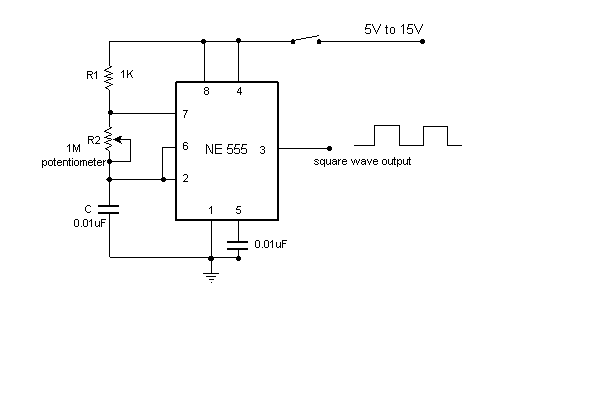
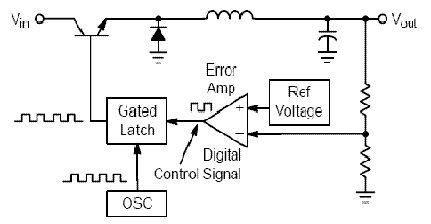
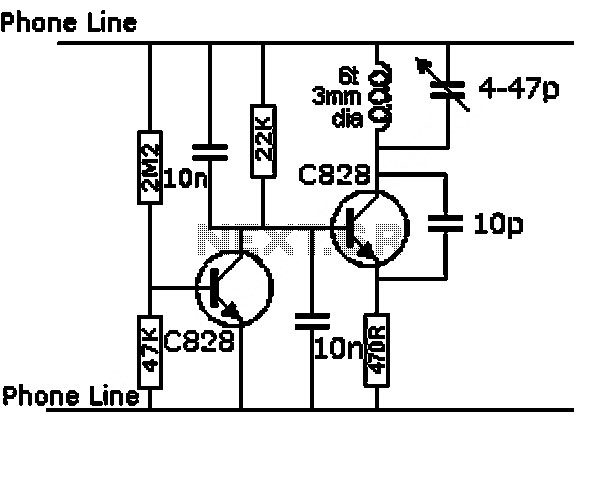
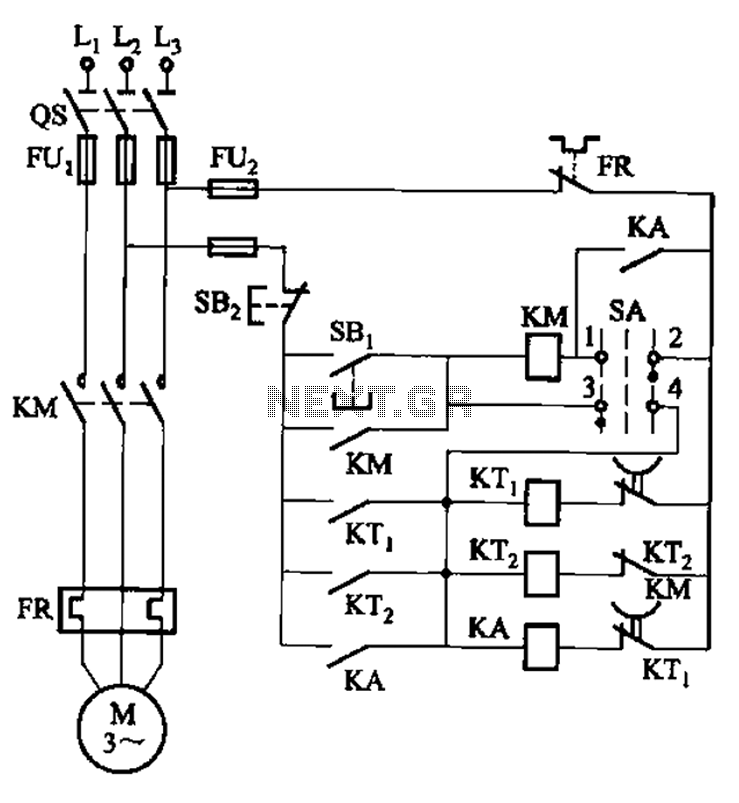
Half-wave rectifier circuit principle
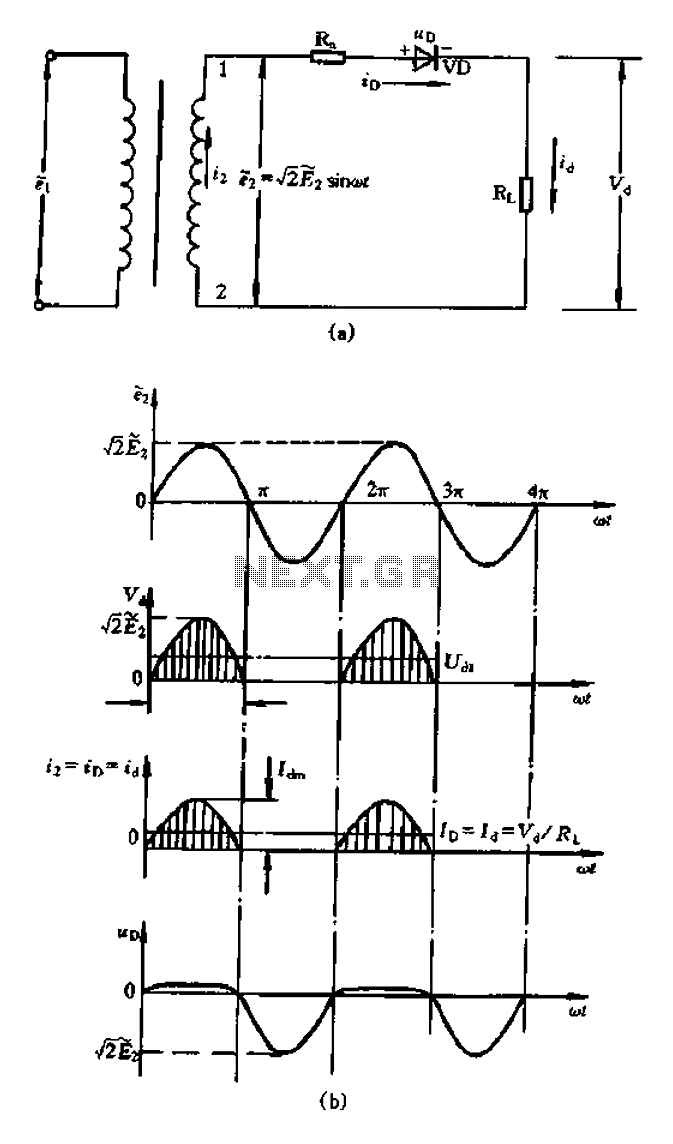
A bridge rectifier capacitor filter serves as a primary power supply for current amplifier circuits. This power supply configuration is straightforward and offers enhanced performance. The bridge rectifier circuit is a full-wave rectifying circuit, meaning it converts both the positive and negative half cycles of an AC power supply into a DC output. To explain its operation, consider the half-wave rectifying circuit. The transformer secondary AC voltage, denoted as E2, is responsible for the rectification process. In the positive half cycle, one side of the rectifier conducts, allowing output current to flow to the load. During the negative half cycle, the rectifier becomes non-conductive, resulting in no current flow through the load. Consequently, the load current is only present during the positive half cycle, producing a unidirectional pulsating DC voltage.
The bridge rectifier circuit comprises four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, enabling it to rectify both halves of the AC waveform. When an AC voltage is applied to the input terminals of the bridge, the diodes conduct in pairs, allowing current to flow through the load during both the positive and negative cycles. This results in a continuous output voltage across the load, which is then smoothed by the capacitor filter.
The capacitor filter is connected in parallel with the load and serves to reduce the ripple voltage present in the rectified output. During the conduction phase, the capacitor charges up to the peak voltage of the rectified output. When the diodes stop conducting, the capacitor discharges slowly, supplying current to the load and thereby maintaining a more constant voltage level. The effectiveness of the capacitor filter is determined by its capacitance value; larger capacitance results in lower ripple voltage and a more stable DC output.
In summary, the bridge rectifier capacitor filter is an essential component in power supply circuits for amplifiers, providing a reliable and efficient means of converting AC to DC while ensuring that the output voltage remains stable and suitable for further processing by electronic devices. Bridge rectifier capacitor filter is one of the main power supply of the current amplifier circuit, such a power supply circuit configuration simple one, better performance. A bridge rectifier circuit is a full-wave rectifying circuit, i.e. in the AC power supply both positive and negative half cycles have a DC output. To illustrate how it works, start with about half crossing the rectifier circuit. Figure 7-1 is a half-wave rectifying circuit diagram of the road works. In the drawing power transformer secondary AC voltage e2 E pumping. E2 sin called sin should be the foundation, which the transformer secondary AC voltage E2 has saved values. AC positive half cycle, l is a positive side, 2 side is negative, rectifier VD conduction, the output current to the load RL o in the negative half cycle, l side is negative, the second end is positive, reverse bias rectifier VD nonconductive, no current load circuit.
