Bicolour LED flasher circuit
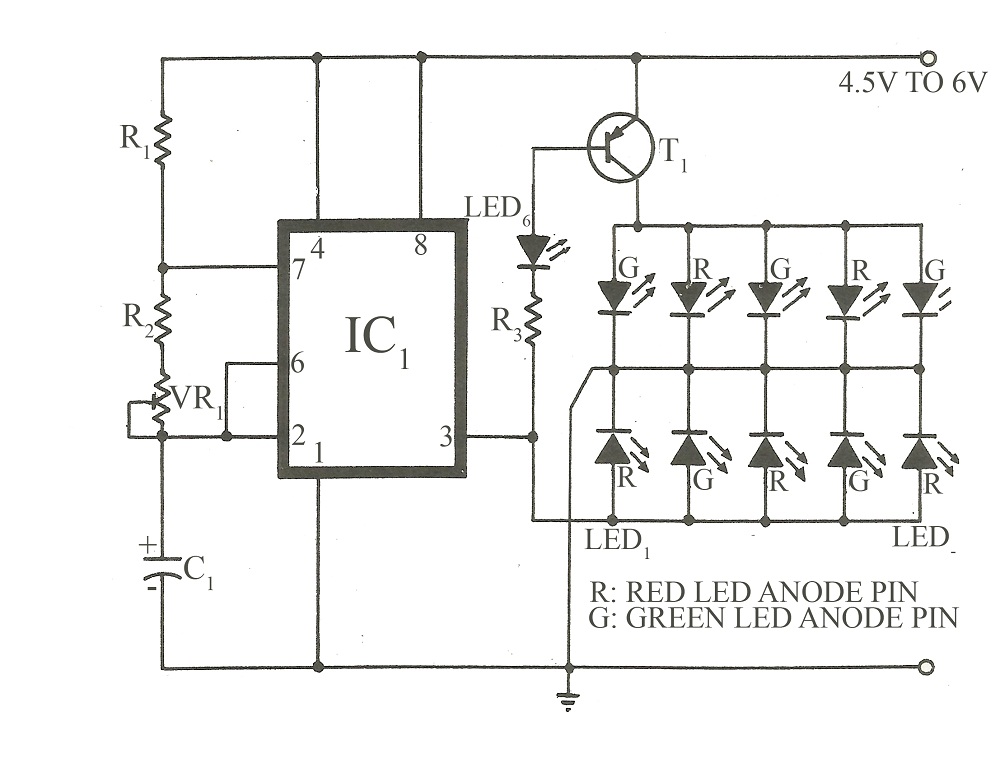
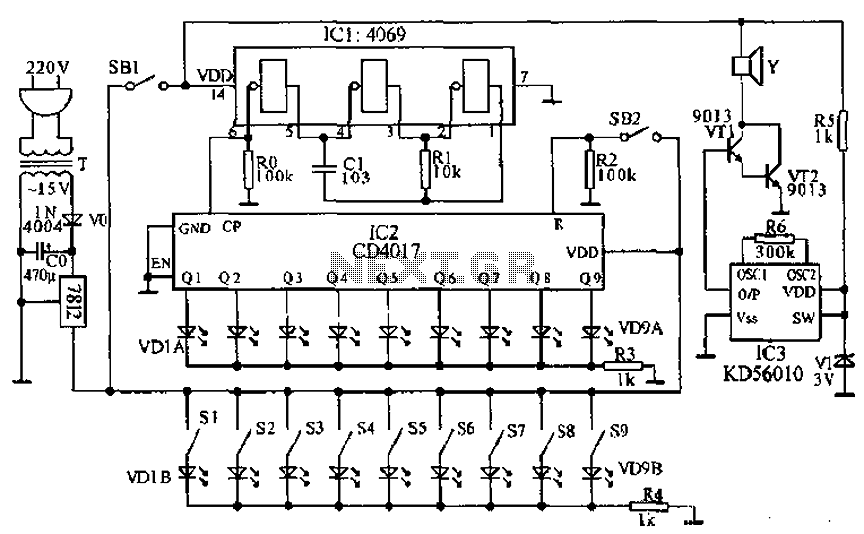
This circuit is similar to various published flasher circuits that utilize the IC 555 as a free-running multivibrator. The primary distinction is in the method of flashing bi-color LEDs. When the output at pin 3 of the IC 555 goes high, it activates one group of LEDs. By inverting the low output of the IC using a PNP transistor (BC558), another group of LEDs is made to flash. As illustrated in the circuit diagram, the LEDs are arranged in an alternately reversed order, creating a "twinkle twinkle little stars" effect. The 100K preset VR1 adjusts the blinking rate. For simplicity, a current-limiting resistor has been omitted, which may result in the red and green LEDs flashing with different intensities due to their varying threshold voltages.
