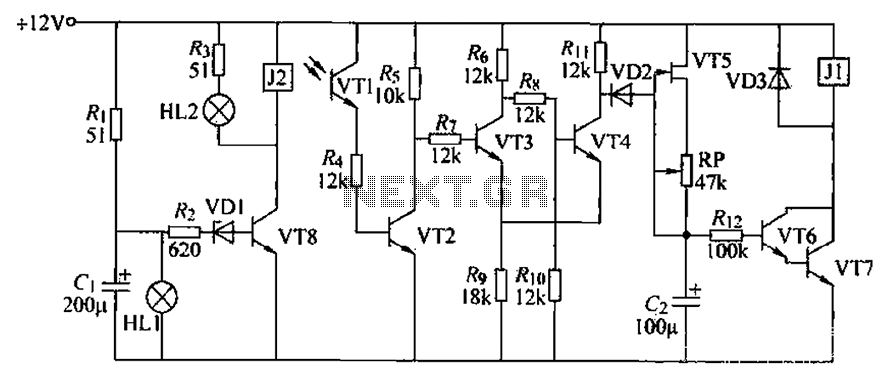
Passive tone control circuit
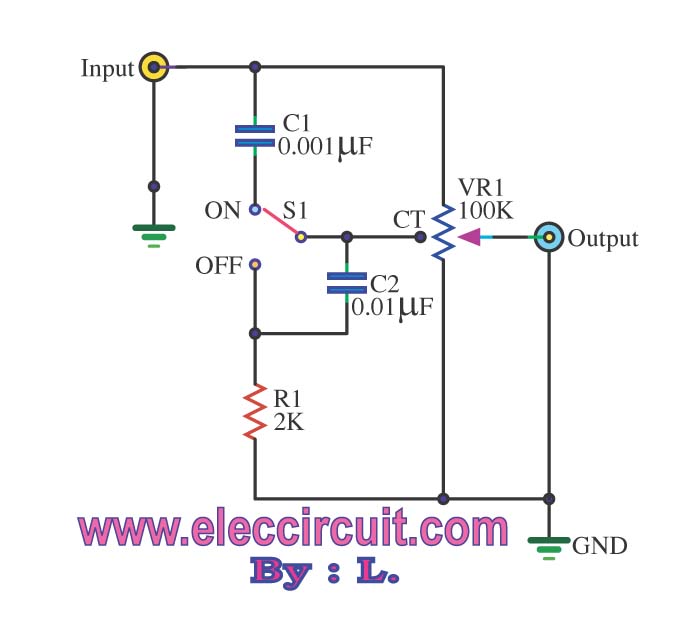
The passive tone control circuit is designed to adjust the bass without expansion, utilizing resistors (R) and capacitors (C). It functions as a frequency filter and is easy to construct, requiring no external power supply. This circuit can be connected directly to the output of a power amplifier. When an input sound signal is received, the circuit separates it into two pathways. The first pathway alters low frequencies using components such as R1, C1, C2, and R2, with VR1 allowing fine adjustment of the low-frequency range. The second pathway processes high frequencies through components like C4, R5, and C5, with VR2 enabling fine-tuning of the treble frequencies. The outputs from both frequency filters are combined through R3 and R4, while C3 serves to eliminate noise from the output.
The passive tone control circuit is an essential component in audio signal processing, allowing users to tailor the sound characteristics of an audio system. This circuit utilizes a straightforward design that leverages passive components, making it cost-effective and easy to implement.
The low-frequency filter pathway consists of R1 and C1, which form a first-order low-pass filter. The resistor R2 is connected in series to provide a variable resistance that can be adjusted using the variable resistor VR1. This arrangement allows for the attenuation of high-frequency signals, enabling the user to enhance the bass response of the audio output. The values of R1, C1, and R2 can be selected based on the desired cutoff frequency, which determines the range of frequencies that will be affected by the adjustment.
In the high-frequency filter pathway, components C4, R5, and C5 form a first-order high-pass filter. Similar to the low-frequency pathway, VR2 is used to vary the resistance of R5, allowing for fine adjustments to the treble frequencies. The interaction between C4 and R5 dictates the cutoff frequency for the high-pass filter, enabling the user to boost or reduce the presence of higher frequency sounds.
The final output of the circuit is achieved by combining the outputs from both filters through R3 and R4. This configuration ensures that the modifications made to both low and high frequencies are preserved in the final audio signal. Additionally, C3 plays a crucial role in filtering out unwanted noise, enhancing the overall quality of the audio output.
In summary, the passive tone control circuit is a valuable tool for audio enthusiasts and engineers, providing an effective means of shaping sound quality without the need for complex power supplies or active components. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice for various audio applications, from home audio systems to professional sound equipment.The Passive tone control circuit be the circuit fines the bass that has no the expansion but will give kind equipment R and C. It perform filter frequency then the circuit that build easy and must not use power supply. By can concede the porch with part power amplifier of output immediately. When feed input come in sound signal will that come in t o separate is 2 the way by first way will change to come to a part filters low frequency for example R1, C1, C2, R2. By have VR1 be formed fine expansion way ratio low frequency is or sound in the sense of second a signal will change to come to a part filters tall frequency for example C4, R5, C5 by have VR2 be formed fine the value of tall frequency or treble a signal that depart a part filter tall frequency and low change R3 and R4 congregate then go out still output.
By have C3 perform eradicate the noise goes out. 🔗 External reference
The passive tone control circuit is an essential component in audio signal processing, allowing users to tailor the sound characteristics of an audio system. This circuit utilizes a straightforward design that leverages passive components, making it cost-effective and easy to implement.
The low-frequency filter pathway consists of R1 and C1, which form a first-order low-pass filter. The resistor R2 is connected in series to provide a variable resistance that can be adjusted using the variable resistor VR1. This arrangement allows for the attenuation of high-frequency signals, enabling the user to enhance the bass response of the audio output. The values of R1, C1, and R2 can be selected based on the desired cutoff frequency, which determines the range of frequencies that will be affected by the adjustment.
In the high-frequency filter pathway, components C4, R5, and C5 form a first-order high-pass filter. Similar to the low-frequency pathway, VR2 is used to vary the resistance of R5, allowing for fine adjustments to the treble frequencies. The interaction between C4 and R5 dictates the cutoff frequency for the high-pass filter, enabling the user to boost or reduce the presence of higher frequency sounds.
The final output of the circuit is achieved by combining the outputs from both filters through R3 and R4. This configuration ensures that the modifications made to both low and high frequencies are preserved in the final audio signal. Additionally, C3 plays a crucial role in filtering out unwanted noise, enhancing the overall quality of the audio output.
In summary, the passive tone control circuit is a valuable tool for audio enthusiasts and engineers, providing an effective means of shaping sound quality without the need for complex power supplies or active components. Its simplicity and effectiveness make it a popular choice for various audio applications, from home audio systems to professional sound equipment.The Passive tone control circuit be the circuit fines the bass that has no the expansion but will give kind equipment R and C. It perform filter frequency then the circuit that build easy and must not use power supply. By can concede the porch with part power amplifier of output immediately. When feed input come in sound signal will that come in t o separate is 2 the way by first way will change to come to a part filters low frequency for example R1, C1, C2, R2. By have VR1 be formed fine expansion way ratio low frequency is or sound in the sense of second a signal will change to come to a part filters tall frequency for example C4, R5, C5 by have VR2 be formed fine the value of tall frequency or treble a signal that depart a part filter tall frequency and low change R3 and R4 congregate then go out still output.
By have C3 perform eradicate the noise goes out. 🔗 External reference