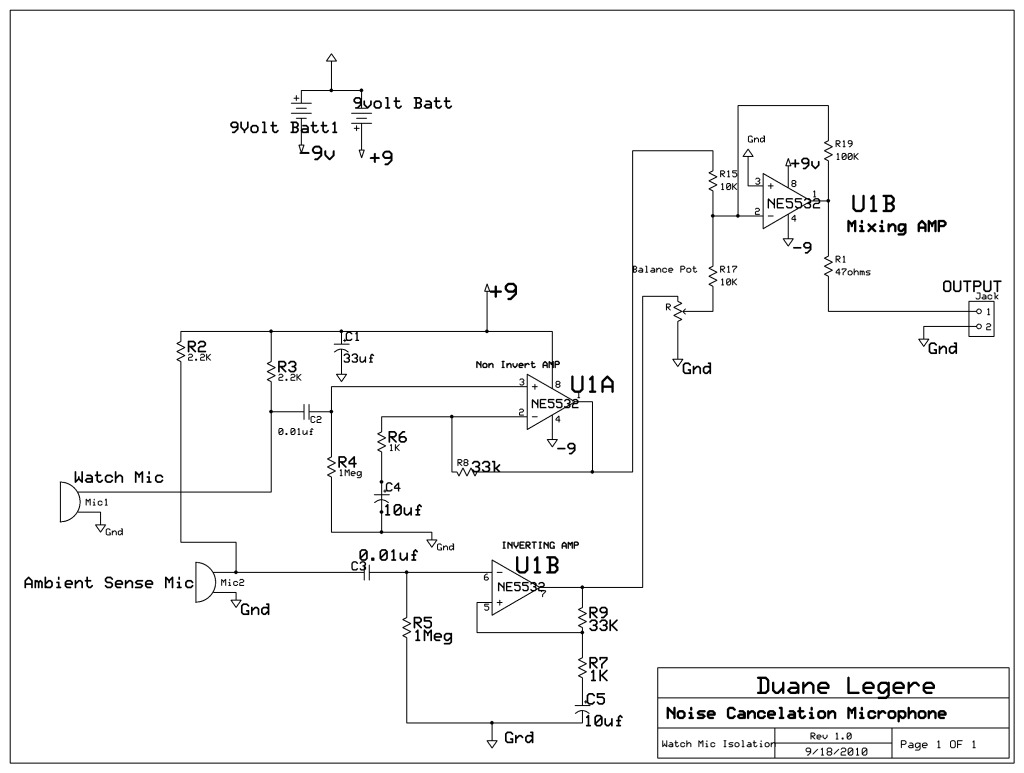
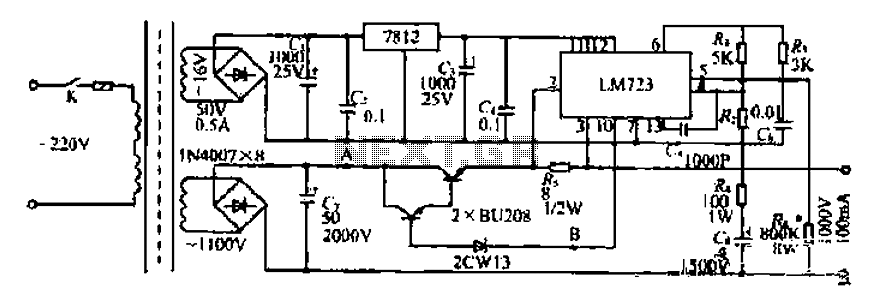
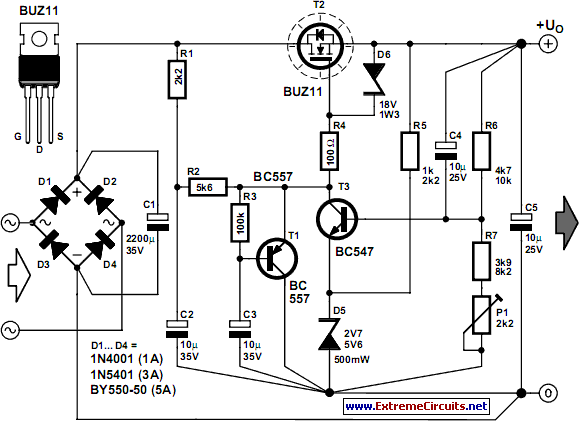
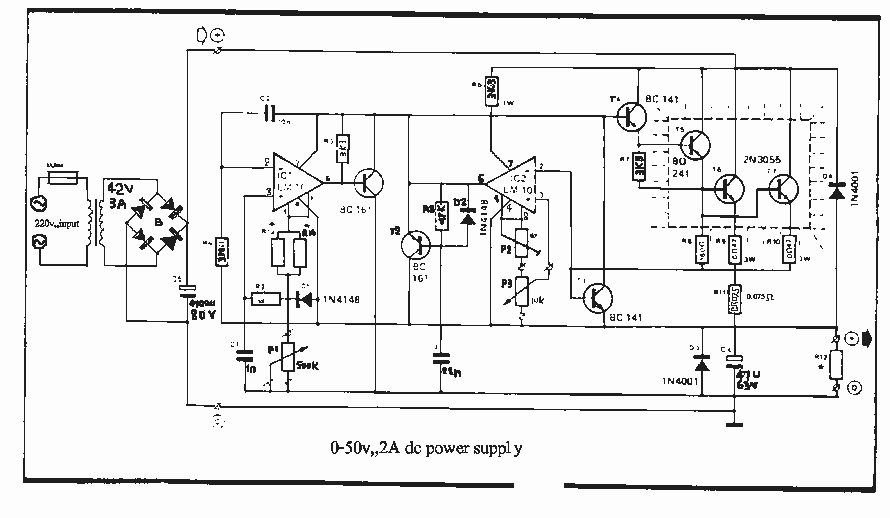
DC fan control circuit for power amplifier Schematic Diagram
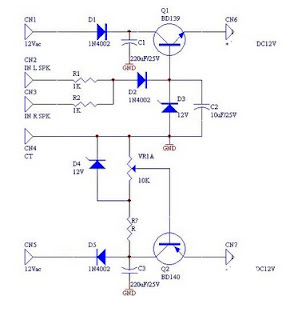
DC fan control circuit for a power amplifier. It features a variable speed DC fan that operates based on the input signal. The speed of the fan's rotation is dependent on the amplitude of the input signal received from the speaker lines. In the absence of a signal, the fan will operate at a slow speed determined by the setting of variable resistor VR1. The input power can be directly sourced from the main transformer, which has a 12V center-tapped configuration, eliminating the need for an additional transformer.
The DC fan control circuit is designed to enhance the cooling efficiency of power amplifiers by modulating the fan speed according to the audio signal levels. The circuit utilizes a variable resistor (VR1) to set a minimum fan speed, ensuring that the fan operates even when there is no significant audio signal, thereby preventing overheating of the amplifier components.
The circuit typically consists of a transistor or operational amplifier configured to sense the input signal from the amplifier's speaker output. As the input signal increases, the transistor or operational amplifier adjusts the voltage applied to the fan, thereby increasing its speed. This response allows for a dynamic cooling solution that adapts to the thermal requirements of the amplifier, improving performance and reliability.
The power supply for this circuit is conveniently derived from the existing transformer used in the amplifier, which provides a 12V center-tapped output. This design choice simplifies the overall circuit layout and reduces component count, making it an efficient solution for integrating fan control into power amplifier systems.
In summary, the DC fan control circuit for a power amplifier is an essential component that not only ensures optimal thermal management but also contributes to the longevity and performance of the audio equipment.DC fan control circuit for power amplifier. Variable speed DC fan This series of works based on the input signal. Speed / fan rotation depending on size of the