PCB designing using KiCAD Tutorial

This is a brief guide to help users begin with KiCAD. The tutorial focuses on a simple astable multivibrator circuit utilizing the 555 timer IC.
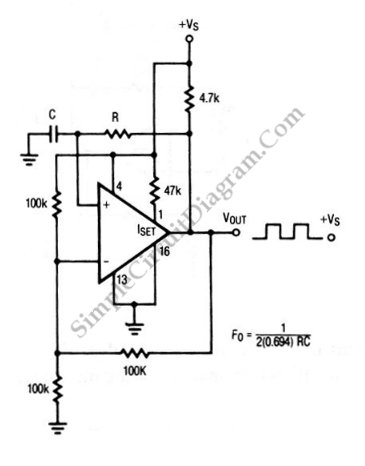
The astable multivibrator circuit using the 555 timer IC is a fundamental electronic configuration that generates a continuous square wave output without requiring any external triggering. The 555 timer, a versatile integrated circuit, can be configured in various modes, and the astable mode is particularly useful for applications such as clock pulses, LED flashers, and tone generation.
In the astable configuration, the 555 timer operates between two states: high and low, continuously switching between them at a frequency determined by external resistors and capacitors. The circuit typically includes two resistors, R1 and R2, and a capacitor, C1, connected to the 555 timer in the following manner:
1. **Connections**:
- Pin 1 (GND) is connected to the ground.
- Pin 8 (VCC) is connected to the positive supply voltage, typically between 4.5V to 15V.
- Pin 2 (Trigger) and Pin 6 (Threshold) are connected together and also connected to the junction of R2 and C1.
- Pin 3 (Output) provides the square wave output.
- Pin 4 (Reset) is connected to VCC to disable the reset functionality.
- Pin 5 (Control Voltage) is often connected to ground through a capacitor (typically 0.01 µF) to filter noise.
- Pin 7 (Discharge) is connected to the junction of R1 and R2.
2. **Operation**:
- When power is applied, C1 begins charging through R1 and R2. The voltage across C1 increases until it reaches 2/3 of VCC, at which point the 555 timer switches its output to low, causing C1 to discharge through R2 and pin 7 until it drops below 1/3 of VCC. This cycle repeats, generating a continuous square wave.
3. **Frequency Calculation**:
- The frequency (f) of the output square wave can be calculated using the formula:
\[
f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \times C1}
\]
- The duty cycle, which determines the ratio of the high state to the total period, can also be calculated, typically resulting in a duty cycle less than 50% due to the configuration of the resistors.
This simple astable multivibrator circuit demonstrates the basic principles of timing and oscillation in electronics, providing a practical application for the 555 timer IC in various projects.Here is a quick guide, which will help you to get started off with kiCAD. In this tutorial we will be considering a simple astable multivibrator circuit using 555 timer IC 🔗 External reference
The astable multivibrator circuit using the 555 timer IC is a fundamental electronic configuration that generates a continuous square wave output without requiring any external triggering. The 555 timer, a versatile integrated circuit, can be configured in various modes, and the astable mode is particularly useful for applications such as clock pulses, LED flashers, and tone generation.
In the astable configuration, the 555 timer operates between two states: high and low, continuously switching between them at a frequency determined by external resistors and capacitors. The circuit typically includes two resistors, R1 and R2, and a capacitor, C1, connected to the 555 timer in the following manner:
1. **Connections**:
- Pin 1 (GND) is connected to the ground.
- Pin 8 (VCC) is connected to the positive supply voltage, typically between 4.5V to 15V.
- Pin 2 (Trigger) and Pin 6 (Threshold) are connected together and also connected to the junction of R2 and C1.
- Pin 3 (Output) provides the square wave output.
- Pin 4 (Reset) is connected to VCC to disable the reset functionality.
- Pin 5 (Control Voltage) is often connected to ground through a capacitor (typically 0.01 µF) to filter noise.
- Pin 7 (Discharge) is connected to the junction of R1 and R2.
2. **Operation**:
- When power is applied, C1 begins charging through R1 and R2. The voltage across C1 increases until it reaches 2/3 of VCC, at which point the 555 timer switches its output to low, causing C1 to discharge through R2 and pin 7 until it drops below 1/3 of VCC. This cycle repeats, generating a continuous square wave.
3. **Frequency Calculation**:
- The frequency (f) of the output square wave can be calculated using the formula:
\[
f = \frac{1.44}{(R1 + 2R2) \times C1}
\]
- The duty cycle, which determines the ratio of the high state to the total period, can also be calculated, typically resulting in a duty cycle less than 50% due to the configuration of the resistors.
This simple astable multivibrator circuit demonstrates the basic principles of timing and oscillation in electronics, providing a practical application for the 555 timer IC in various projects.Here is a quick guide, which will help you to get started off with kiCAD. In this tutorial we will be considering a simple astable multivibrator circuit using 555 timer IC 🔗 External reference