Therefore, during each cycle of the AC voltage, the load current through only half cycle current, load voltage Vd is unidirectional pulsating DC voltage, shown in Figure 7-1 (b). A cycle of AC Ji is 2, the entire stream after the DC output voltage can be expressed as:
The bridge rectifier circuit comprises four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, enabling it to rectify both halves of the AC waveform. When an AC voltage is applied to the input terminals of the bridge, the diodes conduct in pairs, allowing current to flow through the load during both the positive and negative cycles. This results in a continuous output voltage across the load, which is then smoothed by the capacitor filter.
The capacitor filter is connected in parallel with the load and serves to reduce the ripple voltage present in the rectified output. During the conduction phase, the capacitor charges up to the peak voltage of the rectified output. When the diodes stop conducting, the capacitor discharges slowly, supplying current to the load and thereby maintaining a more constant voltage level. The effectiveness of the capacitor filter is determined by its capacitance value; larger capacitance results in lower ripple voltage and a more stable DC output.
In summary, the bridge rectifier capacitor filter is an essential component in power supply circuits for amplifiers, providing a reliable and efficient means of converting AC to DC while ensuring that the output voltage remains stable and suitable for further processing by electronic devices. Bridge rectifier capacitor filter is one of the main power supply of the current amplifier circuit, such a power supply circuit configuration simple one, better performance. A bridge rectifier circuit is a full-wave rectifying circuit, i.e. in the AC power supply both positive and negative half cycles have a DC output. To illustrate how it works, start with about half crossing the rectifier circuit. Figure 7-1 is a half-wave rectifying circuit diagram of the road works. In the drawing power transformer secondary AC voltage e2 E pumping. E2 sin called sin should be the foundation, which the transformer secondary AC voltage E2 has saved values. AC positive half cycle, l is a positive side, 2 side is negative, rectifier VD conduction, the output current to the load RL o in the negative half cycle, l side is negative, the second end is positive, reverse bias rectifier VD nonconductive, no current load circuit.
Therefore, during each cycle of the AC voltage, the load current through only half cycle current, load voltage Vd is unidirectional pulsating DC voltage, shown in Figure 7-1 (b). A cycle of AC Ji is 2, the entire stream after the DC output voltage can be expressed as: