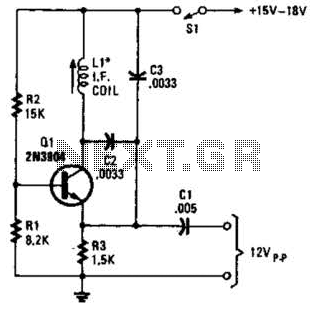
Square Wave Oscillator using Comparator/Op-Amp
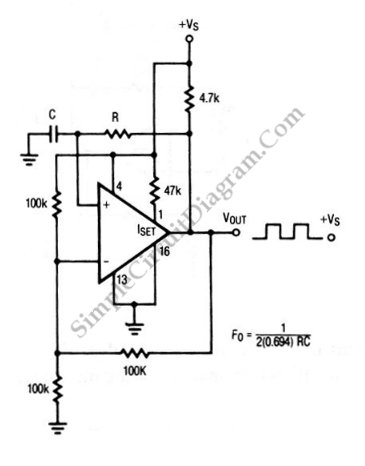
The circuit depicted in this schematic diagram is a square-wave oscillator circuit. The primary component of this oscillator circuit is the LP165/365 comparator.
The square-wave oscillator circuit utilizes the LP165/365 comparator to generate a continuous square wave output. The operation of this circuit relies on the feedback mechanism that establishes a stable oscillation frequency. The comparator serves as the central element, comparing two input voltages: a reference voltage and the voltage derived from the output through a resistor-capacitor (RC) network.
In typical configurations, the circuit includes a resistor (R) and capacitor (C) connected in series, which determines the timing characteristics of the oscillation. The charging and discharging of the capacitor through the resistor create a time delay that influences the frequency of the output waveform. The output of the comparator toggles between high and low states as the voltage across the capacitor reaches the threshold levels set by the reference voltage.
The frequency of oscillation can be calculated using the formula \( f = \frac{1}{T} \), where \( T \) is the time period of one complete cycle. The time period is influenced by the values of the resistor and capacitor, and it can be adjusted to achieve the desired frequency. The output waveform is typically a symmetrical square wave, characterized by equal high and low durations.
For practical applications, additional components such as diodes or additional comparators may be incorporated to shape the waveform or enhance stability. The design may also include provisions for power supply decoupling to ensure reliable operation in various environments. Overall, the square-wave oscillator circuit based on the LP165/365 comparator is a versatile and widely used configuration in various electronic applications, including clock generation, signal modulation, and waveform generation.The circuit shown in this schematic diagram is a square-wave oscillator circuit. The main component of this oscillator circuit is LP165/365 comparator. As.. 🔗 External reference
The square-wave oscillator circuit utilizes the LP165/365 comparator to generate a continuous square wave output. The operation of this circuit relies on the feedback mechanism that establishes a stable oscillation frequency. The comparator serves as the central element, comparing two input voltages: a reference voltage and the voltage derived from the output through a resistor-capacitor (RC) network.
In typical configurations, the circuit includes a resistor (R) and capacitor (C) connected in series, which determines the timing characteristics of the oscillation. The charging and discharging of the capacitor through the resistor create a time delay that influences the frequency of the output waveform. The output of the comparator toggles between high and low states as the voltage across the capacitor reaches the threshold levels set by the reference voltage.
The frequency of oscillation can be calculated using the formula \( f = \frac{1}{T} \), where \( T \) is the time period of one complete cycle. The time period is influenced by the values of the resistor and capacitor, and it can be adjusted to achieve the desired frequency. The output waveform is typically a symmetrical square wave, characterized by equal high and low durations.
For practical applications, additional components such as diodes or additional comparators may be incorporated to shape the waveform or enhance stability. The design may also include provisions for power supply decoupling to ensure reliable operation in various environments. Overall, the square-wave oscillator circuit based on the LP165/365 comparator is a versatile and widely used configuration in various electronic applications, including clock generation, signal modulation, and waveform generation.The circuit shown in this schematic diagram is a square-wave oscillator circuit. The main component of this oscillator circuit is LP165/365 comparator. As.. 🔗 External reference