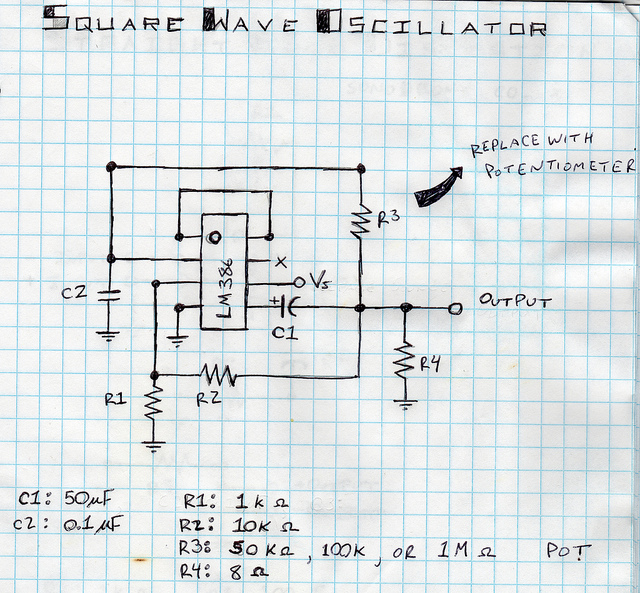
Sawtooth Wave Generator
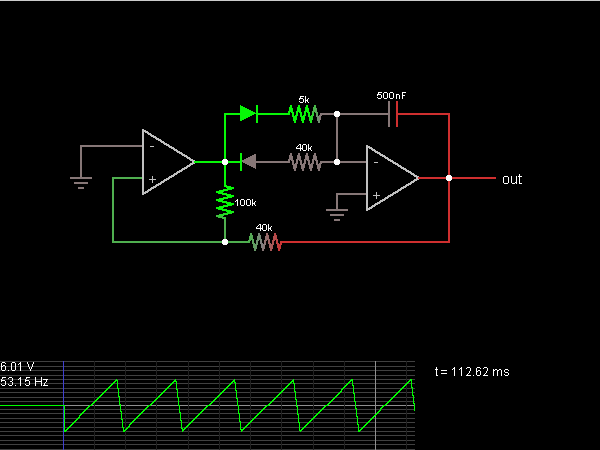
This is the sawtooth wave generator circuit diagram, accompanied by a detailed explanation of its operational principles. An electronic circuit simulator is available to assist in designing the sawtooth wave generator circuit and simulating it online for enhanced understanding.
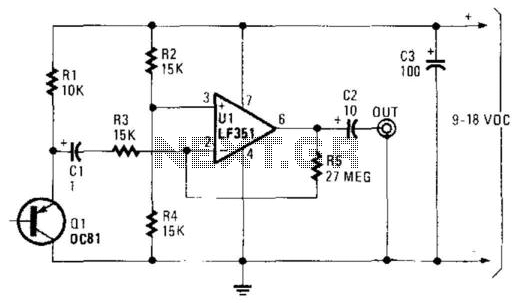
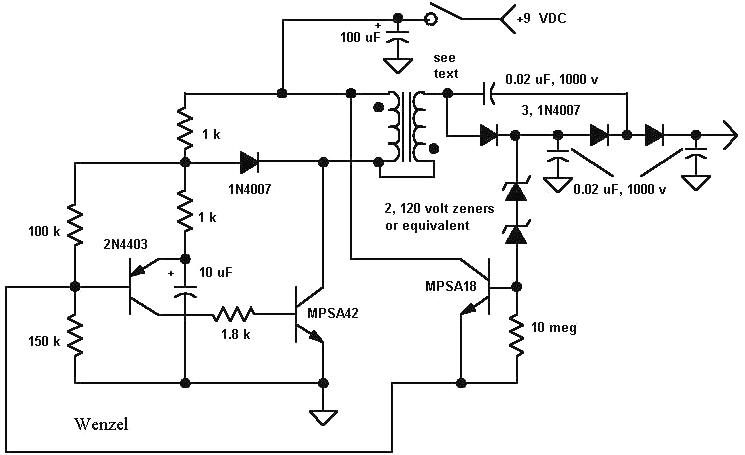
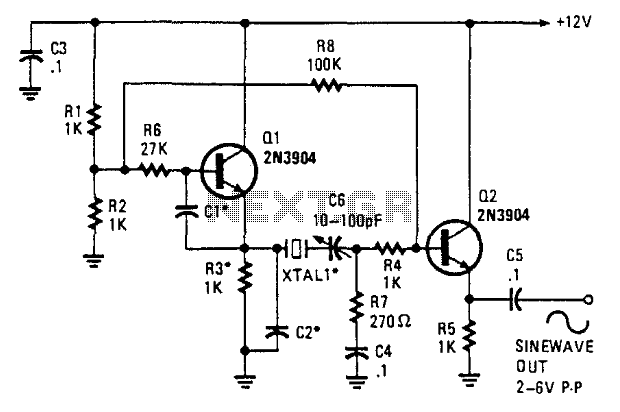
The sawtooth wave generator is an essential circuit used in various applications, including audio synthesis, signal modulation, and timing applications. The fundamental operation of this circuit is based on the linear charging and rapid discharging of a capacitor.
