simple accu charger circuit
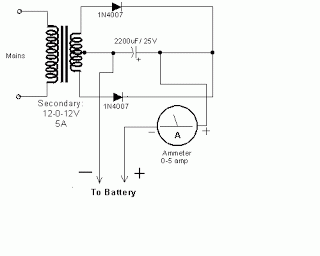
The Accu charger circuit is straightforward and simple to construct, requiring no more than ten components. In addition to its ease of assembly, this charger circuit is also cost-effective and highly efficient. The circuit requires a power supply from a transformer that steps down the 220V AC voltage to approximately 12-13 volts, which is then input into the circuit. The output of the circuit provides 12V DC, suitable for charging a 12V battery.
The Accu charger circuit's design typically includes a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, and a voltage regulator, along with additional components such as resistors and diodes to ensure proper operation. The transformer is essential for reducing the high voltage AC supply to a safer level suitable for charging batteries. The output from the transformer is then fed into a full-wave rectifier, which converts the AC voltage to DC voltage.
Following rectification, a smoothing capacitor is used to filter out any ripple in the DC output, resulting in a more stable voltage that can be used to charge the battery without causing damage. A voltage regulator may also be included to maintain a consistent output voltage, ensuring that the battery is charged efficiently and safely.
Additional components, such as protection diodes, can be added to prevent reverse polarity, which could potentially damage the circuit or the battery. The overall design emphasizes efficiency and simplicity, making it an ideal solution for basic battery charging needs. This circuit is particularly suitable for applications where cost and ease of use are critical, such as in small battery-operated devices or backup power supplies.The Accu charger circuit is very simple and easy to make, because it only requires a few components are also not more than 10 components. Besides easy charger circuit is also very cheap and very efficient. This circuit requires power supply from a transformer that comes from an AC voltage 220 and diuturunkan be 12-13 volts and then enter to-circuit an
d 12 Volt DC output allows for charging 12V battery 🔗 External reference
The Accu charger circuit's design typically includes a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, and a voltage regulator, along with additional components such as resistors and diodes to ensure proper operation. The transformer is essential for reducing the high voltage AC supply to a safer level suitable for charging batteries. The output from the transformer is then fed into a full-wave rectifier, which converts the AC voltage to DC voltage.
Following rectification, a smoothing capacitor is used to filter out any ripple in the DC output, resulting in a more stable voltage that can be used to charge the battery without causing damage. A voltage regulator may also be included to maintain a consistent output voltage, ensuring that the battery is charged efficiently and safely.
Additional components, such as protection diodes, can be added to prevent reverse polarity, which could potentially damage the circuit or the battery. The overall design emphasizes efficiency and simplicity, making it an ideal solution for basic battery charging needs. This circuit is particularly suitable for applications where cost and ease of use are critical, such as in small battery-operated devices or backup power supplies.The Accu charger circuit is very simple and easy to make, because it only requires a few components are also not more than 10 components. Besides easy charger circuit is also very cheap and very efficient. This circuit requires power supply from a transformer that comes from an AC voltage 220 and diuturunkan be 12-13 volts and then enter to-circuit an
d 12 Volt DC output allows for charging 12V battery 🔗 External reference