Catalyst Granted Patent on LED Driver Technology

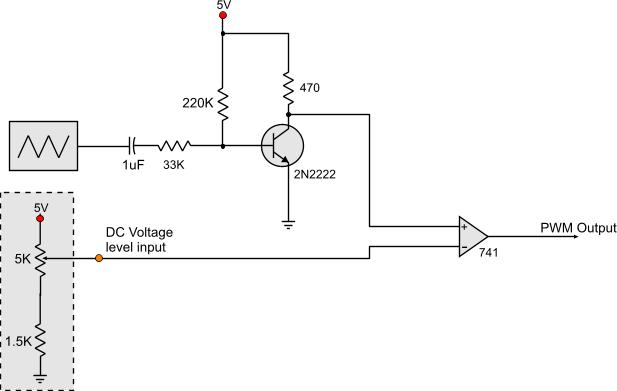
Catalyst Semiconductor, Inc. (NASDAQ:CATS), a supplier of analog, mixed-signal, and non-volatile memory semiconductors, announced it has received a patent for a unique step-down switching regulator circuit architecture applicable to step-down regulators for driving high brightness LEDs. The patent, titled "LED current bias control using step-down regulator" (patent number 7,323,828), was developed to simplify the design of high brightness LED lighting in emerging household, commercial, and automotive lighting applications.
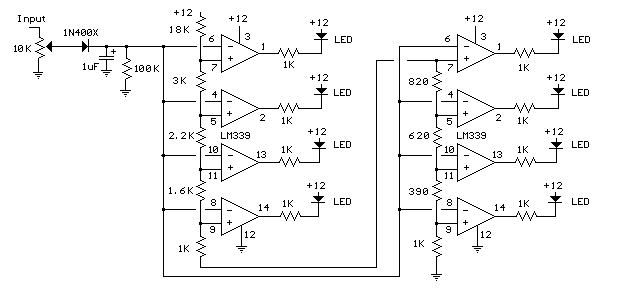
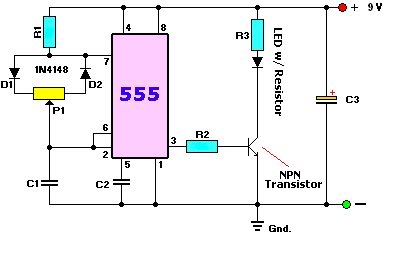
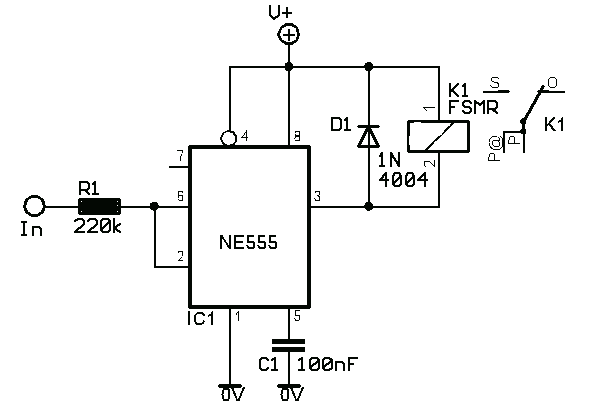
The patented step-down switching regulator circuit architecture is designed to enhance the efficiency and performance of LED drivers. This innovative circuit allows for precise control of the current supplied to high brightness LEDs, ensuring optimal illumination while minimizing power loss.
The architecture employs a feedback mechanism that adjusts the output voltage in response to changes in the load, maintaining a constant current through the LED. This is crucial for applications where consistent brightness is required, such as in automotive headlights or commercial lighting fixtures.
The circuit typically includes components such as an inductor, a switch (often a MOSFET), a diode, and capacitors. The inductor stores energy when the switch is closed and releases it to the load when the switch is open, effectively reducing the voltage while maintaining the necessary current. This method is particularly beneficial in applications where space and thermal management are critical, as it allows for smaller passive components and reduced heat generation compared to traditional linear regulators.
Furthermore, the design is expected to facilitate easier integration into existing lighting systems, promoting broader adoption of high brightness LEDs in various sectors. The patent represents a significant advancement in LED driver technology, addressing the growing demand for efficient and reliable lighting solutions in modern applications.Catalyst Semiconductor, Inc. (NASDAQ:CATS)a supplier of analog, mixed-signal and non-volatile memory semiconductors, announced it has received a patent for a unique step-down switching regulator circuit architecture applicable to step-down regulators for driving high brightness LEDs. The patent, titled ?LED current bias control using step-down regulator? (patent number 7,323,828), was developed to simplify the design of high brightness LED lighting in emerging household, commercial and automotive lighting applications..
🔗 External reference
The patented step-down switching regulator circuit architecture is designed to enhance the efficiency and performance of LED drivers. This innovative circuit allows for precise control of the current supplied to high brightness LEDs, ensuring optimal illumination while minimizing power loss.
The architecture employs a feedback mechanism that adjusts the output voltage in response to changes in the load, maintaining a constant current through the LED. This is crucial for applications where consistent brightness is required, such as in automotive headlights or commercial lighting fixtures.
The circuit typically includes components such as an inductor, a switch (often a MOSFET), a diode, and capacitors. The inductor stores energy when the switch is closed and releases it to the load when the switch is open, effectively reducing the voltage while maintaining the necessary current. This method is particularly beneficial in applications where space and thermal management are critical, as it allows for smaller passive components and reduced heat generation compared to traditional linear regulators.
Furthermore, the design is expected to facilitate easier integration into existing lighting systems, promoting broader adoption of high brightness LEDs in various sectors. The patent represents a significant advancement in LED driver technology, addressing the growing demand for efficient and reliable lighting solutions in modern applications.Catalyst Semiconductor, Inc. (NASDAQ:CATS)a supplier of analog, mixed-signal and non-volatile memory semiconductors, announced it has received a patent for a unique step-down switching regulator circuit architecture applicable to step-down regulators for driving high brightness LEDs. The patent, titled ?LED current bias control using step-down regulator? (patent number 7,323,828), was developed to simplify the design of high brightness LED lighting in emerging household, commercial and automotive lighting applications..
🔗 External reference