Car Headlight Alarm circuit diagram
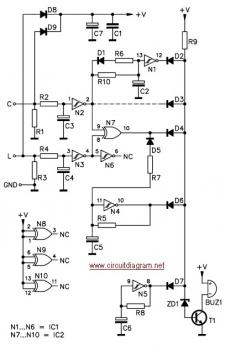
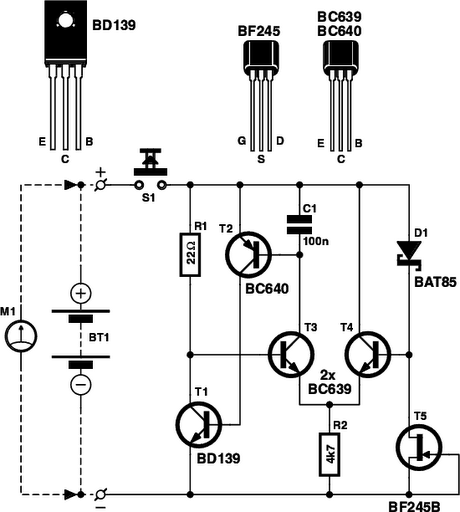
The circuit is designed to ensure that the headlights or side lights are automatically switched off after the ignition contact is turned off. This prevents the occurrence of a dead battery due to headlights being inadvertently left on.
The circuit utilizes a relay or a transistor switch to control the power supply to the headlights based on the ignition status. When the ignition is turned on, the circuit allows current to flow to the headlights, enabling them to operate normally. Once the ignition is turned off, the relay or transistor is triggered to interrupt the power supply to the headlights, effectively turning them off.
The schematic typically includes an ignition switch, a relay or transistor, and the headlight circuit. The ignition switch is connected to the control terminal of the relay or the base of the transistor. When the ignition is active, the relay is energized, closing the circuit and allowing current to flow to the headlights. Upon turning off the ignition, the relay de-energizes or the transistor turns off, cutting off the power to the headlights.
To ensure reliability, additional components such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF from damaging the control circuitry. A capacitor can also be integrated to provide a delay if desired, allowing for a brief period during which the headlights remain on after ignition off, enhancing visibility when exiting the vehicle.
This circuit is essential in automotive applications to enhance user convenience and prevent battery drain, thereby improving the overall efficiency and reliability of the vehicle’s electrical system.First, to indicate that the head lights (or the side lights) should be switched off after switching off the ignition contact. With this circuit, there should be no dead battery due to headlights that were left on. 🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes a relay or a transistor switch to control the power supply to the headlights based on the ignition status. When the ignition is turned on, the circuit allows current to flow to the headlights, enabling them to operate normally. Once the ignition is turned off, the relay or transistor is triggered to interrupt the power supply to the headlights, effectively turning them off.
The schematic typically includes an ignition switch, a relay or transistor, and the headlight circuit. The ignition switch is connected to the control terminal of the relay or the base of the transistor. When the ignition is active, the relay is energized, closing the circuit and allowing current to flow to the headlights. Upon turning off the ignition, the relay de-energizes or the transistor turns off, cutting off the power to the headlights.
To ensure reliability, additional components such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF from damaging the control circuitry. A capacitor can also be integrated to provide a delay if desired, allowing for a brief period during which the headlights remain on after ignition off, enhancing visibility when exiting the vehicle.
This circuit is essential in automotive applications to enhance user convenience and prevent battery drain, thereby improving the overall efficiency and reliability of the vehicle’s electrical system.First, to indicate that the head lights (or the side lights) should be switched off after switching off the ignition contact. With this circuit, there should be no dead battery due to headlights that were left on. 🔗 External reference