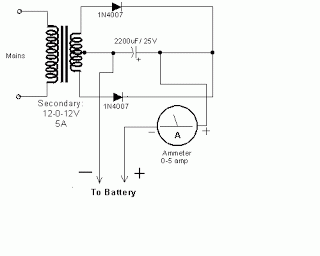
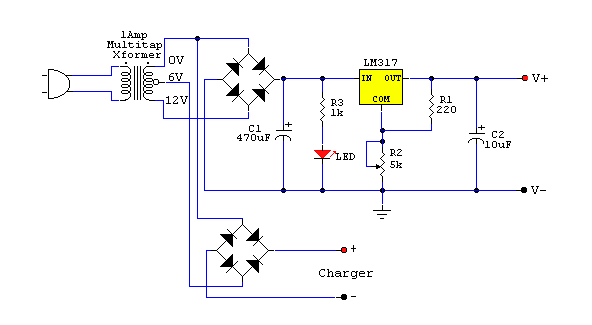
charger
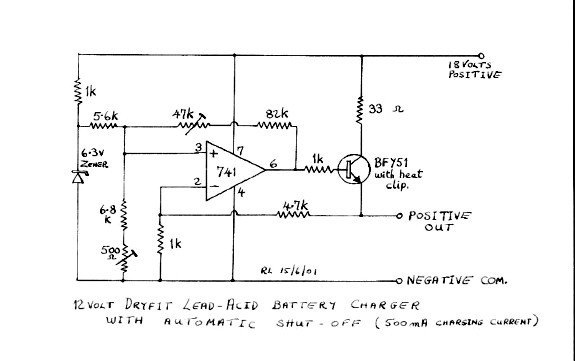
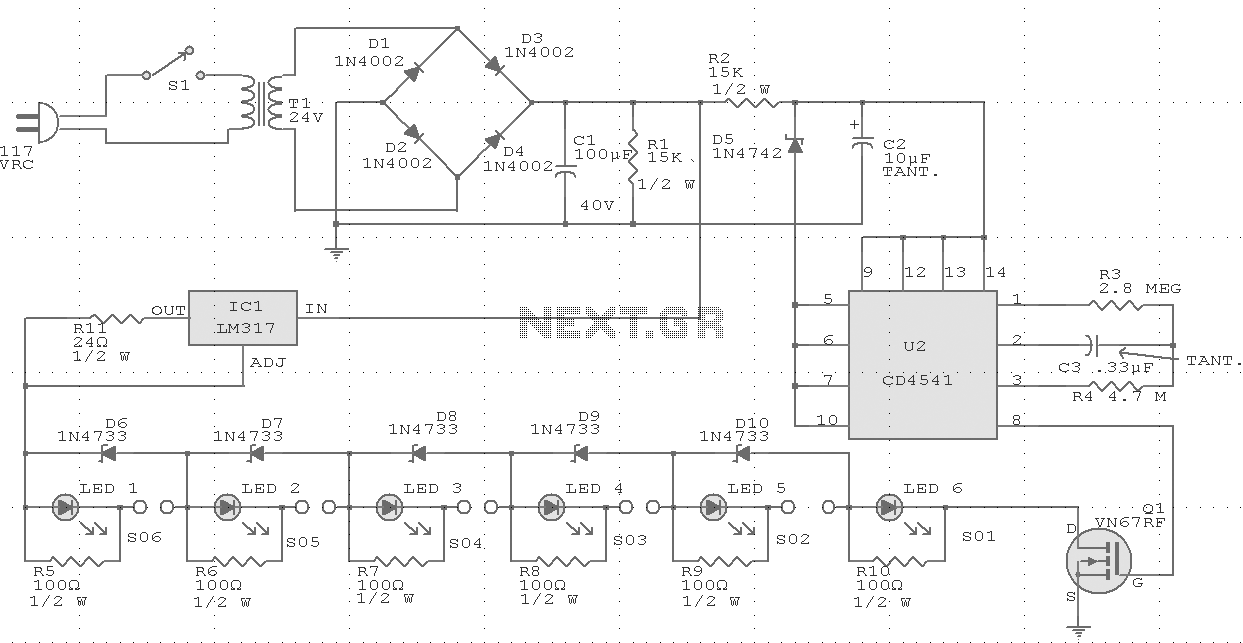
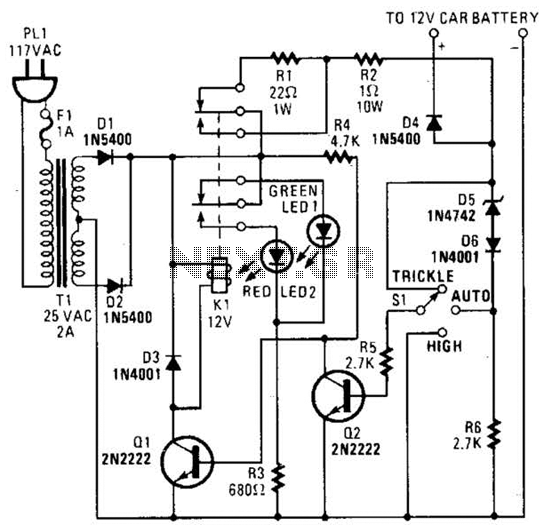
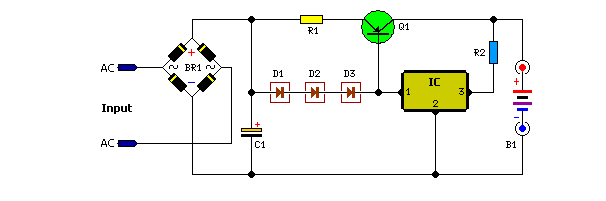
The circuit was constructed on a Vero board and tested with a large electrolytic capacitor in place of a battery. A 500-ohm preset resistor determines the output voltage, while a 47k preset resistor regulates the hysteresis and establishes the voltage threshold for reactivating the charger. This circuit operates in a cycle, turning on and off to maintain the battery charge without overcharging.
