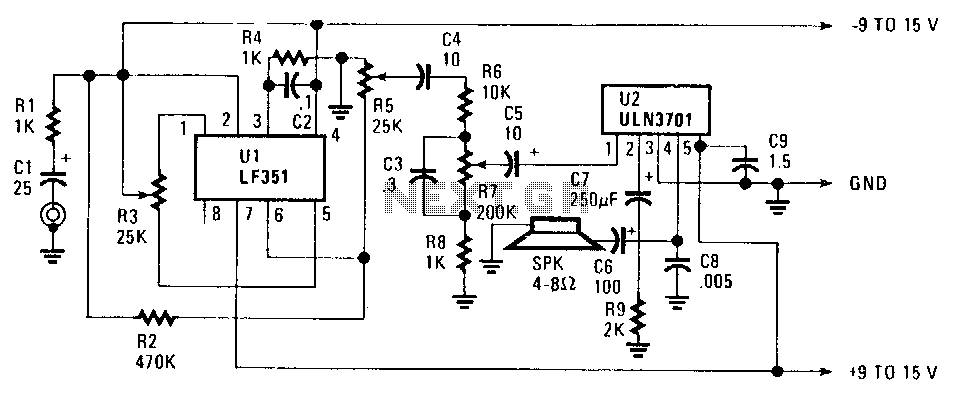
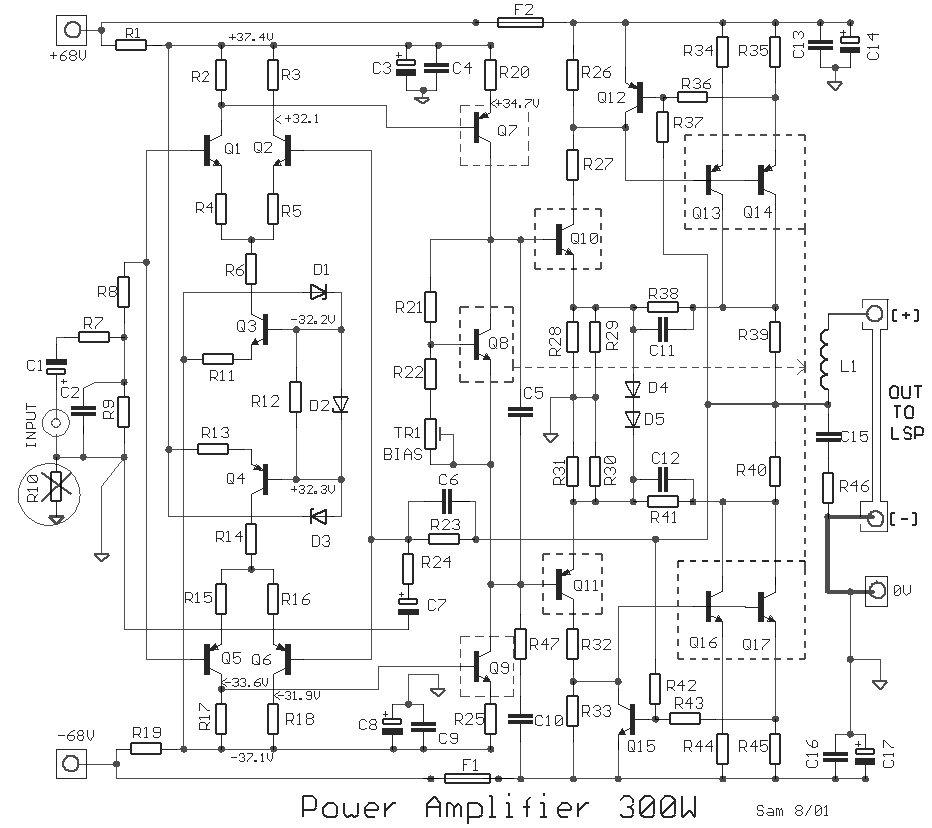
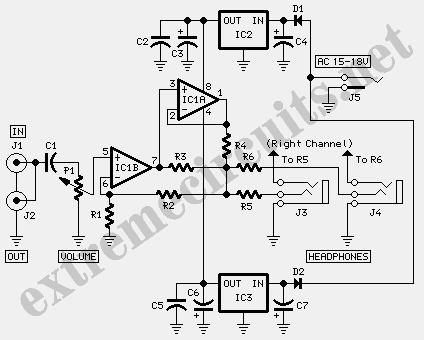
For capacitor C3, a 100pF capacitor is placed across resistor R2. The circuit functions similarly to previous configurations, although no explanation is provided. The purpose of this component may be self-evident to experienced users, but it may not be clear to those who are new to analog electronics. It can be assumed that this capacitor is serving a stabilizing function, but the specific impact on circuit operation without it is unclear.
In this circuit, capacitor C3 is strategically positioned across resistor R2 to enhance the stability of the overall system. This configuration is commonly employed in various analog circuits to filter high-frequency noise and improve transient response. The 100pF value of C3 indicates that it is designed to block low-frequency signals while allowing high-frequency signals to pass through, thereby smoothing out fluctuations in voltage across R2.
The presence of C3 can be crucial in preventing oscillations that may arise from feedback loops or other dynamic interactions within the circuit. By providing a low-impedance path for high-frequency signals, C3 helps to maintain the desired performance of the circuit, ensuring that it operates as intended. Without this capacitor, the circuit could experience increased noise susceptibility and potentially unstable behavior, particularly in high-frequency applications.
Understanding the role of C3 in this context is essential for analyzing the circuit's performance. It is important to consider the implications of removing this component, as it could lead to degraded signal integrity and introduce unwanted artifacts in the output. For those new to analog electronics, grasping these concepts will aid in comprehending the intricate balance of components within a circuit and their collective influence on overall functionality.For C3, the 100pF across R2. The circuit does exactly the same thing, once again with no explanation. Apparently the utility ought to be obvious, but I`m new to earnest analog electronics. I can only assume that it`s stabilizing something, but I don`tknow how the operation would suffer without it. 🔗 External reference
In this circuit, capacitor C3 is strategically positioned across resistor R2 to enhance the stability of the overall system. This configuration is commonly employed in various analog circuits to filter high-frequency noise and improve transient response. The 100pF value of C3 indicates that it is designed to block low-frequency signals while allowing high-frequency signals to pass through, thereby smoothing out fluctuations in voltage across R2.
The presence of C3 can be crucial in preventing oscillations that may arise from feedback loops or other dynamic interactions within the circuit. By providing a low-impedance path for high-frequency signals, C3 helps to maintain the desired performance of the circuit, ensuring that it operates as intended. Without this capacitor, the circuit could experience increased noise susceptibility and potentially unstable behavior, particularly in high-frequency applications.
Understanding the role of C3 in this context is essential for analyzing the circuit's performance. It is important to consider the implications of removing this component, as it could lead to degraded signal integrity and introduce unwanted artifacts in the output. For those new to analog electronics, grasping these concepts will aid in comprehending the intricate balance of components within a circuit and their collective influence on overall functionality.For C3, the 100pF across R2. The circuit does exactly the same thing, once again with no explanation. Apparently the utility ought to be obvious, but I`m new to earnest analog electronics. I can only assume that it`s stabilizing something, but I don`tknow how the operation would suffer without it. 🔗 External reference