input signal coming from speaker lines. If there is no signal then the fan will spin slowly according to the setting VR1. Input supply can be taken directly from the main transformer power amplifier, 12V CT 12V, so no need to increase the transformer again. You are reading the Circuits of DC fan control circuit for power amplifier And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference
The DC fan control circuit is designed to enhance the cooling efficiency of power amplifiers by modulating the fan speed according to the audio signal levels. The circuit utilizes a variable resistor (VR1) to set a minimum fan speed, ensuring that the fan operates even when there is no significant audio signal, thereby preventing overheating of the amplifier components.
The circuit typically consists of a transistor or operational amplifier configured to sense the input signal from the amplifier's speaker output. As the input signal increases, the transistor or operational amplifier adjusts the voltage applied to the fan, thereby increasing its speed. This response allows for a dynamic cooling solution that adapts to the thermal requirements of the amplifier, improving performance and reliability.
The power supply for this circuit is conveniently derived from the existing transformer used in the amplifier, which provides a 12V center-tapped output. This design choice simplifies the overall circuit layout and reduces component count, making it an efficient solution for integrating fan control into power amplifier systems.
In summary, the DC fan control circuit for a power amplifier is an essential component that not only ensures optimal thermal management but also contributes to the longevity and performance of the audio equipment.DC fan control circuit for power amplifier. Variable speed DC fan This series of works based on the input signal. Speed / fan rotation depending on size of the input signal coming from speaker lines. If there is no signal then the fan will spin slowly according to the setting VR1. Input supply can be taken directly from the main transformer power amplifier, 12V CT 12V, so no need to increase the transformer again. You are reading the Circuits of DC fan control circuit for power amplifier And this circuit permalink url it is 🔗 External reference