Radio-controlled toy car
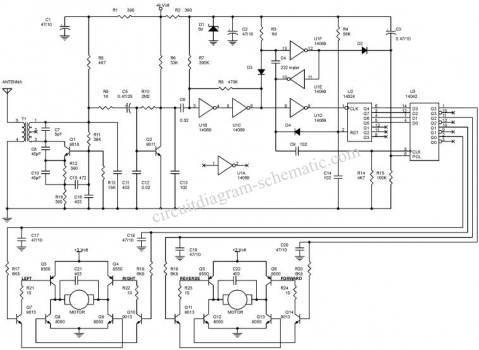
This circuit diagram represents a radio-controlled system, commonly utilized in toy car applications for children. The circuit comprises two main components: the transmitter and the receiver circuits. The transmitter circuit generates radio signals through an oscillator circuit built with transistor Q1 (9016). The operating frequency of this oscillator is determined by the crystal Y1, which is rated at 27.145 MHz. A critical aspect of this oscillator circuit includes components T1, L1, and L2, which will be discussed in detail later.
The transmitter circuit begins with the oscillator, which is responsible for generating a stable radio frequency signal. Transistor Q1 (9016) functions as the main active device in this oscillator configuration, providing the necessary gain and switching capabilities. The frequency of oscillation is finely tuned by the crystal Y1, ensuring that the emitted signals remain within the designated frequency band for radio communication.
The oscillator's performance is significantly influenced by the inductor components L1 and L2, which are carefully selected to resonate with the crystal frequency. These inductors, in conjunction with T1, form a tank circuit that is essential for maintaining the stability and purity of the oscillation. The design must ensure minimal distortion and a clean signal output, which is crucial for effective communication between the transmitter and receiver.
The receiver circuit is designed to capture the radio signals transmitted by the oscillator. It typically includes an RF amplifier to boost the received signal strength, followed by a demodulator that extracts the original control signals from the modulated carrier wave. The receiver's performance is equally critical, as it must effectively filter out noise and interference while maintaining the integrity of the control commands sent to the toy car.
The entire system is powered by a suitable DC power source, which must be regulated to ensure consistent operation of both the transmitter and receiver circuits. Proper grounding and shielding techniques should also be implemented to minimize electromagnetic interference, which can adversely affect the performance of the circuit.
Overall, this radio-controlled circuit diagram is a fundamental representation of how toy cars can be remotely operated, showcasing the essential components and their roles in the transmission and reception of radio signals. Understanding each part's function and interaction is vital for troubleshooting and enhancing the circuit's performance in practical applications.This circuit is a circuit diagram of the radio-controlled, usually in the toy car application children. Circuit diagram consists of 2 parts of the circuit sender and receiver circuits. To the circuit sending radio signals generated by the oscillator circuit formed by transistors Q1 9016, operating frequency of the oscillator is determined by the crystal Y1 is worth 27.145 MHz.
A very critical part of this oscillator circuit is T1, L1 and L2, which specifically discussed separately at the end of. 🔗 External reference
The transmitter circuit begins with the oscillator, which is responsible for generating a stable radio frequency signal. Transistor Q1 (9016) functions as the main active device in this oscillator configuration, providing the necessary gain and switching capabilities. The frequency of oscillation is finely tuned by the crystal Y1, ensuring that the emitted signals remain within the designated frequency band for radio communication.
The oscillator's performance is significantly influenced by the inductor components L1 and L2, which are carefully selected to resonate with the crystal frequency. These inductors, in conjunction with T1, form a tank circuit that is essential for maintaining the stability and purity of the oscillation. The design must ensure minimal distortion and a clean signal output, which is crucial for effective communication between the transmitter and receiver.
The receiver circuit is designed to capture the radio signals transmitted by the oscillator. It typically includes an RF amplifier to boost the received signal strength, followed by a demodulator that extracts the original control signals from the modulated carrier wave. The receiver's performance is equally critical, as it must effectively filter out noise and interference while maintaining the integrity of the control commands sent to the toy car.
The entire system is powered by a suitable DC power source, which must be regulated to ensure consistent operation of both the transmitter and receiver circuits. Proper grounding and shielding techniques should also be implemented to minimize electromagnetic interference, which can adversely affect the performance of the circuit.
Overall, this radio-controlled circuit diagram is a fundamental representation of how toy cars can be remotely operated, showcasing the essential components and their roles in the transmission and reception of radio signals. Understanding each part's function and interaction is vital for troubleshooting and enhancing the circuit's performance in practical applications.This circuit is a circuit diagram of the radio-controlled, usually in the toy car application children. Circuit diagram consists of 2 parts of the circuit sender and receiver circuits. To the circuit sending radio signals generated by the oscillator circuit formed by transistors Q1 9016, operating frequency of the oscillator is determined by the crystal Y1 is worth 27.145 MHz.
A very critical part of this oscillator circuit is T1, L1 and L2, which specifically discussed separately at the end of. 🔗 External reference