The described circuit employs the widely used 555 timer IC configured in astable mode, which allows it to produce a continuous square wave output. The configuration includes a timing resistor connected to pin 7 (discharge) and a timing capacitor connected to pin 6 (threshold), which together determine the frequency of the output signal. The output at pin 3 alternates between high and low states, controlling the activation of the LEDs.
In this specific design, the bi-color LEDs are arranged in a manner that enhances the visual effect. When the output from the 555 timer is high, one color of the LEDs illuminates, while the PNP transistor BC558 is triggered to allow the other color to flash when the output is low. This arrangement creates a visually appealing alternation between colors.
The inclusion of a 100K variable resistor (VR1) allows for adjustment of the blinking rate, providing flexibility in the timing of the LED flashes. The absence of current-limiting resistors simplifies the circuit but introduces a risk of unequal brightness between the red and green LEDs. Each LED type has a different forward voltage drop, which can lead to one color appearing brighter than the other during operation.
Overall, this circuit is an effective and simple design for creating an eye-catching LED flashing effect, suitable for decorative lighting or signaling applications. The use of the 555 timer ensures reliability and ease of implementation, making it accessible for hobbyists and educators alike.Basically this circuit is similar to some flasher circuits already published in using IC555 as a free running multivibrator. The only difference lies in the way it flash using bi-colour LEDs. When output at pin 3 of IC 555 goes high it operates on group of LEDs. By inverting the IC`s low output by pnp transistor BC558 the other group of LEDs is m ade to flash. AS shown in circuit diagram the LEDs are arranged in alternately reversed order so that a twinkle twinkle little stars effect is produced. The 100K preset VR1 sets the blinking rate. To maintain simplicity I omitted the current limiting resistor. So, the red and green LEDs may not flash with equal intensity (as they require different threshold voltage).
🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs the widely used 555 timer IC configured in astable mode, which allows it to produce a continuous square wave output. The configuration includes a timing resistor connected to pin 7 (discharge) and a timing capacitor connected to pin 6 (threshold), which together determine the frequency of the output signal. The output at pin 3 alternates between high and low states, controlling the activation of the LEDs.
In this specific design, the bi-color LEDs are arranged in a manner that enhances the visual effect. When the output from the 555 timer is high, one color of the LEDs illuminates, while the PNP transistor BC558 is triggered to allow the other color to flash when the output is low. This arrangement creates a visually appealing alternation between colors.
The inclusion of a 100K variable resistor (VR1) allows for adjustment of the blinking rate, providing flexibility in the timing of the LED flashes. The absence of current-limiting resistors simplifies the circuit but introduces a risk of unequal brightness between the red and green LEDs. Each LED type has a different forward voltage drop, which can lead to one color appearing brighter than the other during operation.
Overall, this circuit is an effective and simple design for creating an eye-catching LED flashing effect, suitable for decorative lighting or signaling applications. The use of the 555 timer ensures reliability and ease of implementation, making it accessible for hobbyists and educators alike.Basically this circuit is similar to some flasher circuits already published in using IC555 as a free running multivibrator. The only difference lies in the way it flash using bi-colour LEDs. When output at pin 3 of IC 555 goes high it operates on group of LEDs. By inverting the IC`s low output by pnp transistor BC558 the other group of LEDs is m ade to flash. AS shown in circuit diagram the LEDs are arranged in alternately reversed order so that a twinkle twinkle little stars effect is produced. The 100K preset VR1 sets the blinking rate. To maintain simplicity I omitted the current limiting resistor. So, the red and green LEDs may not flash with equal intensity (as they require different threshold voltage).
🔗 External reference