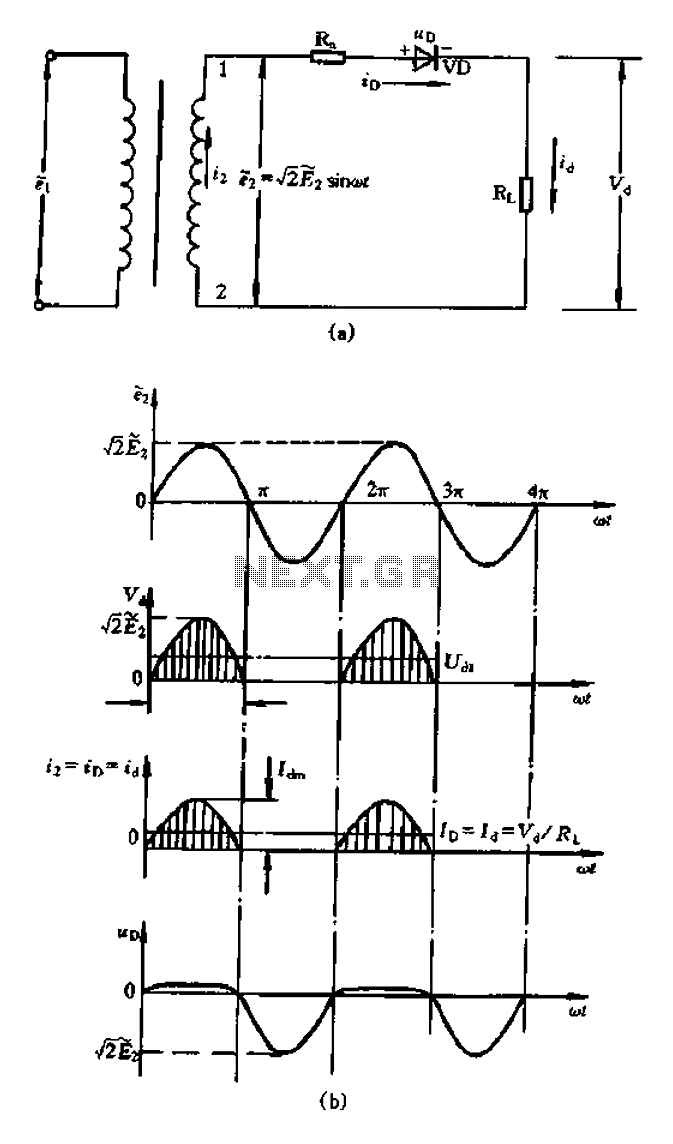
The core components typically include a resistor, a capacitor, and an operational amplifier or a transistor, depending on the design requirements. The capacitor charges through the resistor, creating a linear voltage increase over time. Once the voltage across the capacitor reaches a predefined threshold, a comparator or a transistor switches states, rapidly discharging the capacitor to initiate the next cycle of the waveform.
The frequency of the sawtooth wave can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values, allowing for flexibility in output frequency. The output can be taken from the junction of the resistor and capacitor or directly from the output of the comparator or transistor.
In a typical schematic, the power supply is connected to the operational amplifier or transistor, providing the necessary voltage levels for operation. The output waveform is characterized by a linear rise followed by a sharp drop, which is the defining feature of the sawtooth wave.
This circuit can be simulated using electronic circuit simulation software, which provides a visual representation of the waveform and allows for real-time adjustments to component values. This simulation capability aids in understanding the behavior of the circuit under various conditions and assists in troubleshooting and optimization before physical implementation.This is the Sawtooth Wave Generator circuit diagram with the detailed explanation of its working principles. The electronic circuit simulator helps you to design the Sawtooth Wave Generator circuit and to simulate it online for better understanding..
🔗 External reference
The sawtooth wave generator is an essential circuit used in various applications, including audio synthesis, signal modulation, and timing applications. The fundamental operation of this circuit is based on the linear charging and rapid discharging of a capacitor.
The core components typically include a resistor, a capacitor, and an operational amplifier or a transistor, depending on the design requirements. The capacitor charges through the resistor, creating a linear voltage increase over time. Once the voltage across the capacitor reaches a predefined threshold, a comparator or a transistor switches states, rapidly discharging the capacitor to initiate the next cycle of the waveform.
The frequency of the sawtooth wave can be adjusted by varying the resistor and capacitor values, allowing for flexibility in output frequency. The output can be taken from the junction of the resistor and capacitor or directly from the output of the comparator or transistor.
In a typical schematic, the power supply is connected to the operational amplifier or transistor, providing the necessary voltage levels for operation. The output waveform is characterized by a linear rise followed by a sharp drop, which is the defining feature of the sawtooth wave.
This circuit can be simulated using electronic circuit simulation software, which provides a visual representation of the waveform and allows for real-time adjustments to component values. This simulation capability aids in understanding the behavior of the circuit under various conditions and assists in troubleshooting and optimization before physical implementation.This is the Sawtooth Wave Generator circuit diagram with the detailed explanation of its working principles. The electronic circuit simulator helps you to design the Sawtooth Wave Generator circuit and to simulate it online for better understanding..
🔗 External reference