The described circuit utilizes a Vero board, a popular prototyping platform known for its simplicity in creating electronic circuits. The choice of a large electrolytic capacitor instead of a battery for testing purposes allows for observing the circuit's behavior without the risk of battery damage from incorrect charging conditions.
The 500-ohm preset resistor plays a crucial role in setting the output voltage of the circuit. By adjusting this resistor, the user can fine-tune the voltage level to meet the requirements of the connected load or battery. The output voltage is critical for ensuring that the connected device operates correctly and efficiently.
The 47k preset resistor is integral to the hysteresis control mechanism. Hysteresis is essential in preventing the circuit from rapidly toggling on and off around the threshold voltage, which could lead to instability. By setting a specific voltage at which the charger reactivates, the 47k resistor helps ensure that the battery remains charged without entering a state of overcharge. This feature is particularly important for prolonging battery life and maintaining optimal performance.
The cycling behavior of the circuit is indicative of a charge control system, which is designed to monitor battery voltage levels and adjust the charging state accordingly. When the voltage drops below a predetermined level, the circuit activates to recharge the battery. Once the battery reaches the desired voltage, the circuit deactivates, preventing overcharging. This on-off cycling continues, ensuring a consistent and safe charging process.
In conclusion, the described circuit is a well-designed solution for battery charging applications, featuring adjustable output voltage and hysteresis control to enhance performance and reliability. The use of a Vero board facilitates easy modifications and testing, making it suitable for prototyping and development purposes.The circuit was built on Vero board and tested using a large value electrolytic capacitor instead of a battery. The 500 ohm preset resistor sets the actual output voltage. The 47k preset controls the hysteresis and sets the voltage at which the charger switches on again. The circuit will cycle on and off and if correctly set will keep the b attery charged without overcharging it. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit utilizes a Vero board, a popular prototyping platform known for its simplicity in creating electronic circuits. The choice of a large electrolytic capacitor instead of a battery for testing purposes allows for observing the circuit's behavior without the risk of battery damage from incorrect charging conditions.
The 500-ohm preset resistor plays a crucial role in setting the output voltage of the circuit. By adjusting this resistor, the user can fine-tune the voltage level to meet the requirements of the connected load or battery. The output voltage is critical for ensuring that the connected device operates correctly and efficiently.
The 47k preset resistor is integral to the hysteresis control mechanism. Hysteresis is essential in preventing the circuit from rapidly toggling on and off around the threshold voltage, which could lead to instability. By setting a specific voltage at which the charger reactivates, the 47k resistor helps ensure that the battery remains charged without entering a state of overcharge. This feature is particularly important for prolonging battery life and maintaining optimal performance.
The cycling behavior of the circuit is indicative of a charge control system, which is designed to monitor battery voltage levels and adjust the charging state accordingly. When the voltage drops below a predetermined level, the circuit activates to recharge the battery. Once the battery reaches the desired voltage, the circuit deactivates, preventing overcharging. This on-off cycling continues, ensuring a consistent and safe charging process.
In conclusion, the described circuit is a well-designed solution for battery charging applications, featuring adjustable output voltage and hysteresis control to enhance performance and reliability. The use of a Vero board facilitates easy modifications and testing, making it suitable for prototyping and development purposes.The circuit was built on Vero board and tested using a large value electrolytic capacitor instead of a battery. The 500 ohm preset resistor sets the actual output voltage. The 47k preset controls the hysteresis and sets the voltage at which the charger switches on again. The circuit will cycle on and off and if correctly set will keep the b attery charged without overcharging it. 🔗 External reference