h bridge using mosfet transistor pwm
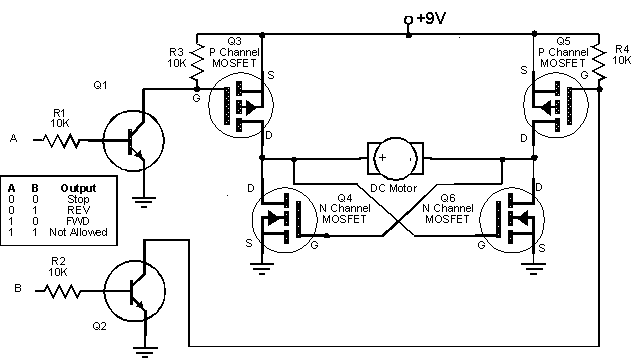
Create an H-Bridge for controlling a DC brushed motor using PWM. One bridge will control one DC motor. The bridge will have three inputs: A, B, and PWM. Inputs A and B will determine the direction of the motor, while the PWM signal will control the motor's speed regardless of the direction it spins. It is necessary to add protection diodes, but the initial inquiry is whether the circuit will function with PWM. Inputs A and B will dictate the motor's direction, and the same PWM signal will regulate its speed whether it spins clockwise or counterclockwise. The transistors connected to inputs A and B are 2N3904, while the P and N MOSFETs in the bridge will be IRF7317, and the MOSFET controlling PWM will be IRF7905. The motor operates at 6V with a maximum current draw of 1.1A, and the PWM frequency is set at 1kHz.
The H-Bridge circuit is designed to control a DC brushed motor by allowing bidirectional operation through the use of pulse-width modulation (PWM) for speed control. The configuration consists of two pairs of transistors, where each pair is responsible for switching the motor's connection to the power supply in opposite polarities.
In this setup, the inputs A and B are connected to the bases of the 2N3904 transistors, which act as signal amplifiers to drive the gates of the MOSFETs. The IRF7317 MOSFETs are used in the H-Bridge configuration to handle the high current and voltage required by the motor. The MOSFET IRF7905 is specifically designated for PWM control, allowing for efficient speed modulation of the motor.
The operation of the H-Bridge can be summarized as follows: when input A is high and input B is low, the motor will spin in one direction (e.g., clockwise). Conversely, when input A is low and input B is high, the motor will spin in the opposite direction (e.g., counterclockwise). The PWM signal, applied to the gate of the IRF7905 MOSFET, modulates the effective voltage supplied to the motor, thereby controlling its speed. The frequency of the PWM signal is set at 1kHz, which is suitable for many DC motors, providing a smooth operation without audible noise.
Protection diodes should be added across the MOSFETs to prevent back EMF generated by the motor from damaging the transistors and MOSFETs during switching. It is crucial to ensure that the selected components can handle the maximum current draw of 1.1A at the operating voltage of 6V. Proper heat dissipation techniques should also be considered for the MOSFETs to prevent thermal overload during operation.
This H-Bridge configuration is a versatile solution for controlling DC brushed motors in various applications, allowing for precise speed and direction control through simple input signals.Make H-Bridge for controlling DC brushed motor with PWM. One bridge will control 1 DC motor. Bridge will have 3 inputs: A, B and PWM. A and B will be direction control while one PWM signal will control motor speed no matter in which direction it will spin. Will this circuit work (of course ill have to add protection diodes but first i want to know if it will work with PWM) A and
B will select direction of motor and no matter if it will spin clockwise or counterclockwise same one PWM signal will set its speed. Transistors connected to A and B are 2n3904, P and N mosfets of bridge will be IRF7317 and mosfet with PWM will be IRF7905.
Motor voltage is 6V and maximum current draw is 1. 1A. PWM freq 1kHz 🔗 External reference
The H-Bridge circuit is designed to control a DC brushed motor by allowing bidirectional operation through the use of pulse-width modulation (PWM) for speed control. The configuration consists of two pairs of transistors, where each pair is responsible for switching the motor's connection to the power supply in opposite polarities.
In this setup, the inputs A and B are connected to the bases of the 2N3904 transistors, which act as signal amplifiers to drive the gates of the MOSFETs. The IRF7317 MOSFETs are used in the H-Bridge configuration to handle the high current and voltage required by the motor. The MOSFET IRF7905 is specifically designated for PWM control, allowing for efficient speed modulation of the motor.
The operation of the H-Bridge can be summarized as follows: when input A is high and input B is low, the motor will spin in one direction (e.g., clockwise). Conversely, when input A is low and input B is high, the motor will spin in the opposite direction (e.g., counterclockwise). The PWM signal, applied to the gate of the IRF7905 MOSFET, modulates the effective voltage supplied to the motor, thereby controlling its speed. The frequency of the PWM signal is set at 1kHz, which is suitable for many DC motors, providing a smooth operation without audible noise.
Protection diodes should be added across the MOSFETs to prevent back EMF generated by the motor from damaging the transistors and MOSFETs during switching. It is crucial to ensure that the selected components can handle the maximum current draw of 1.1A at the operating voltage of 6V. Proper heat dissipation techniques should also be considered for the MOSFETs to prevent thermal overload during operation.
This H-Bridge configuration is a versatile solution for controlling DC brushed motors in various applications, allowing for precise speed and direction control through simple input signals.Make H-Bridge for controlling DC brushed motor with PWM. One bridge will control 1 DC motor. Bridge will have 3 inputs: A, B and PWM. A and B will be direction control while one PWM signal will control motor speed no matter in which direction it will spin. Will this circuit work (of course ill have to add protection diodes but first i want to know if it will work with PWM) A and
B will select direction of motor and no matter if it will spin clockwise or counterclockwise same one PWM signal will set its speed. Transistors connected to A and B are 2n3904, P and N mosfets of bridge will be IRF7317 and mosfet with PWM will be IRF7905.
Motor voltage is 6V and maximum current draw is 1. 1A. PWM freq 1kHz 🔗 External reference