Check the three-phase motor with broken bars
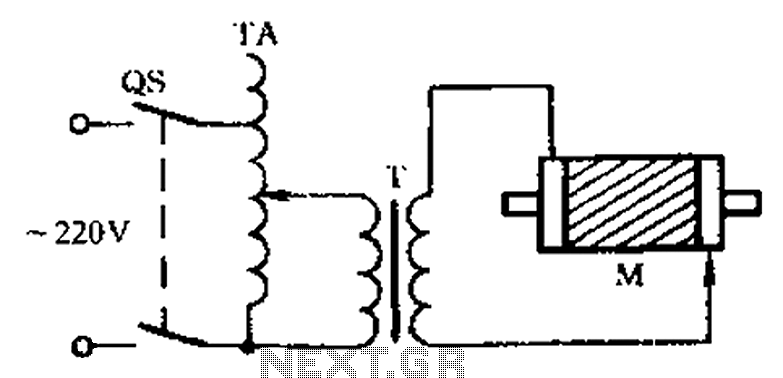
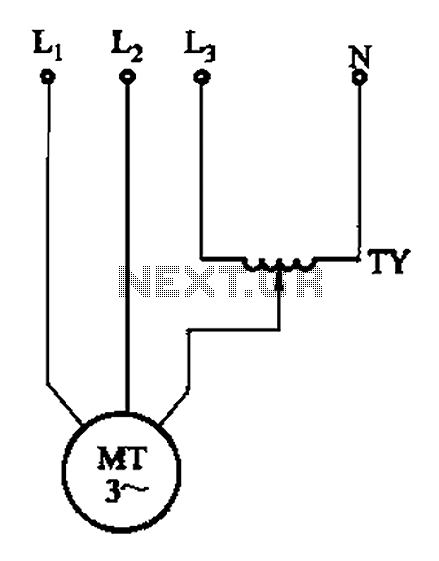
The circuit diagram illustrates a three-phase motor equipped with an inspection circuit designed to detect broken bars.
The circuit for a three-phase motor with a broken bar inspection system typically consists of several key components that work together to monitor the health of the motor's rotor. The inspection circuit is crucial for identifying faults that could lead to reduced efficiency or catastrophic failure.
In this setup, the three-phase motor is powered by a three-phase supply, which provides the necessary torque and speed for operation. The inspection circuit includes current sensors placed in each phase line to monitor the current flowing through the motor. These sensors can be Hall effect sensors or current transformers, which provide real-time feedback on the electrical conditions of the motor.
The output from the current sensors is fed into a microcontroller or a dedicated monitoring unit. This unit processes the signals and compares the current readings against predefined thresholds. If the current in any phase deviates significantly from the expected value, it may indicate a broken bar in the rotor. The microcontroller can then trigger an alarm or an indicator light to alert maintenance personnel of the potential issue.
Additional components in the circuit may include resistors for signal conditioning, capacitors for noise filtering, and possibly an interface for communication with a supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system. The design must ensure that the inspection circuit is robust enough to operate under the motor's environmental conditions, which may include vibrations and temperature fluctuations.
In summary, the three-phase motor with a broken bar inspection circuit is an essential system for ensuring reliable motor operation, minimizing downtime, and enhancing overall maintenance practices. As shown in the three-phase motor with broken bars of inspection circuit:
The circuit for a three-phase motor with a broken bar inspection system typically consists of several key components that work together to monitor the health of the motor's rotor. The inspection circuit is crucial for identifying faults that could lead to reduced efficiency or catastrophic failure.
In this setup, the three-phase motor is powered by a three-phase supply, which provides the necessary torque and speed for operation. The inspection circuit includes current sensors placed in each phase line to monitor the current flowing through the motor. These sensors can be Hall effect sensors or current transformers, which provide real-time feedback on the electrical conditions of the motor.
The output from the current sensors is fed into a microcontroller or a dedicated monitoring unit. This unit processes the signals and compares the current readings against predefined thresholds. If the current in any phase deviates significantly from the expected value, it may indicate a broken bar in the rotor. The microcontroller can then trigger an alarm or an indicator light to alert maintenance personnel of the potential issue.
Additional components in the circuit may include resistors for signal conditioning, capacitors for noise filtering, and possibly an interface for communication with a supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system. The design must ensure that the inspection circuit is robust enough to operate under the motor's environmental conditions, which may include vibrations and temperature fluctuations.
In summary, the three-phase motor with a broken bar inspection circuit is an essential system for ensuring reliable motor operation, minimizing downtime, and enhancing overall maintenance practices. As shown in the three-phase motor with broken bars of inspection circuit: